(Press-News.org) Alexandria, Va. — Most people are familiar with the Great 1906 San Francisco Earthquake and are aware of the earthquake risk posed to the Bay Area — and much of California — by the San Andreas Fault. Most people are not aware, however, that a cluster of large earthquakes struck the San Andreas and quite a few nearby faults in the 17th and 18th centuries. That cluster, according to new research, released about the same amount of energy throughout the Bay Area as the 1906 quake. Thus, it appears that the accumulated stress on the region's faults could be released in a series of moderate to large quakes on satellite faults, rather than a single great event on the San Andreas. But how this information might change the hazard forecast for the Bay Area is uncertain, scientists say.
INFORMATION:
Read more about the recently uncovered paleoseismic evidence and what earthquake clustering might indicate for hazard risks in the September issue of EARTH Magazine: http://bit.ly/1l1prPr.
For more stories about the science of our planet, check out EARTH magazine online or subscribe at http://www.earthmagazine.org. The September issue, now available on the digital newsstand, features stories about how scientists are using digital cameras to create 3-D topographical maps, how warm river water is melting Arctic sea ice, and a jaunt through the spectacular rocks of the Australian Outback, plus much, much more.
Keep up to date with the latest happenings in Earth, energy and environment news with EARTH magazine online at: http://www.earthmagazine.org/. Published by the American Geosciences Institute, EARTH is your source for the science behind the headlines.
The American Geosciences Institute is a nonprofit federation of 49 geoscientific and professional associations that represents more than 250,000 geologists, geophysicists and other earth scientists. Founded in 1948, AGI provides information services to geoscientists, serves as a voice of shared interests in the profession, plays a major role in strengthening geoscience education, and strives to increase public awareness of the vital role the geosciences play in society's use of resources, resiliency to natural hazards, and interaction with the environment.
EARTH Magazine: The Bay Area's next 'big one could strike as a series of quakes
2014-09-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research decodes virus-host interactions in ocean dead zones
2014-09-16
A complex web of interaction between viruses, bacteria, and their environment is becoming ever more untangled by a growing international collaboration between Matthew Sullivan, associate professor in the University of Arizona's Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Steven Hallam from the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, Canada.
"Bacteria are drivers of nutrient and energy cycles that power the earth," Sullivan said. "As the climate is changing, so are the environments these bacteria live in, and they in turn loop back to impact their environments. ...
New research shows tornadoes occurring earlier in 'Tornado Alley'
2014-09-16
BOZEMAN, Mont. -- Peak tornado activity in the central and southern Great Plains of the United States is occurring up to two weeks earlier than it did half a century ago, according to a new Montana State University study whose findings could help states in "Tornado Alley" better prepare for these violent storms.
Tornado records from Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and northern Texas – an area of high tornado activity dubbed "Tornado Alley" -- show that peak tornado activity is starting and ending earlier than it did 60 years ago.
Peak tornado activity, which occurs ...
Long-term results of RTOG 0236 confirm good primary tumor control, positive 5-year survival rates
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—Patients with inoperable, early-stage lung cancer who receive stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) have a five-year survival rate of 40 percent, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting. Such a positive survival rate is encouraging considering that historically conventional RT resulted in poor tumor control for patients with inoperable lung cancer. This study is an update of RTOG 0236, originally published in 2010 , and also conducted by the original researchers ...
Politics divide coastal residents' views of environment, UNH research finds
2014-09-16
DURHAM, N.H. – From the salmon-rich waters of Southeast Alaska to the white sand beaches of Florida's Gulf Coast to Downeast Maine's lobster, lumber and tourist towns, coastal residents around the U.S. share a common characteristic: their views about coastal environments divide along political lines. That's a primary finding of a new study by University of New Hampshire sociologists published this month in the journal Society & Natural Resources.
"We found a lot of environment-related differences from place to place to place. Each environment is different so that's just ...
Artworks are people!
2014-09-16
Not all things are created equally. We don't view a Picasso sculpture in the same way we look at a hammer, for example — no matter how fancy the hammer.
The reason? We see the Picasso more as a person than an object, according to new research from the University of Chicago Booth School of Business.
And in some cases, we make distinctions between artworks — say, an exact replica of a piece created by the artist, versus one created by a different artist.
Art, in other words, is an extension of the creator, write Professor Daniel M. Bartels of Chicago Booth, and Professor ...
For electronics beyond silicon, a new contender emerges
2014-09-16
Cambridge, Mass. – September 16, 2014 – Silicon has few serious competitors as the material of choice in the electronics industry. Yet transistors, the switchable valves that control the flow of electrons in a circuit, cannot simply keep shrinking to meet the needs of powerful, compact devices; physical limitations like energy consumption and heat dissipation are too significant.
Now, using a quantum material called a correlated oxide, Harvard researchers have achieved a reversible change in electrical resistance of eight orders of magnitude, a result the researchers ...
NASA's Global Hawk and satellites investigating Hurricane Edouard today
2014-09-16
The unmanned Global Hawk aircraft that's part of NASA's airborne Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel, or HS3 mission was winging its way to Hurricane Edouard on September 16. In addition to the Global Hawk, various NASA satellites are continually providing data on the Atlantic hurricane.
Scientific instruments aboard NASA's remotely piloted Global Hawk aircraft have been studying the hurricane over the last couple of days, and the Global Hawk returned to Edouard again today, September 16. Two of the instruments aboard the Global Hawk that will study Edouard are the S-HIS ...
Cancer patients with malignant spinal cord compression have preserved mobility
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—Mobility is equally preserved in cancer patients suffering from malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) who receive a single dose of 10 Gy of radiation therapy (RT), compared to patients who receive five daily doses of 4 Gy of RT each, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
Malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) is a complication of metastatic cancer mostly with bone involvement that occurs when a tumor's secondary deposit presses on the spinal cord and ...
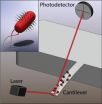
And so they beat on, flagella against the cantilever
2014-09-16
WASHINGTON D.C., September 16, 2014 – A team of researchers at Boston University and Stanford University School of Medicine has developed a new model to study the motion patterns of bacteria in real time and to determine how these motions relate to communication within a bacterial colony.
The researchers chemically attached colonies of Escherichia coli bacteria to a microcantilever – a microscopic beam anchored at one end, similar to a diving board – thus coupling its motion to that of the bacteria. As the cantilever itself isn't doesn't generate any vibrations, or 'noise,' ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Odile knocking at US Southwest
2014-09-16
Tropical Storm Odile continues to drench western Mexico and has now entered into the U.S. Southwest. On September 15, NASA's Terra satellite saw Odile's northernmost edge crossing the Mexican border into southern California. NOAA's GOES-East satellite on September 16 showed Odile's outer bands were already bringing storms to southern Arizona.
NASA Sees Odile Knocking on U.S. Border
On Sept. 15 at 2:35 p.m. EDT, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite saw the northern fringes of Hurricane Odile straddling the border ...