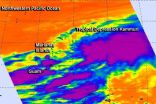
(Press-News.org) Strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation in tropical low pressure System 98W were seen on infrared satellite imagery and were a clue to forecasters that the storm was intensifying. Early on Sept. 24, the storm intensified into Tropical Depression Kammuri far north of Guam.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Kammuri on Sept. 24 at 12:23 a.m. EDT. Kammuri is a large storm and strong thunderstorms covered a long area within the somewhat elongated circulation. The circulation center was near the western edge of the massive extent of clouds. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard Aqua gathered infrared temperature data on the storm's clouds. The data was false-colored at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. The strongest thunderstorms had cloud-top temperatures near -63F/-53C reaching high into the troposphere (lowest layer of the atmosphere) and with the potential to generate heavy rain.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center bulleting on Sept. 24 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) noted that Kammuri had maximum sustained winds near 30 knots (34.5 mph/55.5 kph). It was centered about 320 miles northeast of Saipan, near 19.3 north latitude and 149.3 east longitude. At the time, the depression had It was moving to the north-northwestward at 4 knots (4.6 mph/7.4 kph).
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Kammuri to intensify into a typhoon and move to the north-northwest passing near the island of Iwo To on Sept. 27.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees System 98W become Tropical Depression Kammuri
2014-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Arabic tweets point to US influence as fuel for anti-Americanism
2014-09-24
An analysis of millions of Arabic-language tweets confirms high levels of anti-Americanism there, provides new and interesting information about attitudes in the Middle East toward particular U.S. actions, and charts a path for using Twitter to measure public sentiment in ways opinion polls cannot.
The findings also highlight policy challenges — and opportunities — for the United States in the Middle East, said Amaney Jamal, a professor of politics at Princeton University who conducted the research with colleagues at Princeton and Harvard University.
"Can the U.S. ...
Better information about prenatal testing leads to fewer tests
2014-09-24
A clinical trial led by UC San Francisco has found that when pregnant women are educated about their choices on prenatal genetic testing, the number of tests actually drops, even when the tests are offered with no out-of-pocket costs.
The findings underscore the need for clear information on all prenatal testing options and their possible outcomes, including the option of no testing, before pregnant women decide whether or not to have genetic testing, the authors said.
The study also suggests that some women may have undergone prenatal screening for Down syndrome ...
'Skin-like' device monitors cardiovascular and skin health
2014-09-24
A new wearable medical device can quickly alert a person if they are having cardiovascular trouble or if it's simply time to put on some skin moisturizer, reports a Northwestern University and University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign study.
The small device, approximately five centimeters square, can be placed directly on the skin and worn 24/7 for around-the-clock health monitoring. The wireless technology uses thousands of tiny liquid crystals on a flexible substrate to sense heat. When the device turns color, the wearer knows something is awry.
"Our device is mechanically ...
Eyeless Mexican cavefish eliminate circadian rhythm to save energy
2014-09-24
Eyeless Mexican cavefish show no metabolic circadian rhythm in either light and dark or constant dark conditions, according to a study published September 24, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Damian Moran from Lund University, Sweden, and colleagues.
The Mexican tetra fish has two variants, a fully-eyed fish living close to the surface and a blind, deep water, cave-dwelling fish. Scientists in this study used these two fish to study evolutionary adaptation in fish residing in near or total darkness. The two fish types experience differences in daily light exposure, ...
Evolution of snake courtship and combat behavior
2014-09-24
A small study suggests snakes may have developed courtship and male-to-male combat behavior, such as moving undulations, neck biting, and spur-poking, over time, according to a study published September 24, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Phil Senter from Fayetteville State University and colleagues.
Behaviors involved in courtship and male-to-male combat have been recorded in over 70 snake species from five families in the clade Boidae and Colubroidea, but before now, scientists had yet to look for evolutionary relationships between these behaviors. The authors ...
From rats to humans: Project NEUWalk closer to clinical trials
2014-09-24
Lausanne, Switzerland. EPFL scientists have discovered how to control the limbs of a completely paralyzed rat in real time to help it walk again. Their results are published today in Science Translational Medicine.
Building on earlier work in rats, this new breakthrough is part of a more general therapy that could one day be implemented in rehabilitation programs for people with spinal cord injury, currently being developed in a European project called NEUWalk. Clinical trials could start as early as next summer using the new Gait Platform now assembled at the CHUV ...
Immune activity shortly after surgery holds big clue to recovery rate, Stanford team finds
2014-09-24
The millions of people who undergo major surgery each year have no way of knowing how long it will take them to recover from the operation. Some will feel better within days. For others, it will take a month or more. Right now, doctors can't tell individual patients which category they'll fit into.
Now, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered that the activity level of a small set of immune cells during the first 24 hours after surgery provides strong clues to how quickly patients will bounce back from surgery-induced fatigue and pain, ...
Stanford scientists use stem cells to learn how common mutation in Asians affects heart health
2014-09-24
Over 500 million people worldwide carry a genetic mutation that disables a common metabolic protein called ALDH2. The mutation, which predominantly occurs in people of East Asian descent, leads to an increased risk of heart disease and poorer outcomes after a heart attack. It also causes facial flushing when carriers drink alcohol.
Now researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have learned for the first time specifically how the mutation affects heart health. They did so by comparing heart muscle cells made from induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPS ...
The plus side of population aging
2014-09-24
Around the world, people are living longer and having fewer children, leading to a population that is older, on average, than in the past. On average, life expectancy in developed countries has risen at a pace of three months per year, and fertility has fallen below replacement rate in the majority of Europe and other developed countries.
Most academic discussion of this trend has so far focused on potential problems it creates, including challenges to pension systems, economic growth, and healthcare costs.
But according to a new study published today in the journal PLOS ...
Brain scans reveal 'gray matter' differences in media multitaskers
2014-09-24
Simultaneously using mobile phones, laptops and other media devices could be changing the structure of our brains, according to new University of Sussex research.
A study published today (24 September) reveals that people who frequently use several media devices at the same time have lower grey-matter density in one particular region of the brain compared to those who use just one device occasionally.
The research supports earlier studies showing connections between high media-multitasking activity and poor attention in the face of distractions, along with emotional ...