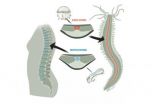
(Press-News.org) Thoughts of the family tree may not be uppermost in the mind of a person suffering from a slipped disc, but those spinal discs provide a window into our evolutionary past. They are remnants of the first vertebrate skeleton, whose origins now appear to be older than had been assumed. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found that, unexpectedly, this skeleton most likely evolved from a muscle. The study, carried out in collaboration with researchers at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute in Janelia Farm, USA, is published today in Science.
Humans are part of a group of animals called chordates, whose defining feature is a rod of cartilage that runs lengthwise along the middle of their body, under their spinal chord. This structure, called the notochord, was the first vertebrate skeleton. It is present in human embryos, and is replaced with the backbone as we develop, with the cartilage reduced to those tell-tale discs. Since starfish, sea urchins and related animals have no such structure, scientists assumed the notochord had emerged in a relatively recent ancestor, after our branch of the evolutionary tree split away from the 'starfish branch'.
"People simply haven't been looking beyond our direct relatives, but that means you could be fooled, if the structure appeared earlier and that single group lost it," says Detlev Arendt from EMBL, who led the study. "And in fact, when we looked at a broader range of animals, this is what we found."
Antonella Lauri and Thibaut Brunet, both in Arendt's lab, identified the genetic signature of the notochord – the combination of genes that have to be turned on for a healthy notochord to form. When they found that the larva of the marine worm Platynereis has a group of cells with that same genetic signature, the scientists teamed up with Philipp Keller's group at Janelia Farm to use state-of-the-art microscopy to follow those cells as the larva developed. They found that the cells form a muscle that runs along the animal's midline, precisely where the notochord would be if the worm were a chordate. The researchers named this muscle the axochord, as it runs along the animal's axis. A combination of experimental work and combing through the scientific literature revealed that most of the animal groups that sit between Platynereis and chordates on the evolutionary tree also have a similar, muscle-based structure in the same position.
The scientists reason that such a structure probably first emerged in an ancient ancestor, before all these different animal groups branched out on their separate evolutionary paths. Such a scenario would also explain why the lancelet amphioxus, a 'primitive' chordate, has a notochord with both cartilage and muscle. Rather than having acquired the muscle independently, amphioxus could be a living record of the transition from muscle-based midline to cartilaginous notochord.
The shift from muscle to cartilage could have come about because a stiffened central rod would make swimming more efficient, the scientists postulate.
INFORMATION:
A video relating to this study can be found at: http://youtu.be/78zuEh6EoKE.
From worm muscle to spinal discs
An evolutionary surprise
2014-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New family of materials for energy-efficient information storage and processing
2014-09-12
Switching the polarity of a magnet using an electric field (magnetoelectric memory [MEM] effect), can be a working principle of the next-generation technology for information processing and storage. Multiferroic materials are promising candidates for the MEM effect, due to the coexistence of electric and magnetic orders. On the other hand, the coexistence of spontaneous electric and magnetic polarizations is rare in known materials, which hinders the application potential of the MEM effect. This article briefly reviews a new family of multiferroic materials—hexagonal rare ...
Conjecture on the lateral growth of Type I collagen fibrils
2014-09-12
Whatever the origin and condition of extraction of type I collagen fibrils, in vitro as well as in vivo, the radii of their circular circular cross sections stay distributed in a range going from 50 to 100 nm for the most part of them. Jean Charvolin and Jean-Francois Sadoc from the solid state physique laboratory at the Paris-Sud University propose therefore that, once the growth of the fibrils has been triggered by external biological factors, their lateral size be limited by internal physical stresses generated during the growth. Their conjecture is based ...
Extension of standard model by knot algebra
2014-09-12
This paper makes a connection between the quantum group SLq(2), which described knots, and the elementary particles of the standard model. The elements of the fundamental (j = 1/2) representation of SLq(2) are interpreted as creation operators for preons. The preons interact through a preonic vector field defined by elements of the adjoint (j = 1) representation. The leptons and quarks then appear (as required by the electroweak data) as elements of the j = 3/2 representation. Unexpectedly the electroweak quantum numbers of the so defined preons, leptons, and quarks agree ...
Scientists show that nicotine withdrawal reduces response to rewards across species
2014-09-12
Cigarette smoking is a leading cause of preventable death worldwide and is associated with approximately 440,000 deaths in the United States each year, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but nearly 20 percent of the U.S. population continues to smoke cigarettes. While more than half of U.S. smokers try to quit every year, less than 10 percent are able to remain smoke-free, and relapse commonly occurs within 48 hours of smoking cessation. Learning about withdrawal and difficulty of quitting can lead to more effective treatments to help smokers ...
Favoritism linked to drug use in 'disengaged' families
2014-09-12
Before you revive the debate about which sibling in your family is the favorite, you'll want to know what the latest research shows.
Brigham Young University professor Alex Jensen analyzed 282 families with teenage siblings for a study that appears in the Journal of Family Psychology. Favoritism in parenting is a complex topic for sure, but here are some important take-aways.
Does it really matter?
Yes, at least for some families. Jensen looked at perceived preferential treatment in different types of family dynamics. For families that aren't very close to each other ...
Brain inflammation dramatically disrupts memory retrieval networks, UCI study finds
2014-09-12
Irvine, Calif., Sept. 10, 2014 — Brain inflammation can rapidly disrupt our ability to retrieve complex memories of similar but distinct experiences, according to UC Irvine neuroscientists Jennifer Czerniawski and John Guzowski.
Their study – which appears today in the Journal of Neuroscience – specifically identifies how immune system signaling molecules, called cytokines, impair communication among neurons in the hippocampus, an area of the brain critical for discrimination memory. The findings offer insight into why cognitive deficits occurs in people undergoing chemotherapy ...
No innocent bystander: Cartilage contributes to arthritis
2014-09-12
Melbourne researchers have discovered that cartilage plays an active role in the destruction and remodelling of joints seen in rheumatoid arthritis, rather than being an 'innocent bystander' as previously thought.
Dr Tommy Liu, Professor Ian Wicks, Dr Kate Lawler, Dr Ben Croker and colleagues from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute made the discovery while investigating the role of the protein SOCS3 in controlling inflammation during rheumatoid arthritis. The study was published in the journal Arthritis and Rheumatology.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects more than 400,000 ...
A meta-analysis of 3 types of peer norms and their relation with adolescent sexual behavior
2014-09-12
Researchers at Utrecht University and the New York State Psychiatric Institute collaborated on a meta-analysis of research on adolescent sexual behavior. The goal was to analyze how this behavior is related to adolescents' perceptions of three types of sexual peer norms, including how sexually active their peers are, how much their peers would approve of being sexually active, or how much they feel pressured by their peers to have sex. Awareness that these are different ways in which peers can affect adolescents' sexual behaviors is important for parents, teachers, and ...
Protein appears to protect against bone loss in arthritis
2014-09-12
AUGUSTA, Ga. – A small protein named GILZ appears to protect against the bone loss that often accompanies arthritis and its treatment, researchers report.
Arthritis as well as aging prompt the body to make more fat than bone, and the researchers have previously shown GILZ can restore a more youthful, healthy mix. It also tamps down inflammation, a major factor in arthritis.
Now they have early evidence that GILZ might one day be a better treatment option for arthritis patients than widely used synthetic glucocorticoids, which actually increase bone loss, said Dr. Xingming ...
Dendritic cells affect onset and progress of psoriasis
2014-09-12
Different types of dendritic cells in human skin have assorted functions in the early and more advanced stages of psoriasis report researchers in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine. The scientists suggest that new strategies to regulate the composition of dendritic cells in psoriatic skin lesions might represent an approach for the future treatment of the disease.
"We urgently need new ways to treat psoriasis, treatments that will deliver improved benefits to patients and reduce the incidence of known side effects for existing drugs," says EMBO Member Maria Sibilia, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] From worm muscle to spinal discsAn evolutionary surprise