(Press-News.org) Nanocomposite oxide ceramics have potential uses as ferroelectrics, fast ion conductors, and nuclear fuels and for storing nuclear waste, generating a great deal of scientific interest on the structure, properties, and applications of these blended materials.
"The interfaces separating the different crystalline regions determine the transport, electrical, and radiation properties of the material as a whole," said Pratik Dholabhai, principal Los Alamos National Laboratory researcher on the project. "It is in the chemical makeup of these interfaces where we can improve features such as tolerance against radiation damage and fast ion conduction."
A composite is a material containing grains, or chunks, of several different materials. In a nanocomposite, the size of each of these grains is on the order of nanometers, roughly 1000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. In the context of nuclear energy, composites have been proposed for the fuel itself, as a way for example, to improve the basic properties of the material, such as the thermal conductivity. It is the thermal conductivity that dictates how efficiently energy can be extracted from the fuel. Composites have also been created to store the by-products of the nuclear energy cycle, nuclear waste, where the different components of the composite can each store a different part of the waste.
However, composites have much broader applications. The interfaces provide regions of unique electronic and ionic properties and have been studied for enhance conductivity for applications related to batteries and fuel cells.
Mysteries of Misfit Dislocations
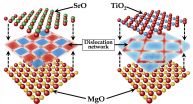
Using simulations that explicitly account for the position of each atom within the material, the Los Alamos research team examined the interface between SrTiO3 and MgO, demonstrating, for the first time, a strong dependence of the dislocation structure at oxide heterointerfaces on the termination chemistry. SrTiO3 can be viewed like a layer cake, with alternating planes of SrO and TiO2. Thus, in principle, when matching SrTiO3 with another material, there is a choice as to which layer is in contact with the other material. The simulations reveal that SrO- and TiO2-terminated interfaces exhibit remarkably different atomic structures. These structures, characterized by so-called misfit dislocations that form when the two materials do not exactly match in size, dictate the functional properties of the interface, such as the conductivity.
The observed relationship between the termination chemistry and the dislocation structure of the interface offers potential avenues for tailoring transport properties and radiation damage resistance of oxide nanocomposites by controlling the termination chemistry at the interface. This could lead to new functional materials in a number of technological areas. "We believe that this discovery, that the interface structure is sensitive to the chemistry of the interface, will open the door for new research directions in oxide nanocomposites," said Blas Uberuaga, lead researcher on the effort.
INFORMATION:
The research is described in a paper out this week in Nature Communications, "Termination chemistry-driven dislocation structure at SrTiO3/MgO heterointerfaces." The digital object identifier code for the paper is 10.1038/ncomm6043. The work was funded by the Center for Materials at Irradiation and Mechanical Extremes (CMIME), an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science.
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, The Babcock & Wilcox Company, and URS for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
Los Alamos researchers uncover properties in nanocomposite oxide ceramics for reactor fuel
Misfit dislocations are key to transport properties across material interfaces
2014-09-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Beating stress outdoors? Nature group walks may improve mental health
2014-09-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — They are common suggestions to remedy stress: You just need a breath of fresh air. Walk it off. Get out and see people.
Turns out all those things combined may in fact make you feel better – a lot better – a new large scale study suggests.
Group nature walks are linked with significantly lower depression, less perceived stress and enhanced mental health and well-being, according to the study conducted by the University of Michigan, with partners from De Montfort University, James Hutton Institute, and Edge Hill University in the United Kingdom. The ...
Paraffins to cut energy consumption in homes
2014-09-23
Thermal energy storage is a common strategy in energy production systems in which the period of production does not coincide with that of consumption. This happens with the production of hot water by means of solar thermal panels, for example; here, hot water is produced during sunlight hours when demand is lower. It is also the case in residential cogeneration, where heat and electrical power are simultaneously generated but not so demand. In both cases, storing the heat allows production to be decoupled from demand, thus making the integration of these technologies into ...
Advancing the understanding of an understudied food allergy disorder
2014-09-23
Investigators at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have published the first study to extensively characterize eosinophilic gastritis (EG). The study, published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, found that EG is a systemic disorder that has high levels of eosinophils in the blood and gastrointestinal tract, involves a series of allergy-associated-immune mechanisms and has a gene expression pattern (transcriptome) that is distinct from that of a related disorder, eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders are chronic ...
Gene mutation discovered in blood disorder
2014-09-23
An international team of scientists has identified a gene mutation that causes aplastic anemia, a serious blood disorder in which the bone marrow fails to produce normal amounts of blood cells. Studying a family in which three generations had blood disorders, the researchers discovered a defect in a gene that regulates telomeres, chromosomal structures with crucial roles in normal cell function.
"Identifying this causal defect may help suggest future molecular-based treatments that bypass the gene defect and restore blood cell production," said study co-leader Hakon Hakonarson, ...
NASA sees Tropical Depression Fung-Wong becoming more frontal
2014-09-23
Tropical Depression Fung-Wong skirted the coast of mainland China and is moving through the East China Sea. NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data that showed strongest thunderstorms were stretched out as the storm continues to look more frontal in nature.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Fung-Wong on Sept. 22 at 1:23 p.m. EDT, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument read cloud top temperatures. AIRS detected strongest, highest storms, those with the coldest cloud tops stretched out from northwest to southeast giving the depression ...
New research suggests sleep apnea screening before surgery
2014-09-23
Scheduled for surgery? New research suggests that you may want to get screened and treated for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) before going under the knife. According to a first-of-its-kind study in the October issue of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), patients with OSA who are diagnosed and treated for the condition prior to surgery are less likely to develop serious cardiovascular complications such as cardiac arrest or shock.
"OSA is a common disorder that affects millions and is associated with an increased ...
Recreating the stripe patterns found in animals by engineering synthetic gene networks
2014-09-23
VIDEO:
Researchers at the CRG try to understand how networks of genes work together to create specific patterns like stripes.
They have gone beyond studying individual networks and have created computational and...
Click here for more information.
Pattern formation is essential in the development of animals and plants. The central problem in pattern formation is how can genetic information be translated in a reliable manner to give specific spatial patterns of cellular differentiation. ...
Airway muscle-on-a-chip mimics asthma
2014-09-23
The majority of drugs used to treat asthma today are the same ones that were used 50 years ago. New drugs are urgently needed to treat this chronic respiratory disease, which causes nearly 25 million people in the United States alone to wheeze, cough, and find it difficult at best to take a deep breath.
But finding new treatments is tough: asthma is a patient-specific disease, so what works for one person doesn't necessarily work for another, and the animal models traditionally used to test new drug candidates often fail to mimic human responses – costing tremendous ...
Eating five a day may keep the blues away
2014-09-23
Fruit and vegetable consumption could be as good for your mental as your physical health, new research suggests.
The research, conducted by the University of Warwick's Medical School using data from the Health Survey for England, and published by BMJ Open focused on mental wellbeing and found that high and low mental wellbeing were consistently associated with an individual's fruit and vegetable consumption.
33.5% of respondents with high mental wellbeing ate five or more portions of fruit and vegetables a day, compared with only 6.8% who ate less than one portion. ...
Southampton scientists grow a new challenger to graphene
2014-09-23
A team of researchers from the University of Southampton's Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) has developed a new way to fabricate a potential challenger to graphene.
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms in a honeycomb lattice, is increasingly being used in new electronic and mechanical applications, such as transistors, switches and light sources, thanks to the unprecedented properties it offers: very low electrical resistance, high thermal conductivity and mechanically stretchable yet harder than diamond.
Now, ORC researchers have developed molybdenum di-sulphide ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
[Press-News.org] Los Alamos researchers uncover properties in nanocomposite oxide ceramics for reactor fuelMisfit dislocations are key to transport properties across material interfaces