(Press-News.org) Bottom Line: A treatment designed to help older individuals deal with complicated grief (CG) after the loss of a loved one appeared to be more effective than using a treatment designed for depression.
Authors: M. Katherine Shear, M.D., of the Columbia University School of Social Work, New York, and colleagues.
Background: About 9 percent of bereaved older women experience CG, a serious and debilitating mental health problem associated with functional impairment and increased suicidality. The symptoms can include prolonged grief, frequent thoughts and memories of the deceased, and difficulty imagining a meaningful future. Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) is a well-known treatment for depression but observations suggest that CG symptoms do not respond well to IPT.
How the Study Was Conducted: The study was a randomized clinical trial that enrolled 151 patients (average age 66 years) from the New York metropolitan area from August 2008 to January 2013. The authors developed a targeted CG treatment (CGT) based on an attachment therapy model. The aim was to resolve grief complications and facilitate natural mourning. The model focused on loss and restoration. IPT discussed bereavement effects on mood, encouraged realistic assessment of the deceased, talked about the death and worked to enhance relationships and activities in the present. The 151 individuals were divided into CGT (n= 74) or IPT (n=77) to receive 16 sessions delivered about weekly. The average time since the loss of a spouse, partner, parent, child or another relative or friend was 3.2 years.
Results: Both treatments helped improve CG symptoms. However, the response rate for CGT was more than twice that for IPT (CGT, 52 individuals [70.5 percent] vs. IPT, 24 individuals [32 percent]). There was a greater change in illness severity (22 individuals [35.2 percent]) in the CGT group vs. (41 individuals [64.1 percent]) in the IPT group who were still at least moderately ill. Symptom reduction per week also was greater in the CGT group.
Discussion: "Complicated grief is an under recognized public health problem that likely affects millions of people in the United States, many of them elderly. … Given a growing elderly population, increased rates of bereavement with age, and the distress and impairment associated with CG, effective treatment should have important public health outcomes."
INFORMATION:
(JAMA Psychiatry. Published online September 24, 2014. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1242. Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com.)
Editor's Note: An author made a conflict of interest disclosure. This study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Media Advisory: To contact author M. Katherine Shear, M.D., call Mary-Lea Cox Awanohara at 212-851-2327 or email mlc2144@columbia.edu or call Dacia Morris at 646-774-8724 or email Morrisd@nyspi.columbia.edu.
To place an electronic embedded link to this study in your story The link for this study will be live at the embargo time: http://archpsyc.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1242.
Clinical trial examined treatment for complicated grief in older individuals
2014-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Family-based therapies can treat anorexia in teens, Stanford/Packard study finds
2014-09-24
Two different family-based therapies are both effective at combating anorexia nervosa in teenagers, according to the largest study ever to compare two such treatments for the life-threatening eating disorder.
The findings, from a multisite study led by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine, add to a growing body of evidence supporting the value of parents' involvement in anorexia treatment.
The results, which will be published Sept. 24 in JAMA Psychiatry, follow prior Stanford research that found a family-based approach was twice as effective as ...
NIH study supports camels as primary source of MERS-CoV transmission
2014-09-24
National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Colorado State University (CSU) scientists have provided experimental evidence supporting dromedary camels as the primary reservoir, or carrier, of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). The study, designed by scientists from CSU and NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, involved three healthy camels exposed through the eyes, nose and throat to MERS-CoV isolated from a patient. Each camel developed a mild upper respiratory tract infection consistent with what scientists have observed throughout ...
When David beats Goliath
2014-09-24
Body size has long been recognized to play a key role in shaping species interactions, with larger species usually winning conflicts with their smaller counterparts. But Queen's University biologist Paul Martin has found that occasionally, small species of birds can dominate larger species during aggressive interactions, particularly when they interact with distantly related species.
The new findings provide evidence that the evolution of certain traits can allow species to overcome the disadvantage of a smaller size.
"We want to understand why species live where they ...
First mouse model for ALS dementia
2014-09-24
CHICAGO --- The first animal model for ALS dementia, a form of ALS that also damages the brain, has been developed by Northwestern Medicine® scientists. The advance will allow researchers to directly see the brains of living mice, under anesthesia, at the microscopic level. This will allow direct monitoring of test drugs to determine if they work.
This is one of the latest research findings since the ALS Ice Bucket Challenge heightened interest in the disease and the need for expanded research and funding.
"This new model will allow rapid testing and direct monitoring ...
Findings give hope to plant extract as possible lupus treatment
2014-09-24
HOUSTON, Sept. 24, 2014 – New findings by a biomedical engineer and his team at the University of Houston (UH) raise hope for a new class of drugs to treat lupus that may not include the long list of adverse risks and side effects often associated with current treatments for this disease.
Lupus, or systemic lupus erythematosus, is a progressive, degenerative disease in which the immune system turns against itself, attacking a person's healthy tissue, cells and organs. Symptoms range from debilitating pain and fatigue to organ failure and a host of other impairments. ...
Captive whooping cranes released into the wild
2014-09-24
NECEDAH, Wis. – Four whooping crane chicks raised in captivity began their integration into the wild Saturday as part of the continuing effort to increase the wild population of this endangered species.
The cranes, hatched and raised by their parents at the U.S. Geological Survey's Patuxent Wildlife Research Center in Laurel, Maryland, were released on the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service's Necedah National Wildlife Refuge in Wisconsin.
The chicks, about six-months old, are part of an experimental rearing and release method referred to as "parent-rearing." The parent-reared ...
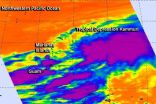
NASA sees System 98W become Tropical Depression Kammuri
2014-09-24
Strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation in tropical low pressure System 98W were seen on infrared satellite imagery and were a clue to forecasters that the storm was intensifying. Early on Sept. 24, the storm intensified into Tropical Depression Kammuri far north of Guam.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Kammuri on Sept. 24 at 12:23 a.m. EDT. Kammuri is a large storm and strong thunderstorms covered a long area within the somewhat elongated circulation. The circulation center was near the western edge of the massive extent of clouds. ...
Arabic tweets point to US influence as fuel for anti-Americanism
2014-09-24
An analysis of millions of Arabic-language tweets confirms high levels of anti-Americanism there, provides new and interesting information about attitudes in the Middle East toward particular U.S. actions, and charts a path for using Twitter to measure public sentiment in ways opinion polls cannot.
The findings also highlight policy challenges — and opportunities — for the United States in the Middle East, said Amaney Jamal, a professor of politics at Princeton University who conducted the research with colleagues at Princeton and Harvard University.
"Can the U.S. ...
Better information about prenatal testing leads to fewer tests
2014-09-24
A clinical trial led by UC San Francisco has found that when pregnant women are educated about their choices on prenatal genetic testing, the number of tests actually drops, even when the tests are offered with no out-of-pocket costs.
The findings underscore the need for clear information on all prenatal testing options and their possible outcomes, including the option of no testing, before pregnant women decide whether or not to have genetic testing, the authors said.
The study also suggests that some women may have undergone prenatal screening for Down syndrome ...
'Skin-like' device monitors cardiovascular and skin health
2014-09-24
A new wearable medical device can quickly alert a person if they are having cardiovascular trouble or if it's simply time to put on some skin moisturizer, reports a Northwestern University and University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign study.
The small device, approximately five centimeters square, can be placed directly on the skin and worn 24/7 for around-the-clock health monitoring. The wireless technology uses thousands of tiny liquid crystals on a flexible substrate to sense heat. When the device turns color, the wearer knows something is awry.
"Our device is mechanically ...