(Press-News.org) This paper makes a connection between the quantum group SLq(2), which described knots, and the elementary particles of the standard model. The elements of the fundamental (j = 1/2) representation of SLq(2) are interpreted as creation operators for preons. The preons interact through a preonic vector field defined by elements of the adjoint (j = 1) representation. The leptons and quarks then appear (as required by the electroweak data) as elements of the j = 3/2 representation. Unexpectedly the electroweak quantum numbers of the so defined preons, leptons, and quarks agree with the corresponding quantum numbers of the elementary constituents conjectured earlier by Harari and Shupe.
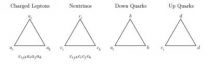
In the schematic figure displayed here the leptons and quarks are composed of preons (a, b, c, d) as shown a, b, c, d are the elements of the fundamental representation of the SLq(2) a_i and c_i are also elements of the fundamental representation of SU(3).
In the SLq(2) extension of the standard model, the field operators of the standard model are renormalized by knot factors which are representations of SLq(2), and the couplings of the standard model Lagrangian are thereby modified by SLq(2) form factors. A similar development leads to a Lagrangian for preons.
Since the SLq(2) extension of the standard model describes a finer level of structure than the standard model, there are many open problems, including questions concerning gravitational binding, the existence of free preons, and the renormalization of the Lagrangian dynamics.
INFORMATION:
The study can be found at http://www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/S0217751X14500924 in the volume 29, issue 15 of the International Journal of Modern Physics A.
Extension of standard model by knot algebra
2014-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists show that nicotine withdrawal reduces response to rewards across species
2014-09-12
Cigarette smoking is a leading cause of preventable death worldwide and is associated with approximately 440,000 deaths in the United States each year, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but nearly 20 percent of the U.S. population continues to smoke cigarettes. While more than half of U.S. smokers try to quit every year, less than 10 percent are able to remain smoke-free, and relapse commonly occurs within 48 hours of smoking cessation. Learning about withdrawal and difficulty of quitting can lead to more effective treatments to help smokers ...
Favoritism linked to drug use in 'disengaged' families
2014-09-12
Before you revive the debate about which sibling in your family is the favorite, you'll want to know what the latest research shows.
Brigham Young University professor Alex Jensen analyzed 282 families with teenage siblings for a study that appears in the Journal of Family Psychology. Favoritism in parenting is a complex topic for sure, but here are some important take-aways.
Does it really matter?
Yes, at least for some families. Jensen looked at perceived preferential treatment in different types of family dynamics. For families that aren't very close to each other ...
Brain inflammation dramatically disrupts memory retrieval networks, UCI study finds
2014-09-12
Irvine, Calif., Sept. 10, 2014 — Brain inflammation can rapidly disrupt our ability to retrieve complex memories of similar but distinct experiences, according to UC Irvine neuroscientists Jennifer Czerniawski and John Guzowski.
Their study – which appears today in the Journal of Neuroscience – specifically identifies how immune system signaling molecules, called cytokines, impair communication among neurons in the hippocampus, an area of the brain critical for discrimination memory. The findings offer insight into why cognitive deficits occurs in people undergoing chemotherapy ...
No innocent bystander: Cartilage contributes to arthritis
2014-09-12
Melbourne researchers have discovered that cartilage plays an active role in the destruction and remodelling of joints seen in rheumatoid arthritis, rather than being an 'innocent bystander' as previously thought.
Dr Tommy Liu, Professor Ian Wicks, Dr Kate Lawler, Dr Ben Croker and colleagues from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute made the discovery while investigating the role of the protein SOCS3 in controlling inflammation during rheumatoid arthritis. The study was published in the journal Arthritis and Rheumatology.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects more than 400,000 ...
A meta-analysis of 3 types of peer norms and their relation with adolescent sexual behavior
2014-09-12
Researchers at Utrecht University and the New York State Psychiatric Institute collaborated on a meta-analysis of research on adolescent sexual behavior. The goal was to analyze how this behavior is related to adolescents' perceptions of three types of sexual peer norms, including how sexually active their peers are, how much their peers would approve of being sexually active, or how much they feel pressured by their peers to have sex. Awareness that these are different ways in which peers can affect adolescents' sexual behaviors is important for parents, teachers, and ...
Protein appears to protect against bone loss in arthritis
2014-09-12
AUGUSTA, Ga. – A small protein named GILZ appears to protect against the bone loss that often accompanies arthritis and its treatment, researchers report.
Arthritis as well as aging prompt the body to make more fat than bone, and the researchers have previously shown GILZ can restore a more youthful, healthy mix. It also tamps down inflammation, a major factor in arthritis.
Now they have early evidence that GILZ might one day be a better treatment option for arthritis patients than widely used synthetic glucocorticoids, which actually increase bone loss, said Dr. Xingming ...
Dendritic cells affect onset and progress of psoriasis
2014-09-12
Different types of dendritic cells in human skin have assorted functions in the early and more advanced stages of psoriasis report researchers in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine. The scientists suggest that new strategies to regulate the composition of dendritic cells in psoriatic skin lesions might represent an approach for the future treatment of the disease.
"We urgently need new ways to treat psoriasis, treatments that will deliver improved benefits to patients and reduce the incidence of known side effects for existing drugs," says EMBO Member Maria Sibilia, ...
Gray matter matters when measuring our tolerance of risk
2014-09-12
There is a link between our brain structure and our tolerance of risk, new research suggests.
Dr Agnieszka Tymula, an economist at the University of Sydney, is one of the lead authors of a new study that identifies what might be considered the first stable 'biomarker' for financial risk-attitudes.
Using a whole-brain analysis, Dr Tymula and international collaborators found that the grey matter volume of a region in the right posterior parietal cortex was significantly predictive of individual risk attitudes. Men and women with higher grey matter volume in this region ...
Age and diabetes duration linked to risk of death and macrovascular complications
2014-09-12
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) shows that age (or age at diagnosis) and duration of diabetes disease are linked to the risk of death and marcovascular complications (those in larger blood vessels), whereas only diabetes duration is linked to the risk of microvascular complications (in smaller blood vessels such as those in the eyes). This means younger people with diabetes are more at risk of microvascular complications since they are more likely to have diabetes for longer over their lifetimes ...
The Lancet: Combining gut hormone with insulin proves more effective at controlling type 2 diabetes than other common treatments
2014-09-12
Combined treatment with a drug that mimics the action of a gut hormone and basal insulin [1] is more effective at improving blood sugar control than other anti-diabetic treatments, with similar rates of hypoglycaemia (dangerously low blood sugar levels) and greater weight loss, a systematic review and meta-analysis published in The Lancet shows.
"Achieving normal blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes is compromised by the adverse side effects plaguing currently available treatments. Some anti-diabetic treatments increase risk of hypoglycaemia and weight gain ...