(Press-News.org) As tech company LG demonstrated this summer with the unveiling of its 18-inch flexible screen, the next generation of roll-up displays is tantalizingly close. Researchers are now reporting in the journal ACS Nano a new, inexpensive and simple way to make transparent, flexible transistors — the building blocks of electronics — that could help bring roll-up smartphones with see-through displays and other bendable gadgets to consumers in just a few years.
Yang Yang and colleagues note that transistors are traditionally made in a multi-step photolithography process, which uses light to print a pattern onto a glass or wafer. Not only is this approach costly, it also involves a number of toxic substances. Finding a greener, less-expensive alternative has been a challenge. Recently, new processing techniques using metal oxide semiconductors have attracted attention, but the resulting devices are lacking in flexibility or other essential traits. Yang's team wanted to address these challenges.
The researchers developed inks that create patterns on ultrathin, transparent devices when exposed to light. This light sensitivity precludes the need for harsh substances or high temperatures. "The main application of our transistors is for next-generation displays, like OLED or LCD displays," said Yang. "Our transistors are designed for simple manufacturing. We believe this is an important step toward making flexible electronics widely accessible."
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Science Foundation.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook
'Greener,' low-cost transistor heralds advance in flexible electronics
2014-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Fracking' wastewater that is treated for drinking produces potentially harmful compounds
2014-09-24
Concerns that fluids from hydraulic fracturing, or "fracking," are contaminating drinking water abound. Now, scientists are bringing to light another angle that adds to the controversy. A new study, appearing in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, has found that discharge of fracking wastewaters to rivers, even after passage through wastewater treatment plants, could be putting the drinking water supplies of downstream cities at risk.
William A. Mitch, Avner Vengosh and colleagues point out that the disposal of fracking wastewater poses a major challenge ...
Sam Houston State study finds gang life is short-lived
2014-09-24
HUNTSVILLE, TX 9/24/14 -- Although membership in a gang often is depicted as a lifelong commitment, the typical gang member joins at age 13 and only stays active for about two years, according to a study at Sam Houston State University.
"Gang membership is not a fixed identity or a scarlet letter," said David Pyrooz in an article published in the Journal of Quantitative Criminology. "Media and popular culture have led to misconceptions about gangs and gang membership, chief among them the myth of permanence, as reflected in the quote from West Side Story –'When you're ...
2-D materials' crystalline defects key to new properties
2014-09-24
Understanding how atoms "glide" and "climb" on the surface of 2D crystals like tungsten disulphide may pave the way for researchers to develop materials with unusual or unique characteristics, according to an international team of researchers.
"If we don't understand what is behind the materials' characteristics caused by these defects, then we can't engineer the right properties into devices," said Nasim Alem, assistant professor of materials science and engineering, Penn State. "With a closer look, we might find that some of the defects are no good, that we don't want ...
Wavefront optics emerging as new tool for measuring and correcting vision, reports Optometry and Vision Science
2014-09-24
September 24, 2014 – A technique developed by astronomers seeking a clear view of distant objects in space is being intensively studied as a new approach to measuring and correcting visual abnormalities. The October issue of Optometry and Vision Science, official journal of the American Academy of Optometry, is a theme issue devoted to research on wavefront refraction and correction. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The special issue presents new research on the use of wavefront analysis for assessing subtle, ...
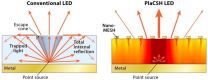
Nanotechnology leads to better, cheaper LEDs for phones and lighting
2014-09-24
Princeton University researchers have developed a new method to increase the brightness, efficiency and clarity of LEDs, which are widely used on smartphones and portable electronics as well as becoming increasingly common in lighting.
Using a new nanoscale structure, the researchers, led by electrical engineering professor Stephen Chou, increased the brightness and efficiency of LEDs made of organic materials (flexible carbon-based sheets) by 58 percent. The researchers also report their method should yield similar improvements in LEDs made in inorganic (silicon-based) ...
Pressure mounts on FDA and industry to ensure safety of food ingredients
2014-09-24
Confusion over a 1997 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) rule that eases the way for food manufacturers to use ingredients "generally regarded as safe," or GRAS, has inspired a new initiative by food makers. Food safety advocates say the current GRAS process allows substances into the food supply that might pose a health risk, while industry defends its record. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN) details what changes are on the table.
Melody M. Bomgardner, a senior editor at C&EN, explains that the rule, which was never finalized, was initially established ...
Higher risk of autism found in children born at short and long interpregnancy intervals
2014-09-24
Washington D.C., September 24, 2014 – A study published in the MONTH 2014 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry found that children who were conceived either less than 1 year or more than 5 years after the birth of their prior sibling were more likely to be diagnosed with autism than children conceived following an interval of 2-5 years.
Using data from the Finnish Prenatal Study of Autism (FIPS-A), a group of researchers led by Keely Cheslack-Postava, PhD, of Columbia University, analyzed records from 7371 children born between ...
Most breast cancer patients who had healthy breast removed at peace with decision
2014-09-24
ROCHESTER, Minn. — More women with cancer in one breast are opting to have both breasts removed to reduce their risk of future cancer. New research shows that in the long term, most have no regrets. Mayo Clinic surveyed hundreds of women with breast cancer who had double mastectomies between 1960 and 1993 and found that nearly all would make the same choice again. The findings are published in the journal Annals of Surgical Oncology.
The study made a surprising finding: While most women were satisfied with their decision whether they followed it with breast reconstruction ...
Solar explosions inside a computer
2014-09-24
The shorter the interval between two explosions in the solar atmosphere, the more likely it is that the second flare will be stronger than the first one. ETH Professor Hans Jürgen Herrmann and his team have been able to demonstrate this, using model calculations. The amount of energy released in solar flares is truly enormous – in fact, it is millions of times greater than the energy produced in volcanic eruptions. Strong explosions cause a discharge of mass from the outer part of the solar atmosphere, the corona. If a coronal mass ejection hits the earth, it can cause ...
Research shows alcohol consumption influenced by genes
2014-09-24
How people perceive and taste alcohol depends on genetic factors, and that influences whether they "like" and consume alcoholic beverages, according to researchers in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
In the first study to show that the sensations from sampled alcohol vary as a function of genetics, researchers focused on three chemosensory genes -- two bitter-taste receptor genes known as TAS2R13 and TAS2R38 and a burn receptor gene, TRPV1. The research was also the first to consider whether variation in the burn receptor gene might influence alcohol sensations, ...