(Press-News.org) As people spend more and more time in the workplace, it's natural for co-workers to develop close bonds — what's often referred to as a "workplace spouse" or an "office wife."
But when it comes to pay raises, promotions and other measures of career success, it's the husband or wife at home who may be exerting a bigger influence on workplace performance, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis. "Our study shows that it is not only your own personality that influences the experiences that lead to greater occupational success, but that your spouse's personality matters too," said Joshua Jackson, PhD, assistant professor of psychology in Arts & Sciences and lead author of the study.
Although we marry "for better for worse, for richer for poorer," this study is among the first to demonstrate that the personality traits of the spouse we choose may play a role in determining whether our chosen career makes us richer or poorer.
"The experiences responsible for this association are not likely isolated events where the spouse convinces you to ask for a raise or promotion," Jackson said. "Instead, a spouse's personality influences many daily factors that sum up and accumulate across time to afford one the many actions necessary to receive a promotion or a raise."
Forthcoming in the journal Psychological Science, the findings are based on a five-year study of nearly 5,000 married people ranging in age from 19 to 89, with both spouses working in about 75 percent of the sample.
Jackson and co-author Brittany Solomon, a graduate student in psychology at Washington University, analyzed data on study participants who took a series of psychological tests to assess their scores on five broad measures of personality — openness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism and conscientiousness.
In an effort to gauge whether these spousal personality traits might be seeping into the workplace, they tracked the on-the-job performance of working spouses using annual surveys designed to measure occupational success — self-reported opinions on job satisfaction, salary increases and the likelihood of being promoted.
Workers who scored highest on measures of occupational success tended to have a spouse with a personality that scored high for conscientiousness, and this was true whether or not both spouses worked and regardless of whether the working spouse was male or female, the study found.
Jackson and Solomon also tested several theories for how a spouse's personality traits, especially conscientiousness, might influence their partner's performance in the workplace. Their findings suggest that having a conscientious spouse contributes to workplace success in three ways.
First, through a process known as outsourcing, the working spouse may come to rely on his or her partner to handle more of the day-to-day household chores, such as paying bills, buying groceries and raising children. Workers also may be likely to emulate some of the good habits of their conscientious spouses, bringing traits such as diligence and reliability to bear on their own workplace challenges. Finally, having a spouse that keeps your personal life running smoothly may simply reduce stress and make it easier to maintain a productive work-life balance.
While previous research with romantic partners has shown that a bad experience in one social context can bleed over into another (a bad day at work can lead to a grumpy spouse and a tense night at home, for example), the Jackson/Solomon study goes beyond this to suggest that these sort of patterns exist day-in and day-out, exerting a subtle, but important influence on our performance in environments far removed from our home lives and our spouses.
The findings, they suggest, also have interesting implications for how we go about choosing romantic partners. While previous research suggests that people seeking potential mates tend to look for partners who score high on agreeableness and low on narcissism, this study suggests that people with ambitious career goals may be better served to seek supportive partners with highly conscientious personalities.
"This is another example where personality traits are found to predict broad outcomes like health status or occupational success, as in this study," Jackson said. "What is unique to this study is that your spouse's personality has an influence on such important life experiences."
INFORMATION: END
Spouse's personality influences career success, study finds
Husbands, wives may influence behavior in the workplace
2014-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Marcellus drilling boom may have led to too many hotel rooms
2014-09-18
Drilling in Pennsylvania's Marcellus Shale region led to a rapid increase in both the number of hotels and hotel industry jobs, but Penn State researchers report that the faltering occupancy rate may signal that there are now too many hotel rooms.
"Demand is still high in many of the counties in the Marcellus Shale region, but the occupancy rate is starting to come down," said Daniel Mount, an associate professor in hospitality management. "The case could be made that this is a sign that hotels were overbuilt."
Marcellus drilling operations generated approximately $685 ...
Survey: Fortune 500 employees can expect to pay more for health insurance
2014-09-18
Employees working for Fortune 500 companies can expect to pay higher employee contributions for their health insurance, according to a survey of chief human resource officers about the impact of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (also known as PPACA or Obamacare) conducted by the Darla Moore School of Business at the University of South Carolina this past May/June.
Patrick Wright, a professor in strategic human resource management, directs the annual the HR@Moore Survey of Chief HR Officers. The survey is distributed to more than 560 CHROs of Fortune 500 ...
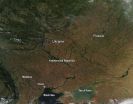
Agricultural fires in the Ukraine
2014-09-18
Numerous fires (marked with red dots) are burning in Eastern Europe, likely as a result of regional agricultural practices. The body of water at the lower left of this true-color Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) image is the Sea of Azov. The Sea is bordered by Ukraine to the northwest, west and southwest and by Russia to the northeast, east, and southeast. To its left is the Black Sea.
The location, widespread nature, and number of fires suggest that these fires were deliberately set to manage land. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the ...
Professional recommendations against routine prostate cancer screening have little effect
2014-09-18
DETROIT – The effect of guidelines recommending that elderly men should not be routinely screened for prostate cancer "has been minimal at best," according to a new study led by researchers at Henry Ford Hospital.
The study, published as a research letter online in JAMA Internal Medicine, focused on the use of PSA – prostate-specific antigen – to test for prostate cancer.
"We found that the effect of the guidelines recommending against the routine screening of elderly men in particular has been minimal at best," says Jesse Sammon, D.O., a researcher at Henry Ford's Vattikuti ...
New insights on an ancient plague could improve treatments for infections
2014-09-18
DURHAM, N.C. – Dangerous new pathogens such as the Ebola virus invoke scary scenarios of deadly epidemics, but even ancient scourges such as the bubonic plague are still providing researchers with new insights on how the body responds to infections.
In a study published online Sept. 18, 2014, in the journal Immunity, researchers at Duke Medicine and Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School Singapore detail how the Yersinia pestis bacteria that cause bubonic plague hitchhike on immune cells in the lymph nodes and eventually ride into the lungs and the blood stream, where the infection ...
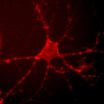
Sensing neuronal activity with light
2014-09-18
For years, neuroscientists have been trying to develop tools that would allow them to clearly view the brain's circuitry in action—from the first moment a neuron fires to the resulting behavior in a whole organism. To get this complete picture, neuroscientists are working to develop a range of new tools to study the brain. Researchers at Caltech have developed one such tool that provides a new way of mapping neural networks in a living organism.
The work—a collaboration between Viviana Gradinaru (BS '05), assistant professor of biology and biological engineering, and ...
No sedative necessary: Scientists discover new 'sleep node' in the brain
2014-09-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A sleep-promoting circuit located deep in the primitive brainstem has revealed how we fall into deep sleep. Discovered by researchers at Harvard School of Medicine and the University at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, this is only the second "sleep node" identified in the mammalian brain whose activity appears to be both necessary and sufficient to produce deep sleep.
Published online in August in Nature Neuroscience, the study demonstrates that fully half of all of the brain's sleep-promoting activity originates from the parafacial ...
Miranda: An icy moon deformed by tidal heating
2014-09-18
Boulder, Colo., USA – Miranda, a small, icy moon of Uranus, is one of the most visually striking and enigmatic bodies in the solar system. Despite its relatively small size, Miranda appears to have experienced an episode of intense resurfacing that resulted in the formation of at least three remarkable and unique surface features -- polygonal-shaped regions called coronae.
These coronae are visible in Miranda's southern hemisphere, and each one is at least 200 km across. Arden corona, the largest, has ridges and troughs with up to 2 km of relief. Elsinore corona has ...
Research milestone in CCHF virus could help identify new treatments
2014-09-18
SAN ANTONIO, September 18, 2014 – New research into the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), a tick-borne virus which causes a severe hemorrhagic disease in humans similar to that caused by Ebolavirus, has identified new cellular factors essential for CCHFV infection. This discovery has the potential to lead to novel targets for therapeutic interventions against the pathogen.
The research, reported in a paper published today in the journal PLoS Pathogens and conducted by scientists at the Texas Biomedical Research Institute and their colleagues, represents ...
Microplastic pollution discovered in St. Lawrence River sediments
2014-09-18
A team of researchers from McGill University and the Quebec government have discovered microplastics (in the form of polyethylene 'microbeads', END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
[Press-News.org] Spouse's personality influences career success, study findsHusbands, wives may influence behavior in the workplace