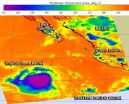
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Kammuri continues to strengthen on its north-northwestern track through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean and NASA's TRMM satellite identified a band of thunderstorms containing heavy rainfall northwest of the storm's center. Meanwhile NASA's Aqua satellite got a look at the entire storm and saw that those bands of storms circled the entire storm.
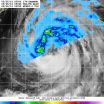
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over the northern half of Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 26 at 1:44 a.m. EDT and the Precipitation Radar instrument saw a strong band of thunderstorms dropping rainfall over 1.2 inches (30.4 mm) per hour. The TRMM satellite is managed by both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
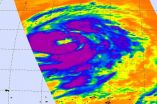
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 26 at 03:11 UTC (Sept. 25 at 11:11 p.m. EDT) and saw strong bands of towering thunderstorms with cold cloud temperatures around the entire storm. Cloud top temperatures exceeded -63F/-53C indicating they extended high into the troposphere and had the potential to generate heavy rainfall, such as what the TRMM satellite observed. Animated enhanced infrared satellite imagery also showed that the low-level circulation center is consolidating as the bands of thunderstorms spiraled into the rounded center.
On Sept. 26 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical Storm Kammuri had maximum sustained winds near 55 knots (63 mph/102 kph). It was centered near 23.5 north latitude and 145.3 east longitude, about 252 nautical miles (290 miles/466.7 km) east-southeast of the island of Iwo To, Japan. Kammuri is moving to the north-northwest at 10 knots (11.5 mph/18.5 kph).
Kammuri is still forecast to intensify as it moves in a north-northwesterly direction through warm sea surface temperatures, toward the island of Iwo To. Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Kammuri to be typhoon strength as it passes east of the island of Iwo To on Sept. 27 and begin weakening on Sept. 29 while curving to the northeast staying from the big island of Japan.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kammuri's spiral bands of soaking thunderstorms
2014-09-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UB study: COPD patients breathe easier with Lung Flute
2014-09-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) report improved symptoms and health status when they use a hand-held respiratory device called the Lung Flute®, according to a new study by the University at Buffalo. Usually caused by smoking, COPD, which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, is the third leading cause of death in the U.S.
The Lung Flute, manufactured by Medical Acoustics, (Buffalo), uses sound waves to break up mucus in the lungs. The device allows patients to clear lung mucus simply by blowing into the hand-held respiratory ...
Penn chemists observe key reaction for producing 'atmosphere's detergent'
2014-09-26
VIDEO:
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such...
Click here for more information.
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such processes help maintain the atmosphere's chemical balance; for ...
National Geographic/GlobeScan study reveals increased concern about environment
2014-09-26
WASHINGTON (Sept. 26, 2014)—A new global analysis released today by the National Geographic Society and GlobeScan finds that concern about environmental problems has increased in most countries surveyed, and that more people now expect global warming will negatively affect them during their lifetime than in 2012. Despite this, National Geographic's Greendex, a comprehensive measure of consumer behavior in 65 areas related to housing, transportation, food and consumer goods, shows that sustainable consumer behavior has only grown slowly.
Results of the 2014 Greendex, a ...
Strategy to reduce side effects in modern cancer therapy
2014-09-26
This news release is available in German. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Vienna (Institute of Inorganic Chemistry) and the Medical University of Vienna (Institute for Cancer Research) has successfully developed a new strategy for reducing the often serious side effects of an important class of modern anticancer drugs (tyrosine kinase inhibitors). The novel drug is supposed to restrict its activity with high selectivity to the malignant tumour.
The occurrence of severe side effects and the development of resistance are two of the biggest ...
Sensitive youngsters
2014-09-26
Young individuals of a species are often more sensitive towards environmental stress than their adult counterparts. Scientists from GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel now observed this effect in the sea star Asterias rubens from the Baltic Sea. In a long-term laboratory experiment that was conducted in the framework of the German research network BIOACID (Biological Impacts of Ocean Acidification), the researchers simulated three different levels of acidification that could be reached in the Baltic Sea by the uptake of additional carbon dioxide (CO2) within ...
Study identifies unexpected clue to peripheral neuropathies
2014-09-26
CINCINNATI – New research shows that disrupting the molecular function of a tumor suppressor causes improper formation of a protective insulating sheath on peripheral nerves – leading to neuropathy and muscle wasting in mice similar to that in human diabetes and neurodegeneration.
Scientists from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center report their findings online Sept. 26 in Nature Communications. The study suggests that normal molecular function of the tumor suppressor gene Lkb1 is essential to an important metabolic transition in cells as peripheral nerves (called ...
NASA identifies cold cloud tops in Tropical Storm Rachel
2014-09-26
NASA's Aqua satellite saw the area of strong thunderstorms with colder cloud tops had grown within the Eastern Pacific Ocean's Tropical Storm Rachel.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the large Tropical Storm Rachel on Sept. 25 at 4:41 p.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument, saw that the extent of colder cloud tops had increased, indicating thunderstorm heights were increasing and it was strengthening. The expansion of those stronger thunderstorms also suggests that the northeasterly wind shear may be relaxing a little. The strongest thunderstorms ...
Underwater robot for port security
2014-09-26
Last week, at the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, MIT researchers unveiled an oval-shaped submersible robot, a little smaller than a football, with a flattened panel on one side that it can slide along an underwater surface to perform ultrasound scans.
Originally designed to look for cracks in nuclear reactors' water tanks, the robot could also inspect ships for the false hulls and propeller shafts that smugglers frequently use to hide contraband. Because of its small size and unique propulsion mechanism — which leaves no visible wake — the ...
Penn team studies nanocrystals by passing them through tiny pores
2014-09-26
An interdisciplinary team of University of Pennsylvania researchers has now applied a cutting-edge technique for rapid gene sequencing toward measuring other nanoscopic structures. By passing nanoscale spheres and rods through a tiny hole in a membrane, the team was able to measure the electrical properties of those structures' surfaces.
Their findings suggest new ways of using this technique, known as "nanopore translocation," to analyze objects at the smallest scale.
The research was led by Marija Drndić, professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy ...
Geisel researchers contribute to study of trained immunity
2014-09-26
Hanover, NH - A study published in the journal Science provides support for a new—and still controversial—understanding of the immune system. The research was conducted by collaborators in the U.S. and Europe, including Robert Cramer, PhD, an assistant professor of microbiology and immunology at the Geisel School of Medicine and member of the Dartmouth Lung Biology Center, and Kelly Shepherdson, PhD, at the time a graduate student in Cramer's lab.
Typically, scientists divide the immune system into two categories: the innate immune response and the adaptive immune response. ...