(Press-News.org) Two years after its release, the HIV-1 drug Ritonavir was pulled from the market. Scientists discovered that the drug had crystallized into a slightly different form—called a polymorph—that was less soluble and made it ineffective as a treatment.
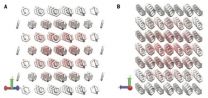
The various patterns that atoms of a solid material can adopt, called crystal structures, can have a huge impact on its properties. Being able to accurately predict the most stable crystal structure for a material has been a longstanding challenge for scientists.
"The holy grail of this particular problem is to say, I've written down this chemical formula for a material, and then just from the formula be able to predict its structure—a goal since the dawn of chemistry," said Garnet K. L. Chan, the A. Barton Hepburn Professor of Theoretical Chemistry at Princeton University. One major bottleneck towards achieving this goal has been to compute the lattice energy—the energy associated with a structure—to sufficient accuracy to distinguish between several competing polymorphs.
Chan's group has now accomplished this task, publishing their results in the journal Science on August 8. The research team demonstrated that new techniques could be used to calculate the lattice energy of benzene, a simple yet important molecule in pharmaceutical and energy research, to sub-kilojoule per mole accuracy—a level of certainty that allows polymorphism to be resolved.
Chan credited this success to the combined application of advances in the field of quantum mechanics over the last 15 years. "Some of these advances allow you to resolve the behavior of electrons more finely, do computations on more atoms more quickly, and allow you to consider more electrons at the same time," Chan said. "It's a triumph of the modern field of quantum chemistry that we can now determine the behavior of Nature to this level of precision."
The group's next goal is to shorten the time it takes to run the desired calculations. These initial calculations consumed several months of computer time, Chan said, but with some practical modifications, future predictions should take only a few hours.
INFORMATION:
Read the full article here:
Yang, J.; Hu, W.; Usvyat, D.; Matthews, D.; Schutz, M.; Chan, G. K. L. "Ab initio determination of the crystalline benzene lattice energy to sub-kilojoule/mol accuracy." Science 2014, 345, 640.
Longstanding bottleneck in crystal structure prediction solved
Benzene lattice energy calculated to sub-kilojoule per mole accuracy
2014-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic 'instruction set' for antibodies knocks down hepatitis C in mice
2014-09-25
A triple-punch of antibodies both prevented hepatitis C infection and wiped out the disease after it had established itself in laboratory mice, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers. Instead of delivering the three antibodies directly, the researchers administered a genetic "instruction set" that, once in a cell, developed into antibodies that target the portions of the virus that do not mutate.
Mice treated with the antibody genetic code resisted becoming infected with hepatitis C when they were exposed to the virus, the researchers reported in ...
On the road to artificial photosynthesis
2014-09-25
The excessive atmospheric carbon dioxide that is driving global climate change could be harnessed into a renewable energy technology that would be a win for both the environment and the economy. That is the lure of artificial photosynthesis in which the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide is used to produce clean, green and sustainable fuels. However, finding a catalyst for reducing carbon dioxide that is highly selective and efficient has proven to be a huge scientific challenge. Meeting this challenge in the future should be easier thanks to new research results ...
Study: Widespread vitamin D deficiency in thyroidectomy patients
2014-09-25
DETROIT – A new study from researchers at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit finds widespread vitamin D deficiency among patients who undergo a thyroidectomy, potentially putting them at greater risk for developing dangerously low blood calcium levels after surgery.
Among the patients in the Henry Ford study, 40 percent had low vitamin D levels prior to surgery. Those more likely to be vitamin D deficient are individuals older than age 50, African Americans, Hispanics and patients undergoing surgery for hyperthyroidism.
"The issue of vitamin D deficiency in patients who ...
How to make stronger, 'greener' cement
2014-09-25
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--Concrete is the world's most-used construction material, and a leading contributor to global warming, producing as much as one-tenth of industry-generated greenhouse-gas emissions. Now a new study suggests a way in which those emissions could be reduced by more than half — and the result would be a stronger, more durable material.
The findings come from the most detailed molecular analysis yet of the complex structure of concrete, which is a mixture of sand, gravel, water, and cement. Cement is made by cooking calcium-rich material, usually limestone, ...
BUSM researchers find NAS treatment needs standardization
2014-09-25
(Boston) – When it comes to treating infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) believe the care for these infants should be consistent and objective, with standardized assessment tools and evidence to back up pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatment choices.
The review paper, which is published online in Addiction Science & Clinical Practice, highlights the need for more research in this field to optimize care for both infants and their mothers.
NAS is a collection of signs and symptoms infants ...
Fecal microbiota transplantation recommended for treatment of C. difficile
2014-09-25
(Vienna, October 26, 2014) The transplantation of faecal microbiota from a healthy donor has been shown in recent clinical studies to be a safe and highly effective treatment for recurrent Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infection and is now recommended in European treatment guidelines.1,2 Faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) has emerged as a revolutionary, potentially life-saving treatment for this common, difficult-to-treat infection, and is showing promise in the management of other microbiota-related conditions.3,4
Presenting at the 22nd United European Gastroenterology ...
In the face of uncertainty, the brain chooses randomness as the best strategy
2014-09-25
AUDIO:
Editor Karen Carniol interviews Dr. Alla Karpova on her latest Cell paper.
Click here for more information.
Past experience is usually a reliable guide for making decisions, but in unpredictable and challenging situations, it might make more sense to take risks. A study published by Cell Press September 25th in the journal Cell shows that, in competitive situations, rats abandon their normal tactic of using past experience to make decisions and instead make random choices ...
How the brain gains control over Tourette syndrome
2014-09-25
Tourette syndrome is a developmental disorder characterized by involuntary, repetitive, and stereotyped movements or utterances. Now researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 25 have new evidence to explain how those with Tourette syndrome in childhood often manage to gain control over those tics. In individuals with the condition, a portion of the brain involved in planning and executing movements shows an unusual increase compared to the average brain in the production of a primary inhibitory neurotransmitter known as GABA.
The paradoxical ...
Modified vitamin D shows promise as treatment for pancreatic cancer
2014-09-25
VIDEO:
Salk scientists find that a vitamin D-derivative makes tumors vulnerable to chemotherapy.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA—A synthetic derivative of vitamin D was found by Salk Institute researchers to collapse the barrier of cells shielding pancreatic tumors, making this seemingly impenetrable cancer much more susceptible to therapeutic drugs.
The discovery has led to human trials for pancreatic cancer, even in advance of its publication today in the journal ...
How physical exercise protects the brain from stress-induced depression
2014-09-25
Physical exercise has many beneficial effects on human health, including the protection from stress-induced depression. However, until now the mechanisms that mediate this protective effect have been unknown. In a new study in mice, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden show that exercise training induces changes in skeletal muscle that can purge the blood of a substance that accumulates during stress, and is harmful to the brain. The study is being published in the prestigious journal Cell.
"In neurobiological terms, we actually still don't know what depression ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
[Press-News.org] Longstanding bottleneck in crystal structure prediction solvedBenzene lattice energy calculated to sub-kilojoule per mole accuracy