(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Sept. 11, 2014—Zooming in on diseased tissue or scanning fragile biological samples are essential tools in medicine and biological research, but this often requires peering through layers of tissue and other materials that can blur and distort the image. Certain modern microscopes can compensate for this, but only for weak aberrations or by using invasive "guide stars," imaging aids that provide a stable reference point.
In a first-of-its-kind demonstration, published today in The Optical Society's (OSA) new high-impact journal Optica, a team of researchers has developed a powerful technique to focus laser light through even the murkiest of surroundings without the need for a guide star. This innovation, a specialized version of an adaptive optics microscope, can resolve a point less than one thousandth of a millimeter across.
"Imagine shining a flashlight through a thick fogbank to try to see a single dot," said Yaron Silberberg, a researcher at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel and co-author on the Optica paper. "The light would become so scattered as it traveled through the fog that you wouldn't be able to make out what was hidden inside. By carefully shaping the light going in, however, it would be possible to home in on your target. That is exactly what the researchers were able to achieve in a way no one has ever done before."
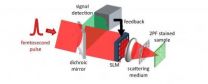
The team modified a standard two-photon scanning microscope—one that uses bursts of laser light to build up a picture point-by-point and then line-by-line—by incorporating a high-resolution wavefront shaping device. Doing so enables the microscope to peer through a visually opaque obscuring layer that would otherwise produce a highly blurred, foggy image.
Wavefront shaping sees through the murk
The wavefront shaping approach is based on "adaptive optics," which is used in both science and medicine, to correct for the blurring of an image by analyzing the way light waves are distorted as they pass through different materials. In astronomy, for example, telescopes with adaptive optics remove the twinkling from starlight to see distant objects as clearly as if the telescope were in space. While adaptive optics works wonders to correct slightly distorted images, such as by atmospheric turbulence, it cannot compensate for severe distortions, such as the scattering by fog or imaging through the shell of an egg.
Yet, recently, this new variation on the adaptive optics approach was shown to handle such tasks. Even when a perfect correction of the distortions is impossible, wavefront shaping can produce a crisp high-contrast image, even through visually opaque barriers.
Breaking free from the guide star
However, wavefront shaping, like adaptive optics, requires a reference point to bring targets into sharp focus. This point—known as a guide star due to its first use in astronomy—must be placed in relatively the same area or field of view as the object being studied. In astronomy, bright nearby stars or powerful lasers are used to adjust the optics of the telescope to produce a nearly perfect image.
In biology and medicine, however, guide stars—for example, an implanted fluorescent particle—need to be physically inserted in to the imaged specimen. This process can interfere with the sample being studied or damage delicate tissue. This is particularly problematic, for example, when trying to study a living embryo inside a shell.
"Until today, all-optical focusing through scattering media required invasively implanting a point-like guide star," said Ori Katz, a scientist at the Langevin Institute in Paris, France, and co-author on the Optica paper. "For the first time, we have shown that it is possible to focus light through visually opaque barriers without using such a guide star."
To achieve this guide-star free imaging, Silberberg and his colleagues used a standard laser scanning two-photon microscope to focus in on a single point behind an obscuring scattering layer.
The laser emits light pulses lasting approximately 100 femtoseconds (a femtosecond is one millionth of a billionth of second), which are directed through the obscuring layer and onto a target. The microscope was able focus in on a point about one thousandth of a millimeter across.
As the light passes through the intervening layer, it becomes highly scattered. In conventional adaptive optics, the returning signal from the guide star would have been measured and then corrected or reshaped, into its original form. With no clear reference point or guide star, however, there would normally be no way of correcting such a highly scattered focus.
The researchers found the answer in the scattered light itself. By using the fact that two-photon fluorescence responds in a so-called nonlinear manner to the intensity of the excitation light, they were able to glean important information about the wavefront required to compensate for the scattering. Rather than the conventional adaptive optics approach, they altered the original pulsed light going in to form a focused beam that they later scanned to generate an image of the fluorescent object hidden behind the obscuring layer.
"What we have discovered is that it's possible to efficiently 'pre-correct' the laser beam using the nonlinear fluorescence signal," noted Katz. "The end result is that instead of having a distorted, blurred light source on the object to be imaged, we have a tightly focused, or in this case, refocused beam of light."
Very recently, other groups have shown that similar focusing is also possible using an acoustic-based guide star. But, according to the researchers, this combined optical/acoustical system is substantially more complicated and the focus is not nearly as sharp.
Future applications in imaging, surgery
The researchers also clarify that their technique is only a basic demonstration of the principle and more work is needed to put it to practical use. "We hope that it can help in microscopic imaging, such as in the direct imaging of embryonic development," said Silberberg. "It may also help in guiding laser surgery."
The next step in developing this technology is to shorten the amount of time it takes to achieve the necessary focus.
"We are excited about this project because it has produced new understanding and a new way of seeing through visually opaque samples," concluded Katz.
INFORMATION:
Paper: O. Katz, E. Small, Y. Guan, Y. Silberberg, "Noninvasive nonlinear imaging through strongly-scattering turbid layers," Optica 3, 170-174 (2014).
EDITOR'S NOTE: Images and an advance copy of the Optica paper are available to members of the media upon request. Contact Jake Lynn at optica@ecius.net or 202.296.2002.
About Optica
Optica is an open-access, online-only journal dedicated to the rapid dissemination of high-impact peer-reviewed research across the entire spectrum of optics and photonics. Published monthly by The Optical Society (OSA), Optica provides a forum for pioneering research to be swiftly accessed by the international community, whether that research is theoretical or experimental, fundamental or applied. Optica maintains a distinguished editorial board of more than 20 associate editors from around the world and is overseen by Editor-in-Chief Alex Gaeta of Cornell University. For more information, visit http://optica.osa.org.
About OSA
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional society for scientists, engineers, students and business leaders who fuel discoveries, shape real-world applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership programs, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of professionals in optics and photonics. For more information, visit http://www.osa.org.
Perfect focus through thick layers may bring better vision to medicine
2014-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The ozone hole has stabilized -- some questions remain
2014-09-11
After the detection of the ozone-depleting properties of CFCs in the 1970s, data from satellite measurements in 1985 startled mankind. A huge hole had been discovered over the Antarctic in the ozone layer that protects the Earth from dangerous, carcinogenic UV rays. Already in 1987 politicians around the world reached agreement on the Montreal Protocol that bans ozone-depleting substances, in particular chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). 197 states have now ratified this international treaty. A series of scientific expert reports has since accompanied the efforts to save the ozone ...
Crop improvement and resistance to pathogens benefits from non-coding RNA studies
2014-09-11
With the rise of emerging economies around the world and a concomitant upgrade of health care systems, the global population has been rapidly expanding. As a consequence, worldwide demand for agricultural products is also growing.
Crops now provide food and the other important resources for seven billion humans.
Food supplies are primarily based on such crops as wheat, maize, rice and vegetables. But as the area of arable land and of cultivated land continues to decline, the future ability to meet the world's food security needs has come under a cloud of uncertainty.
Meanwhile, ...
Last decade's slow-down in global warming enhanced by an unusual climate anomaly
2014-09-11
A hiatus in global warming ongoing since 2001 is due to a combination of a natural cooling phase, known as multidecadal variability (MDV) and a downturn of the secular warming trend. The exact causes of the latter, unique in the entire observational record going back to 1850, are still to be identified, according to an article by the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC).
The earth hasn't warmed at the same pace during the 20th century. The noticeable temperature increases during some periods interspersed with fairly stable or decreasing levels during others ...
The quantum revolution is a step closer
2014-09-11
Theories show how computing devices that operate according to quantum mechanics can solve problems that conventional (classical) computers, including super computers, can never solve. These theories have been experimentally tested for small-scale quantum systems, but the world is waiting for the first definitive demonstration of a quantum device that beats a classical computer.
Now, researchers from the Centre for Quantum Photonics (CQP) at the University of Bristol together with collaborators from the University of Queensland (UQ) and Imperial College London have increased ...
VALUE study reports on accreditation status
2014-09-11
SEPTEMBER 2014 | Ellicott City, MD – The Intersocietal Accreditation Commission (IAC) announced today that researchers from the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have published a manuscript in Vascular Medicine analyzing a random national sample of Medicare beneficiary data to determine the outpatient vascular testing facilities' accreditation status and geographic location. The study manuscript entitled, "Accreditation Status and Geographic Location of Outpatient Vascular Testing Facilities Among Medicare Beneficiaries: The VALUE (Vascular Accreditation, Location ...
Bully victims more likely to suffer night terrors and nightmares by age 12
2014-09-11
Children who are bullied at ages 8-10 are more likely to suffer from sleep walking, night terrors or nightmares by the time they are 12 years old.
In a study published this week in Pediatrics, journal of the American Pediatric Association, Professor Dieter Wolke and Dr Suzet Tanya Lereya from the University of Warwick, found being bullied increases the risk for a category of sleep disorders known as parasomnias. These are sleep-related problems such as nightmares, night terrors or sleep walking.
A cohort of children from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children ...
Study: Cat bites dog
2014-09-11
NEW YORK (September 11, 2014) – A new study led by the Wildlife Conservation Society reveals that in India's human dominated agricultural landscapes, where leopards prowl at night, it's not livestock that's primarily on the menu – it is man's best friend.
The study, which looked at scat samples for leopards in India's Ahmednagar's district in Maharashtra, found that 87 percent of their diet was made up of domestic animals. Domestic dog dominated as the most common prey item at 39 percent and domestic cats were second at 15 percent.
Seventeen percent of the leopard's ...
Is the pattern of brain folding a 'fingerprint' for schizophrenia?
2014-09-11
Philadelphia, PA, September 11, 2014 – Anyone who has seen pictures or models of the human brain is aware that the outside layer, or cortex, of the brain is folded in an intricate pattern of "hills", called gyri, and "valleys", called sulci.
It turns out that the patterns of cortical folding are largely consistent across healthy humans, broadly speaking. However, disturbances in cortical folding patterns suggest deeper disturbances in brain structure and function.
A new study published in the current issue of Biological Psychiatry suggests that schizophrenia is associated ...
How bacteria battle fluoride
2014-09-11
He's not a dentist, but Christopher Miller is focused on fluoride. Two studies from his Brandeis University lab provide new insights into the mechanisms that allow bacteria to resist fluoride toxicity, information that could eventually help inform new strategies for treating harmful bacterial diseases. The studies appear in The Journal of General Physiology (JGP).
Although most animal cells are protected from direct exposure to fluoride, this toxic element is a serious threat to single-celled organisms like bacteria and yeast. As a result, their plasma membranes carry ...
Structure of enzyme seen as target for ALS drugs
2014-09-11
VIDEO:
In this movie, the Dbr1 enzyme rotates 360 degrees. Partially inhibiting Dbr1 could represent a new way to treat most cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), according to a new...
Click here for more information.
SAN ANTONIO, Texas, U.S.A. (Sept. 10, 2014) — Investigators from the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio have determined the first high-resolution structure of an enzyme that, if partially inhibited, could represent ...