(Press-News.org) RESEARCHERS at the University of Huddersfield have collaborated with a colleague at a leading Chinese university to produce a detailed appraisal of a complex new welding technique that could be increasingly valuable to modern industry.
Professor Andrew Ball (pictured below) and his colleague Dr Fengshou Gu, of the University of Huddersfield's Centre for Efficiency and Performance Engineering, teamed up with Professor Xiaocong He of Kunming University of Science and Technology's (KUST) Innovative Manufacturing Research Centre in order to investigate the technique known as Friction Stir Welding (FSW).
Professor Andrew Ball "The University of Huddersfield and Kunming University of Science and Technology have worked very closely together for many years now, and this important publication is one example of the benefits of such international collaboration," said Professor Ball.
Professor He is a Visiting Professor at the University of Huddersfield and makes regular visits. Professor Ball and Dr Gu reciprocate with visits to KUST, the next being planned for Spring 2015.
Further research
Friction Stir Welding is a technique invented in the UK in 1991 that has proved to be an effective means of joining materials that are otherwise hard to weld and for joining plates with different thicknesses or made from different materials. Advanced new technologies, such as FSW, are especially important in modern manufacturing, where there is an increasing need to design lightweight structures and to develop ways of joining them.
Professor He, Professor Ball and Dr Gu carried out the research into FSW over a period of several years, receiving financial backing from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Special Program of the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology. They have now issued their findings in a 66-page article published by the leading international journal Progress in Materials Science.
Dr Fengshou Gu "Progress in Materials Science has an Impact Factor in excess of 25, which is very high for most fields, including engineering. I'm delighted that our work has been published in this prestigious and highly-weighted journal," said Dr Gu (pictured right).
The article reviews the latest developments in the numerical analysis of friction stir welding processes, the microstructures of friction stir welded joints and the properties of friction stir welded structures.
The authors conclude that FSW can be used successfully to join difficult-to-weld materials, but that the technique and scientific understanding of it is still at an early stage in its development. "So far, the development of the FSW process for each new application has remained largely empirical. Scientific, knowledge-based numerical studies are of significant help in understanding the FSW process," they write.
Many challenges remain in the development and analysis of FSW, they conclude, adding that the digest that they have presented in the Progress in Materials Science article is intended to provide the basis for further research.
INFORMATION: END
Progress in materials science
A review of numerical analysis of friction stir welding
2014-09-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Severe periodontitis: Sixth most prevalent health condition in the world
2014-09-26
Alexandria, Va., USA – The International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR) have published a paper titled "Global Burden of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression." The manuscript, by lead researcher Wagner Marcenes (Queen Mary University of London, Institute of Dentistry, Barts and The London School) is published in the OnlineFirst portion of the IADR/AADR Journal of Dental Research (JDR).
The purpose of this study was to consolidate all epidemiological data about severe periodontitis and subsequently to generate internally consistent ...
Morphed images of Hollywood celebrities reveal how neurons make up your mind
2014-09-26
An international team of scientists, involving Professor Rodrigo Quian Quiroga, director of the Centre for Systems Neuroscience and Head of Bioengineering at the University of Leicester, has shown how individual neurons in the human brain react to ambiguous morphed faces.
For this, the researchers used images of celebrities, such as Angelina Jolie and Halle Berry, morphed together to create an ambiguous face which test subjects were asked to identify.
The study found that for the same ambiguous images, the neurons fired according to the subjective perception by the ...
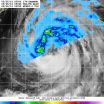
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kammuri's spiral bands of soaking thunderstorms
2014-09-26
Tropical Storm Kammuri continues to strengthen on its north-northwestern track through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean and NASA's TRMM satellite identified a band of thunderstorms containing heavy rainfall northwest of the storm's center. Meanwhile NASA's Aqua satellite got a look at the entire storm and saw that those bands of storms circled the entire storm.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over the northern half of Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 26 at 1:44 a.m. EDT and the Precipitation Radar instrument saw a strong band of thunderstorms ...
UB study: COPD patients breathe easier with Lung Flute
2014-09-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) report improved symptoms and health status when they use a hand-held respiratory device called the Lung Flute®, according to a new study by the University at Buffalo. Usually caused by smoking, COPD, which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, is the third leading cause of death in the U.S.
The Lung Flute, manufactured by Medical Acoustics, (Buffalo), uses sound waves to break up mucus in the lungs. The device allows patients to clear lung mucus simply by blowing into the hand-held respiratory ...
Penn chemists observe key reaction for producing 'atmosphere's detergent'
2014-09-26
VIDEO:
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such...
Click here for more information.
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such processes help maintain the atmosphere's chemical balance; for ...
National Geographic/GlobeScan study reveals increased concern about environment
2014-09-26
WASHINGTON (Sept. 26, 2014)—A new global analysis released today by the National Geographic Society and GlobeScan finds that concern about environmental problems has increased in most countries surveyed, and that more people now expect global warming will negatively affect them during their lifetime than in 2012. Despite this, National Geographic's Greendex, a comprehensive measure of consumer behavior in 65 areas related to housing, transportation, food and consumer goods, shows that sustainable consumer behavior has only grown slowly.
Results of the 2014 Greendex, a ...
Strategy to reduce side effects in modern cancer therapy
2014-09-26
This news release is available in German. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Vienna (Institute of Inorganic Chemistry) and the Medical University of Vienna (Institute for Cancer Research) has successfully developed a new strategy for reducing the often serious side effects of an important class of modern anticancer drugs (tyrosine kinase inhibitors). The novel drug is supposed to restrict its activity with high selectivity to the malignant tumour.
The occurrence of severe side effects and the development of resistance are two of the biggest ...
Sensitive youngsters
2014-09-26
Young individuals of a species are often more sensitive towards environmental stress than their adult counterparts. Scientists from GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel now observed this effect in the sea star Asterias rubens from the Baltic Sea. In a long-term laboratory experiment that was conducted in the framework of the German research network BIOACID (Biological Impacts of Ocean Acidification), the researchers simulated three different levels of acidification that could be reached in the Baltic Sea by the uptake of additional carbon dioxide (CO2) within ...
Study identifies unexpected clue to peripheral neuropathies
2014-09-26
CINCINNATI – New research shows that disrupting the molecular function of a tumor suppressor causes improper formation of a protective insulating sheath on peripheral nerves – leading to neuropathy and muscle wasting in mice similar to that in human diabetes and neurodegeneration.
Scientists from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center report their findings online Sept. 26 in Nature Communications. The study suggests that normal molecular function of the tumor suppressor gene Lkb1 is essential to an important metabolic transition in cells as peripheral nerves (called ...
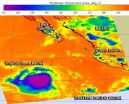
NASA identifies cold cloud tops in Tropical Storm Rachel
2014-09-26
NASA's Aqua satellite saw the area of strong thunderstorms with colder cloud tops had grown within the Eastern Pacific Ocean's Tropical Storm Rachel.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the large Tropical Storm Rachel on Sept. 25 at 4:41 p.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument, saw that the extent of colder cloud tops had increased, indicating thunderstorm heights were increasing and it was strengthening. The expansion of those stronger thunderstorms also suggests that the northeasterly wind shear may be relaxing a little. The strongest thunderstorms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Progress in materials scienceA review of numerical analysis of friction stir welding