(Press-News.org) CHICAGO --- The first animal model for ALS dementia, a form of ALS that also damages the brain, has been developed by Northwestern Medicine® scientists. The advance will allow researchers to directly see the brains of living mice, under anesthesia, at the microscopic level. This will allow direct monitoring of test drugs to determine if they work.
This is one of the latest research findings since the ALS Ice Bucket Challenge heightened interest in the disease and the need for expanded research and funding.
"This new model will allow rapid testing and direct monitoring of drugs in real time," said Northwestern scientist and study senior author Teepu Siddique, M.D. "This will allow scientists to move quickly and accelerate the testing of drug therapies."
The new mouse model has the pathological hallmarks of the disease in humans with mutations in the genes for UBQLN2 (ubliqulin 2) and SQSTM1 (P62) that Siddique and colleagues identified in 2011. That pathology was linked to all forms of ALS and ALS/dementia.
Siddique and Han-Xiang Deng, M.D., the corresponding authors on the paper, said they have reproduced behavioral, neurophysiological and pathological changes in a mouse that mimic this form of dementia associated with ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis).
Siddique is the Les Turner ALS Foundation/Herbert C. Wenske Professor of neurology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a neurologist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Deng is a research professor in neurology at Feinberg.
The study was published Sept. 22 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
It's been difficult for scientists to reproduce the genetic mutations of ALS, especially ALS/dementia in animal models, Siddique noted, which has hampered drug therapy testing.
Five percent or more of ALS cases, also known as Lou Gehrig's Disease, also have ALS/dementia.
"ALS with dementia is an even more vicious disease than ALS alone because it attacks the brain causing changes in behavior and language well as paralysis," Siddique said.
ALS affects an estimated 350,000 people worldwide, with an average survival of three years. In this progressive neurological disorder, the degeneration of neurons leads to muscle weakness and impaired speaking, swallowing and breathing, eventually causing paralysis and death. The associated dementia affects behavior and may affect decision-making, judgment, insight and language.
INFORMATION:
Other Northwestern authors on the paper include first authors George H. Gorrie, Faisal Fecto, Daniel Radzicki, Craig Weiss, Yong Shi, Hongxin Dong, Hong Zhai, Ronggen Fu, Erdong Liu, Sisi Li, Hasan Arrat, Eileen H. Bigio, John F. Disterhoft, Marco Martina and Enrico Mugnaini. Gorrie is now a consultant neurologist in Scotland.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke grants NS050641, NS078504, NS070142, NS081474, NS064091, NS009904, NS078287, and the National Institute on Aging grants AG20506 and AG13854, both of the National Institutes of Health, the Les Turner ALS Foundation, the Vena E. Schaff ALS Research Fund, a Harold Post Research Professorship, the Herbert and Florence C. Wenske Foundation and the Les Turner ALS Foundation/Herbert C. Wenske Foundation Professorship and others.
First mouse model for ALS dementia
Now scientists can directly view drugs' effect on brain
2014-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Findings give hope to plant extract as possible lupus treatment
2014-09-24
HOUSTON, Sept. 24, 2014 – New findings by a biomedical engineer and his team at the University of Houston (UH) raise hope for a new class of drugs to treat lupus that may not include the long list of adverse risks and side effects often associated with current treatments for this disease.
Lupus, or systemic lupus erythematosus, is a progressive, degenerative disease in which the immune system turns against itself, attacking a person's healthy tissue, cells and organs. Symptoms range from debilitating pain and fatigue to organ failure and a host of other impairments. ...
Captive whooping cranes released into the wild
2014-09-24
NECEDAH, Wis. – Four whooping crane chicks raised in captivity began their integration into the wild Saturday as part of the continuing effort to increase the wild population of this endangered species.
The cranes, hatched and raised by their parents at the U.S. Geological Survey's Patuxent Wildlife Research Center in Laurel, Maryland, were released on the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service's Necedah National Wildlife Refuge in Wisconsin.
The chicks, about six-months old, are part of an experimental rearing and release method referred to as "parent-rearing." The parent-reared ...
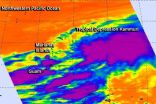
NASA sees System 98W become Tropical Depression Kammuri
2014-09-24
Strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation in tropical low pressure System 98W were seen on infrared satellite imagery and were a clue to forecasters that the storm was intensifying. Early on Sept. 24, the storm intensified into Tropical Depression Kammuri far north of Guam.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Kammuri on Sept. 24 at 12:23 a.m. EDT. Kammuri is a large storm and strong thunderstorms covered a long area within the somewhat elongated circulation. The circulation center was near the western edge of the massive extent of clouds. ...
Arabic tweets point to US influence as fuel for anti-Americanism
2014-09-24
An analysis of millions of Arabic-language tweets confirms high levels of anti-Americanism there, provides new and interesting information about attitudes in the Middle East toward particular U.S. actions, and charts a path for using Twitter to measure public sentiment in ways opinion polls cannot.
The findings also highlight policy challenges — and opportunities — for the United States in the Middle East, said Amaney Jamal, a professor of politics at Princeton University who conducted the research with colleagues at Princeton and Harvard University.
"Can the U.S. ...
Better information about prenatal testing leads to fewer tests
2014-09-24
A clinical trial led by UC San Francisco has found that when pregnant women are educated about their choices on prenatal genetic testing, the number of tests actually drops, even when the tests are offered with no out-of-pocket costs.
The findings underscore the need for clear information on all prenatal testing options and their possible outcomes, including the option of no testing, before pregnant women decide whether or not to have genetic testing, the authors said.
The study also suggests that some women may have undergone prenatal screening for Down syndrome ...
'Skin-like' device monitors cardiovascular and skin health
2014-09-24
A new wearable medical device can quickly alert a person if they are having cardiovascular trouble or if it's simply time to put on some skin moisturizer, reports a Northwestern University and University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign study.
The small device, approximately five centimeters square, can be placed directly on the skin and worn 24/7 for around-the-clock health monitoring. The wireless technology uses thousands of tiny liquid crystals on a flexible substrate to sense heat. When the device turns color, the wearer knows something is awry.
"Our device is mechanically ...
Eyeless Mexican cavefish eliminate circadian rhythm to save energy
2014-09-24
Eyeless Mexican cavefish show no metabolic circadian rhythm in either light and dark or constant dark conditions, according to a study published September 24, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Damian Moran from Lund University, Sweden, and colleagues.
The Mexican tetra fish has two variants, a fully-eyed fish living close to the surface and a blind, deep water, cave-dwelling fish. Scientists in this study used these two fish to study evolutionary adaptation in fish residing in near or total darkness. The two fish types experience differences in daily light exposure, ...
Evolution of snake courtship and combat behavior
2014-09-24
A small study suggests snakes may have developed courtship and male-to-male combat behavior, such as moving undulations, neck biting, and spur-poking, over time, according to a study published September 24, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Phil Senter from Fayetteville State University and colleagues.
Behaviors involved in courtship and male-to-male combat have been recorded in over 70 snake species from five families in the clade Boidae and Colubroidea, but before now, scientists had yet to look for evolutionary relationships between these behaviors. The authors ...
From rats to humans: Project NEUWalk closer to clinical trials
2014-09-24
Lausanne, Switzerland. EPFL scientists have discovered how to control the limbs of a completely paralyzed rat in real time to help it walk again. Their results are published today in Science Translational Medicine.
Building on earlier work in rats, this new breakthrough is part of a more general therapy that could one day be implemented in rehabilitation programs for people with spinal cord injury, currently being developed in a European project called NEUWalk. Clinical trials could start as early as next summer using the new Gait Platform now assembled at the CHUV ...
Immune activity shortly after surgery holds big clue to recovery rate, Stanford team finds
2014-09-24
The millions of people who undergo major surgery each year have no way of knowing how long it will take them to recover from the operation. Some will feel better within days. For others, it will take a month or more. Right now, doctors can't tell individual patients which category they'll fit into.
Now, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered that the activity level of a small set of immune cells during the first 24 hours after surgery provides strong clues to how quickly patients will bounce back from surgery-induced fatigue and pain, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
SwRI develops magnetostrictive probe for safer, more cost-effective storage tank inspections
National report supports measurement innovation to aid commercial fusion energy and enable new plasma technologies
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
[Press-News.org] First mouse model for ALS dementiaNow scientists can directly view drugs' effect on brain