(Press-News.org) Different types of nerves and skin receptors work in concert to produce sensations of touch, University of Chicago neuroscientists argue in a review article published Sept. 22, 2014, in the journal Trends in Neurosciences. Their assertion challenges a long-held principle in the field—that separate groups of nerves and receptors are responsible for distinct components of touch, like texture or shape. They hope to change the way somatosensory neuroscience is taught and how the science of touch is studied.
Sliman Bensmaia, PhD, assistant professor of organismal biology and anatomy at the University of Chicago, and Hannes Saal, PhD, a postdoctoral scholar in Bensmaia's lab, reviewed more than 100 research studies on the physiological basis of touch published over the past 57 years. They argue that evidence once thought to show that different groups of receptors and nerves, or afferents, were responsible for conveying information about separate components of touch to the brain actually demonstrates that these afferents work together to produce the complex sensation.
"Any time you touch an object, all of these afferents are active together," Bensmaia said. "They each convey information about all aspects of an object, whether it's the shape, the texture, or its motion across the skin."
Three different types of afferents convey information about touch to the brain: slowly adapting type 1 (SA1), rapidly adapting (RA) and Pacinian (PC). According to the traditional view, SA1 afferents are responsible for communicating information about shape and texture of objects, RA afferents help sense motion and grip control, and PC afferents detect vibrations.
In the past, Bensmaia said, this classification system has been supported by experiments using mechanical devices to elicit one or more of these specific components of touch. For example, responses to texture are often generated using a rotating, cylindrical drum covered with a Braille-like pattern of raised dots. Study subjects would place a finger on the drum as it rotated, and scientists recorded the neural responses.
Such experiments showed that SA1 afferents responded very strongly to this artificial stimulus, and RA and PC afferents did not, thus the association of SA1s with texture. However, in experiments in which subjects moved a finger across sandpaper—the quintessential example of the type of textures we encounter in the real world—SA1 afferents did not respond at all.
Bensmaia also pointed out discrepancies in the predominant thinking about how we discern shape. Perception of shapes has generally been tested using devices with raised or embossed letters to test a subject's ability to interpret text by touch. These experiments also showed that such inputs produced a strong SA1 response, so they were implicated in perception of shape as well.
In the 1980s, however, researchers developed a device meant to help blind people read by generating vibrating patterns in the shape of letters on an array of pins. While the device was not a commercial success, people were able to use it to detect letter shapes and read, although experiments showed that it activated RA and PC afferents, not the supposedly shape-detecting SA1s.
Bensmaia said such experiments show how devices created to generate artificial stimuli focusing on individual components of the sense of touch can result in misleading findings. Some types of afferents are better than others at detecting texture or shape, for example, but all of them respond in their own way and contribute to the overall sensation.
"To get a good picture of how stimulus information is being conveyed in these afferent populations, you have to look at a diverse set of stimuli that spans the range of what you might feel in everyday tactile experience," he said.
Instead of thinking of individual groups of afferents working separately to process different components of the sense of touch, Bensmaia said we should think of all of them working in concert, much like individual musicians in a band to create its overall sound. Each musician contributes in his or her own way. Emphasizing one instrument or removing another can change the character of a song, but no single sound is responsible for the entire performance.
Adopting this new way of thinking will have far-reaching implications for both the study of the sense of touch and the design of future research, Bensmaia said.
"I think it's going to change neuroscience textbooks, and by extension it's going to change the way somatosensory neuroscience is taught. It's really the starting point for everything."
INFORMATION: END
University of Chicago neuroscientists challenge long-held understanding of the sense of touch
2014-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Variability keeps the body in balance
2014-09-22
Although the heart beats out a very familiar "lub-dub" pattern that speeds up or slows down as our activity increases or decreases, the pattern itself isn't as regular as you might think. In fact, the amount of time between heartbeats can vary even at a "constant" heart rate—and that variability, doctors have found, is a good thing.
Reduced heart rate variability (HRV) has been found to be predictive of a number of illnesses, such as congestive heart failure and inflammation. For athletes, a drop in HRV has also been linked to fatigue and overtraining. However, the underlying ...
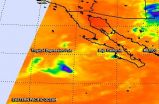
NASA sees Tropical Depression Polo winding down
2014-09-22
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed only a swirl of low-level clouds some deep clouds around Polo's weakening center on Sept. 22 as the storm weakened to a depression.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathered infrared data on Polo on Sept. 22 at 5:11 a.m. EDT, reading cloud top temperatures. There was a small area of high clouds, indicating that most thunderstorms in the depression had weakened or already dissipated except for that area.
At 5 a.m. EDT on Monday, Sept. 22, Tropical Depression Polo's maximum sustained ...
Compound from hops aids cognitive function in young animals
2014-09-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Xanthohumol, a type of flavonoid found in hops and beer, has been shown in a new study to improve cognitive function in young mice, but not in older animals.
The research was just published in Behavioral Brain Research by scientists from the Linus Pauling Institute and College of Veterinary Medicine at Oregon State University. It's another step toward understanding, and ultimately reducing the degradation of memory that happens with age in many mammalian species, including humans.
Flavonoids are compounds found in plants that often give them their ...
Engineers show light can play seesaw at the nanoscale
2014-09-22
University of Minnesota electrical engineering researchers have developed a unique nanoscale device that for the first time demonstrates mechanical transportation of light. The discovery could have major implications for creating faster and more efficient optical devices for computation and communication.
The research paper by University of Minnesota electrical and computer engineering assistant professor Mo Li and his graduate student Huan Li has been published online and will appear in the October issue of Nature Nanotechnology.
Researchers developed a novel nanoscale ...
Graphene imperfections key to creating hypersensitive 'electronic nose'
2014-09-22
Researchers have discovered a way to create a highly sensitive chemical sensor based on the crystalline flaws in graphene sheets. The imperfections have unique electronic properties that the researchers were able to exploit to increase sensitivity to absorbed gas molecules by 300 times.
The study is available online in advance of print in Nature Communications.
Amin Salehi- Khojin, asst professor of mechanical and industrial engineering in the lab with Mohammad Asadi, graduate student and Bijandra Kumar, post doc where they are doing research in graphene sensors. Photo: ...
Gravitational waves according to Planck
2014-09-22
No one has ever directly observed gravitational waves, phenomena predicted by Einstein's theory of General Relativity, and such a discovery would have profound implications for the study of the Universe. Last March, however, the team behind the BICEP2 project made a ground-breaking announcement: the Antarctic observatory had detected a signal referable to gravitational waves. The study claimed to have excluded possible contaminants (other sources that could have generated the same signal) and that the observation was therefore to be considered genuine. But not everyone ...
Miranda: An icy moon deformed by convection
2014-09-22
Boulder, Colo., USA – Miranda, a small, icy moon of Uranus, is one of the most visually striking and enigmatic bodies in the solar system. Despite its relatively small size, Miranda appears to have experienced an episode of intense resurfacing that resulted in the formation of at least three remarkable and unique surface features -- polygonal-shaped regions called coronae.
These coronae are visible in Miranda's southern hemisphere, and each one is at least 200 km across. Arden corona, the largest, has ridges and troughs with up to 2 km of relief. Elsinore corona has ...
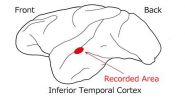
Neurons express 'gloss' using 3 perceptual parameters
2014-09-22
Japanese researchers showed monkeys a number of images representing various glosses and then they measured the responses of 39 neurons by using microelectrodes. They found that a specific population of neurons changed the intensities of the responses linearly according to either the contrast-of-highlight, sharpness-of-highlight, or brightness of the object. This shows that these 3 perceptual parameters are used as parameters when the brain recognizes a variety of glosses. They also found that different parameters are represented by different populations of neurons. This ...
A two-generation lens: Current state policies fail to support families with young children
2014-09-22
September 19, 2014 -- Recent two-generation approaches to reducing poverty that help children and their parents are receiving increasing attention from researchers, advocates, and foundations. By combining education and training for parents to enable them to move to jobs that offer a path out of poverty with high-quality early care and education for children, these programs aim to improve the life opportunities of both. However, according to a new report from the National Center for Children in Poverty (NCCP), State Policies through a Two-Generation Lens, while research ...
Good bowel cleansing is key for high-quality colonoscopy
2014-09-22
Bethesda, MD (Sept. 22, 2014) — The success of a colonoscopy is closely linked to good bowel preparation, with poor bowel prep often resulting in missed precancerous lesions, according to new consensus guidelines released by the U.S. Multi-Society Task force on Colorectal Cancer. Additionally, poor bowel cleansing can result in increased costs related to early repeat procedures. Up to 20 to 25 percent of all colonoscopies are reported to have an inadequate bowel preparation.
"When prescribing bowel preparation for their patients, health-care professionals need to be ...