(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC scientists have discovered new clues about a drug instrumental in treating a certain blood cancer that may provide important targets for researchers searching for cures.
The team investigated whether demethylation of gene bodies induced by the drug 5-Aza-CdR (decitabine), which is used to treat pre-leukemia, could alter gene expression and possibly be a therapeutic target in cancer.
"When we put the drug in cancer cells, we found it not only reactivated some tumor suppressor genes, but it down-regulated the overexpressed oncogene (cancer gene)," said Gangning Liang, Ph.D., associate professor of research, Keck School of Medicine of USC Department of Urology, who is corresponding author on the research. "Overexpression is what turns cancer 'on.' The mechanism by which the drug accomplishes this dual action is by removing DNA methylation in the gene body, which we didn't expect."
DNA methylation is an epigenetic signaling tool used by cells use to turn genes off. DNA methylation is an important component in many cellular processes, including embryonic development. Mistakes in methylation are linked to several human diseases, including cancer.
The research builds upon past research by Peter Jones, Ph.D., D.Sc., former director of the USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Distinguished Professor of Urology and Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, and now director of research at the Van Andel Institute.
"The beginnings of epigenetic therapy, which is now the standard of care for myelodysplastic syndrome, can be traced back to the discovery of the DNA demethylating effects of 5-Azacytidine at Children's Hospital Los Angeles in 1980," Jones said. "Since that time we have always assumed that the drugs act by switching genes on, thus reapplying the 'brakes' to cancer cells. In this paper we show that they may also work by turning down the levels of genes, which have become overexpressed in cancer. In other words, they may also decrease the 'gasoline' and this two pronged mechanism, which was entirely unexpected, may help explain why patients respond to epigenetic therapy."
The research, "Gene body methylation can alter gene expression and is a therapeutic target in cancer," was published online Sept. 25, 2014 in Cancer Cell.
INFORMATION:
The research is funded by National Institutes of Health grants R37 CA-082422 and RO1 CA-124518.
Yang, X., Han, H., DeCarvalho, D.D., Lay, F.D., Jones, P.A., & Liang, G. (2014). Gene body methylation can alter gene expression and is a therapeutic target in cancer.
Cancer Cell, Published online Sept. 25, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.028
ABOUT USC NORRIS COMPREHENSIVE CANCER CENTER
USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center has been leading the fight to make cancer a disease of the past. As one of the eight original comprehensive cancer centers in the United States, its mission is to treat and prevent cancer by advancing and integrating education, research, and personalized patient care. For 40 years, USC Norris has been revolutionizing cancer research with innovative surgical techniques and novel cancer treatments. The cancer center's breakthroughs and discoveries in the field of epigenetics have led the way to a greater understanding of the underlying causes of cancer and new methods of prevention, detection, and treatment. With a multidisciplinary team of more than 250 dedicated scientists and physicians, USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center offers patients hope in the battle against cancer.
ABOUT KECK MEDICINE OF USC
Keck Medicine of USC is the University of Southern California's medical enterprise, one of only two university-based medical systems in the Los Angeles area. Encompassing academic, research and clinical excellence, the medical system attracts internationally renowned experts who teach and practice at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, the region's first medical school; includes the renowned USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, one of the first comprehensive cancer centers established by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States; has a medical faculty practice, the USC Care Medical Group; operates the Keck Medical Center of USC, which includes two acute care hospitals: 401-licensed bed Keck Hospital of USC and 60-licensed bed USC Norris Cancer Hospital; and owns USC Verdugo Hills Hospital, a 158-licensed bed community hospital. It also includes more than 40 outpatient facilities, some at affiliated hospitals, in Los Angeles, Orange, Kern, Tulare and Ventura counties.
U.S. News & World Report ranked Keck Medical Center of USC among the Top 10 in ophthalmology (No. 9), and among the Top 25 hospitals in the United States for urology (No. 20) and cancer care (No. 23). The medical center was also awarded an "A" grade from The Leapfrog Group in March, representing outstanding patient safety practices and overall patient outcomes.
For more information, go to http://www.keckmedicine.org/beyond
USC researchers discover dual purpose of cancer drug in regulating expression of genes
2014-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
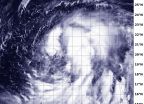
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite sees Tropical Storm Kammuri coming together
2014-09-25
When NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Kammuri the VIIRS instrument aboard took a visible picture of the storm that showed bands of thunderstorms wrapped around its center. The storm appears to be coming together as circulation improves and bands of thunderstorms have been wrapping into the low-level center of circulation.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 25 at 03:13 UTC (Sept. 24 at 11:13 p.m. EDT) and the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard captured a visible picture of ...
Researchers engineer 'Cas9' animal models to study disease and inform drug discovery
2014-09-25
Cambridge, MA, September 25, 2014 — Researchers from the Broad Institute and Massachusetts Institute of Technology have created a new mouse model to simplify application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system for in vivo genome editing experiments. The researchers successfully used the new "Cas9 mouse" model to edit multiple genes in a variety of cell types, and to model lung adenocarcinoma, one of the most lethal human cancers. The mouse has already been made available to the scientific community and is being used by researchers at more than a dozen institutions. A paper describing ...
Satellite catches an oval-shaped Tropical Storm Rachel
2014-09-25
NOAA's GOES-West satellite spotted the eighteenth tropical depression of the Eastern Pacific grow into a tropical storm that was renamed Rachel today, Sept. 25, 2014. Wind shear is affecting the tropical storm, however, so it doesn't have a rounded appearance on satellite imagery.
Tropical Depression 18-E formed on Wednesday, Sept. 24 around 11 a.m. EDT about 285 miles (460 km) south-southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico. Manzanillo is a city in the Manzanillo municipality of the Mexican state of Colima on the country's west coast.
In an infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West ...
Can genetic engineering help food crops better tolerate drought?
2014-09-25
New Rochelle, NY, September 25, 2014—The staggering growth rate of the global population demands innovative and sustainable solutions to increase food production by as much as 70-100% in the next few decades. In light of environmental changes, more drought-tolerant food crops are essential. The latest technological advances and future directions in regulating genes involved in stress tolerance in crops is presented in a Review article in OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, the peer-reviewed interdisciplinary journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. ...
Goats better than chemicals for curbing invasive marsh grass
2014-09-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- Herbivores, not herbicides, may be the most effective way to combat the spread of one of the most invasive plants now threatening East Coast salt marshes, a new Duke University-led study finds.
Phragmites australis, or the common reed, is a rapid colonizer that has overrun many coastal wetlands from New England to the Southeast. A non-native perennial, it can form dense stands of grass up to 10 feet high that block valuable shoreline views of the water, kill off native grasses, and alter marsh function.
Land managers traditionally have used chemical ...
Smallest-possible diamonds form ultra-thin nanothread
2014-09-25
Washington, D.C.— A team including Carnegie's Malcolm Guthrie and George Cody has, for the first time, discovered how to produce ultra-thin "diamond nanothreads" that promise extraordinary properties, including strength and stiffness greater than that of today's strongest nanotubes and polymer fibers. Such exceedingly strong, stiff, and light materials have an array of potential applications, everything from more-fuel efficient vehicles or even the science fictional-sounding proposal for a "space elevator." Their work is published in Nature Materials.
The team—led by ...
Genes causing pediatric glaucoma contribute to future stroke
2014-09-25
(Edmonton, AB) Every year in Canada about 50,000 people suffer from a stroke, caused either by the interruption of blood flow or uncontrolled bleeding in the brain. While many environmental risk factors exist, including high blood pressure and smoking, stroke risk is also frequently inherited. Unfortunately, remarkably little is known regarding stroke's genetic basis.
A study from the University of Alberta, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, extends knowledge of stroke's genetic underpinnings and demonstrates that in some cases it originates in infancy.
The ...
Unlocking long-hidden mechanisms of plant cell division
2014-09-25
AMHERST, Mass. – Along with copying and splitting DNA during division, cells must have a way to break safely into two viable daughter cells, a process called cytokinesis. But the molecular basis of how plant cells accomplish this without mistakes has been unclear for many years.
In a new paper by cell biologist Magdalena Bezanilla of the University of Massachusetts Amherst, she and her doctoral student Shu-Zon Wu present a detailed new model that for the first time proposes how plant cells precisely position a "dynamic and complex" structure called a phragmoplast at the ...
Risk of esophageal cancer decreases with height
2014-09-25
Bethesda, MD (Sept. 25, 2014) — Taller individuals are less likely to develop esophageal cancer and it's precursor, Barrett's esophagus, according to a new study1 in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"Individuals in the lowest quartile of height (under 5'7" for men and 5'2" for women) were roughly twice as likely as individuals in the highest quartile of height (taller than 6' for men and 5'5" for women) to have Barrett's esophagus or esophageal cancer," said Aaron P. Thrift, ...
Putting the squeeze on quantum information
2014-09-25
CIFAR researchers have shown that information stored in quantum bits can be exponentially compressed without losing information. The achievement is an important proof of principle, and could be useful for efficient quantum communications and information storage.
Compression is vital for modern digital communication. It helps movies to stream quickly over the Internet, music to fit into digital players, and millions of telephone calls to bounce off of satellites and through fibre optic cables.
But it has not been clear if information stored in quantum bits, or qubits, ...