(Press-News.org) An international research group led by Junko Ueda, a Japan Society for the Promotion of Science postdoctoral fellow, has made surprising observations that most galaxy collisions in the nearby Universe — within 40 million light-years from Earth — result in so-called disc galaxies. Disc galaxies — including spiral galaxies like the Milky Way and lenticular galaxies — are defined by pancake-shaped regions of dust and gas, and are distinct from the category of elliptical galaxies.
It has, for some time, been widely accepted that merging disc galaxies would eventually form an elliptically shaped galaxy. During these violent interactions the galaxies do not only gain mass as they merge or cannibalise each-other, but they are also changing their shape throughout cosmic time, and therefore changing type along the way.
Computer simulations from the 1970s predicted that mergers between two comparable disc galaxies would result in an elliptical galaxy. The simulations predict that most galaxies today are elliptical, clashing with observations that over 70% of galaxies are in fact disc galaxies. However, more recent simulations have suggested that collisions could also form disc galaxies.
To identify the final shapes of galaxies after mergers observationally, the group studied the distribution of gas in 37 galaxies that are in their final stages of merging. The Atacama Large Millimeter/sub-millimeter Array, or ALMA and several other radio telescopes [1] were used to observe emission from carbon monoxide (CO), an indicator of molecular gas.
The team's research is the largest study of molecular gas in galaxies to date and provides unique insight into how the Milky Way might have formed. Their study revealed that almost all of the mergers show pancake-shaped areas of molecular gas, and hence are disc galaxies in the making. Ueda explains: "For the first time there is observational evidence for merging galaxies that could result in disc galaxies. This is a large and unexpected step towards understanding the mystery of the birth of disc galaxies."
Nonetheless, there is a lot more to discover. Ueda added: "We have to start focusing on the formation of stars in these gas discs. Furthermore, we need to look farther out in the more distant Universe. We know that the majority of galaxies in the more distant Universe also have discs. We however do not yet know whether galaxy mergers are also responsible for these, or whether they are formed by cold gas gradually falling into the galaxy. Maybe we have found a general mechanism that applies throughout the history of the Universe."
INFORMATION:
Notes
The data were obtained by ALMA ; the Combined Array for Research in Millimeter-wave Astronomy: a millimeter array consisting of 23 parabola antennas in California; the Submillimeter Array Submillimeter Array a submillimeter array consisting of eight parabola antennas in Mauna Kea, Hawaii; the Plateau de Bure Interferometer; the NAOJ Nobeyama Radio Observatory 45m radio telescope; USA's National Radio Astronomy Observatory Five College Radio Astronomy Observatory 12m telescope; USA's Five College Radio Astronomy Observatory Five College Radio Astronomy Observatory 14m telescope; IRAM's Observatory/ 30m telescope; and the Swedish-ESO Submillimeter Telescope as a supplement.
More Information
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of Europe, North America and East Asia in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded in Europe by the European Southern Observatory (ESO), in North America by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC) and in East Asia by the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan. ALMA construction and operations are led on behalf of Europe by ESO, on behalf of North America by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), which is managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI) and on behalf of East Asia by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
These observation results were published in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement (August 2014) as Ueda et al. "Cold Molecular Gas in Merger Remnants. I. Formation of Molecular Gas Discs".
The team is composed of Junko Ueda (JSPS postdoctoral fellow/National Astronomical Observatory of Japan [NAOJ]), Daisuke Iono (NAOJ/The Graduate University for Advanced Studies [SOKENDAI]), Min S. Yun (The University of Massachusetts), Alison F. Crocker (The University of Toledo), Desika Narayanan (Haverford College), Shinya Komugi (Kogakuin University/ NAOJ), Daniel Espada (NAOJ/SOKENDAI/Joint ALMA Observatory), Bunyo Hatsukade (NAOJ), Hiroyuki Kaneko (University of Tsukuba), Yoichi Tamura (The University of Tokyo), David J. Wilner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), Ryohei Kawabe (NAOJ/ SOKENDAI/The University of Tokyo) and Hsi-An Pan (Hokkaido University/SOKENDAI/NAOJ)
ESO is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organisation in Europe and the world's most productive ground-based astronomical observatory by far. It is supported by 15 countries: Austria, Belgium, Brazil, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. ESO carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organising cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope, the world's most advanced visible-light astronomical observatory and two survey telescopes. VISTA works in the infrared and is the world's largest survey telescope and the VLT Survey Telescope is the largest telescope designed to exclusively survey the skies in visible light. ESO is the European partner of a revolutionary astronomical telescope ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. ESO is currently planning the 39-metre European Extremely Large optical/near-infrared Telescope, the E-ELT, which will become "the world's biggest eye on the sky".
Links
Research paper on Astro-Ph: http://arxiv.org/abs/1407.6873
Contacts
Junko Ueda
JSPS postdoctoral fellow/NAOJ
Tel: +88 422 34 3117
Email: junko.ueda@nao.ac.jp
Lars Lindberg Christensen
Head of ESO ePOD
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6761
Cell: +49 173 3872 621
Email: lars@eso.org
Masaaki Hiramatsu
NAOJ Chile Observatory EPO officer
Tel: +88 422 34 3630
Email: hiramatsu.masaaki@nao.ac.jp
Violent origins of disc galaxies probed by ALMA
New observations explain why Milky Way-like galaxies are so common in the Universe
2014-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Global shift away from cars saves US$100 trillion, eliminates 1,700 MT of CO2 pollution
2014-09-17
NEW YORK (17 September, 2014)—More than $100 trillion in cumulative public and private spending, and 1,700 megatons of annual carbon dioxide (CO2)—a 40 percent reduction of urban passenger transport emissions—could be eliminated by 2050 if the world expands public transportation, walking and cycling in cities, according to a new report released by the University of California, Davis, and the Institute for Transportation and Development Policy (ITDP).
Further, an estimated 1.4 million early deaths could be avoided annually by 2050 if governments require the strongest ...
'Smart material' chin strap harvests energy from chewing
2014-09-17
A chin strap that can harvest energy from jaw movements has been created by a group of researchers in Canada.
It is hoped that the device can generate electricity from eating, chewing and talking, and power a number of small-scale implantable or wearable electronic devices, such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, electronic hearing protectors and communication devices.
The first results of the device's performance have been published today, 17 September, in IOP Publishing's journal Smart Materials and Structures.
Jaw movements have proved to be one of the most promising ...
World Alzheimer Report 2014 reveals persuasive evidence for dementia risk reduction
2014-09-17
The World Alzheimer Report 2014 'Dementia and Risk Reduction: An analysis of protective and modifiable factors', released today, calls for dementia to be integrated into both global and national public health programmes alongside other major non communicable diseases (NCDs).
Alzheimer's Disease International (ADI) commissioned a team of researchers, led by Professor Martin Prince from King's College London, to produce the report. ADI is publishing this report, in conjunction with World Alzheimer's Day™ (21 September) and as a part of World Alzheimer's Month, an international ...
Diabetes complications make patients more likely to fall down stairs
2014-09-17
New research presented at this year's annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Vienna, Austria, shows that people suffering from diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN)—a complication of diabetes that affects the nerves in the limbs—are likely to sway more during stair climbing, and thus are more likely to fall. Steven Brown, Manchester Metropolitan University, UK, is the lead author on this research, which has been conducted by researchers at Manchester Metropolitan University and the University of Manchester, UK.
Patients with DPN ...
Study shows users of insulin pumps are at 29 percent lower risk of death compared with patients on insulin injections
2014-09-17
A study of more than 18,000 patients with type 1 diabetes has shown that use of insulin pumps to administer insulin rather than treatment with multiple daily insulin injections results in a 29% reduction in all-cause mortality and 43% reduction in the risk of fatal cardiovascular disease (CVD, i.e. coronary heart disease or stroke). The study is presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in Vienna, Austria, and was prepared by Dr Soffia Gudbjörnsdottir, University of Gothenburg, Sweden and colleagues.
Insulin pump treatment (CSII ...
The Lancet: Scientists use modern forensic techniques to identify most likely cause of King Richard III's death
2014-09-17
New research led by the University of Leicester in the UK gives a blow-by-blow account of the injuries inflicted on King Richard III's body at the Battle of Bosworth Field on Aug 22, 1485. Modern forensic analysis of the King's skeletal remains reveals that three of his injuries had the potential to cause death quickly—two to the skull (page 4, figure 4) and one to the pelvis (page 5, figure 6).
The remains of King Richard III—the last English monarch to die in battle—were found under a car park in Leicester by archaeologists from the University of Leicester, and subsequently ...
Urine HPV test could offer non-invasive alternative to conventional smear, improve screening uptake
2014-09-17
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Up to 80% of sexually active women are infected at some point in their lives and infection with specific "high risk" strains of HPV has an established link to cervical cancer.
Current screening by cervical cytology (smear test) is invasive and time-consuming - and in recent years, cervical screening in the UK has fallen below 80%, particularly amongst women aged 25-30. Several studies have suggested that detecting HPV in urine may be a feasible alternative to cervical sampling, but the ...
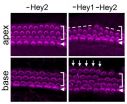
Hey1 and Hey2 ensure inner ear 'hair cells' are made at the right time, in the right place
2014-09-17
Two Johns Hopkins neuroscientists have discovered the "molecular brakes" that time the generation of important cells in the inner ear cochleas of mice. These "hair cells" translate sound waves into electrical signals that are carried to the brain and are interpreted as sounds. If the arrangement of the cells is disordered, hearing is impaired.
A summary of the research will be published in The Journal of Neuroscience on Sept. 16.
"The proteins Hey1 and Hey2 act as brakes to prevent hair cell generation until the time is right," says Angelika Doetzlhofer, Ph.D., an ...
36 Pit Fire in Oregon
2014-09-17
The 36 Pit Fire began on September 13, 2014. The fire is human-caused and is still under investigation. It is currently over 2,300 acres in size and is mostly being fueled by grass and timber. The 36 Pit Fire was calm Monday night due to higher humidity. Yesterday (8/15), firefighters made progress in establishing an anchor point and beginning to construct a fireline on the West and North sides of the fire.
The following resources are working on the fire:
7 20-person Crews
4 Hot Shot Crews
1 large Type 1 Helicopter
2 medium Type 2 Helicopter
2 bulldozer
17 ...
Focus on treatment costs, value: Less radiation for elderly women with early breast cancer
2014-09-16
(September 16th, 2014; San Francisco) – In a healthcare climate where the costs of treatment are increasingly weighed against potential benefit, a Yale study has found that radiation oncologists are using fewer or less-aggressive radiation procedures on elderly women with early-stage breast cancer. The findings are scheduled to be presented at the 56th annual conference of the American Society for Radiation Oncology in San Francisco. (Abstract 131: Evaluating National Practice in Radiotherapy for Elderly Women: Response to a Randomized Trial and Cost Effectiveness on a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] Violent origins of disc galaxies probed by ALMANew observations explain why Milky Way-like galaxies are so common in the Universe