(Press-News.org) HOUSTON – (Sept. 25, 2014) – Recently published prevalence estimates of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) in five Latin American countries — Bolivia, Cuba, Ecuador, Nicaragua and Venezuela — could suggest a new direction for United States foreign policy in the region, according to a tropical-disease expert at Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy.
Dr. Peter Hotez, the fellow in disease and poverty at the Baker Institute, outlined his insights in a new editorial, "The NTDs and Vaccine Diplomacy in Latin America: Opportunities for United States Foreign Policy," published in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. He is available for media interviews on the topic.
"NTDs are commonly found wherever poverty is pervasive and the Latin American and Caribbean region's major NTDs — Chagas disease, cutaneous leishmaniasis, dengue, intestinal helminth infections and malaria (mostly vivax malaria) — are highly endemic in Bolivia, Ecuador, Nicaragua and Venezuela, while dengue is also an important NTD in Cuba," Hotez said. "Approximately 14-15 percent of the cases of these NTDs occur in Bolivia, Ecuador, Nicaragua and Venezuela, despite the fact that these countries only comprise about 10 percent of the region's population."
Hotez said such high numbers of people affected by NTDs afford potential opportunities for the U.S. to work with these countries in programs of science and global health diplomacy. "These programs might include bilateral cooperative efforts to implement disease control and elimination programs for the major NTDs, potentially relying on shared expertise between the U.S. and the disease-endemic countries," he said.
There may also be specific opportunities for "vaccine diplomacy," a form of science diplomacy focused on "joint development of lifesaving vaccines and related technologies" conducted by scientists from "nations that often disagree ideologically" or even those "actively engaged in hostile actions," Hotez said. Both the U.S. and Cuba stand out for their programs of vaccine research and development, with Cuba's Instituto Finlay, for example, belonging to the renowned Developing Countries Vaccine Manufacturers Network. "Joint U.S.-Cuba programs in NTD vaccines, possibly including scientists from Bolivia, Ecuador, Nicaragua or Venezuela, offer additional mechanisms on this front," Hotez said.
Hotez is dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, where he is a professor in the Department of Pediatrics and the Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, head of the Section of Pediatric Tropical Medicine and the Texas Children's Hospital Endowed Chair of Tropical Pediatrics. Hotez is also president of the Sabin Vaccine Institute and Texas Children's Hospital's Center for Vaccine Development.
INFORMATION:
To interview Hotez, contact Jeff Falk, associate director of national media relations at Rice, at jfalk@rice.edu or 713-348-6775.
Follow the Baker Institute via Twitter @BakerInstitute.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Related materials:
Hotez biography: http://bakerinstitute.org/experts/peter-j-hotez.
Founded in 1993, Rice University's Baker Institute ranks among the top 15 university-affiliated think tanks in the world. As a premier nonpartisan think tank, the institute conducts research on domestic and foreign policy issues with the goal of bridging the gap between the theory and practice of public policy. The institute's strong track record of achievement reflects the work of its endowed fellows, Rice University faculty scholars and staff, coupled with its outreach to the Rice student body through fellow-taught classes — including a public policy course — and student leadership and internship programs. Learn more about the institute at http://www.bakerinstitute.org or on the institute's blog, http://blogs.chron.com/bakerblog.
Tropical disease prevalence in Latin America presents opportunity for US
2014-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stem cell transplant does not cure SHIV/AIDS after irradiation of infected rhesus macaques
2014-09-25
A study published on September 25th in PLOS Pathogens reports a new primate model to test treatments that might cure HIV/AIDS and suggests answers to questions raised by the "Berlin patient", the only human thought to have been cured so far.
Being HIV-positive and having developed leukemia, the Berlin patient underwent irradiation followed by a bone-marrow transplant from a donor with a mutation that abolishes the function of the CCR5 gene. The gene codes for a protein that facilitates HIV entry into human cells, and the mutation—in homozygous carriers who, like the donor, ...
Interstellar molecules are branching out
2014-09-25
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (Bonn, Germany), Cornell University (USA), and the University of Cologne (Germany) have for the first time detected a carbon-bearing molecule with a "branched" structure in interstellar space. The molecule, iso-propyl cyanide (i-C3H7CN), was discovered in a giant gas cloud called Sagittarius B2, a region of ongoing star formation close to the center of our galaxy that is a hot-spot for molecule-hunting astronomers. The branched structure of the carbon atoms within the iso-propyl cyanide molecule is unlike the ...
Stone Age site challenges old archaeological assumptions about human technology
2014-09-25
The analysis of artifacts from a 325,000-year-old site in Armenia shows that human technological innovation occurred intermittently throughout the Old World, rather than spreading from a single point of origin, as previously thought.
The study, published today in the journal Science, examines thousands of stone artifacts retrieved from Nor Geghi 1, a unique site preserved between two lava flows dated to 200,000–400,000 years ago. Layers of floodplain sediments and an ancient soil found between these lava flows contain the archaeological material. The dating of volcanic ...
Earth's water is older than the sun
2014-09-25
Washington, D.C.—Water was crucial to the rise of life on Earth and is also important to evaluating the possibility of life on other planets. Identifying the original source of Earth's water is key to understanding how life-fostering environments come into being and how likely they are to be found elsewhere. New work from a team including Carnegie's Conel Alexander found that much of our Solar System's water likely originated as ices that formed in interstellar space. Their work is published in Science.
Water is found throughout our Solar System. Not just on Earth, but ...
Agonizing rabies deaths can be stopped worldwide
2014-09-25
The deadly rabies virus--aptly shaped like a bullet-- can be eliminated among humans by stopping it point-blank among dogs, according to a team of international researchers led by the Paul G. Allen School for Global Animal Health at Washington State University.
Ridding the world of rabies is cost-effective and achievable through mass dog vaccination programs, the scientists report in a paper that appears in the Sept. 26 issue of Science magazine. What's more, they write, because infections occur as a result of interactions between animals and people, a "One Health" approach ...
Heritage of Earth's water gives rise to hopes of life on other planets
2014-09-25
A pioneering new study has shown that water found on Earth predates the formation of the Sun – raising hopes that life could exist on exoplanets, the planets orbiting other stars in our galaxy.
The ground-breaking research set out to discover the origin of the water that was deposited on the Earth as it formed.
It found that a significant fraction of water found on Earth, and across our solar system, predates the formation of the Sun. By showing that water is 'inherited' from the environment when a star is born, the international team of scientists believe other exoplanetary ...
Harvesting hydrogen fuel from the Sun using Earth-abundant materials
2014-09-25
VIDEO:
Science published on Sept. 25, 2014 the latest developments in Michael Grätzel's laboratory at EPFL in the field of hydrogen production from water. By combining a pair of perovskite solar...
Click here for more information.
The race is on to optimize solar energy's performance. More efficient silicon photovoltaic panels, dye-sensitized solar cells, concentrated cells and thermodynamic solar plants all pursue the same goal: to produce a maximum amount of electrons ...
Innovative Stone Age tools were not African invention, say researchers
2014-09-25
A new discovery of thousands of Stone Age tools has provided a major insight into human innovation 325,000 years ago and how early technological developments spread across the world, according to research published in the journal Science.
Researchers from Royal Holloway, University of London, together with an international team from across the United States and Europe, have found evidence which challenges the belief that a type of technology known as Levallois – where the flakes and blades of stones were used to make useful products such as hunting weapons – was invented ...
New discovery could pave the way for spin-based computing
2014-09-25
PITTSBURGH—Electricity and magnetism rule our digital world. Semiconductors process electrical information, while magnetic materials enable long-term data storage. A University of Pittsburgh research team has discovered a way to fuse these two distinct properties in a single material, paving the way for new ultrahigh density storage and computing architectures.
While phones and laptops rely on electricity to process and temporarily store information, long-term data storage is still largely achieved via magnetism. Discs coated with magnetic material are locally oriented ...
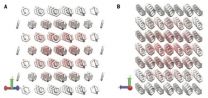
Longstanding bottleneck in crystal structure prediction solved
2014-09-25
Two years after its release, the HIV-1 drug Ritonavir was pulled from the market. Scientists discovered that the drug had crystallized into a slightly different form—called a polymorph—that was less soluble and made it ineffective as a treatment.
The various patterns that atoms of a solid material can adopt, called crystal structures, can have a huge impact on its properties. Being able to accurately predict the most stable crystal structure for a material has been a longstanding challenge for scientists.
"The holy grail of this particular problem is to say, I've written ...