(Press-News.org) Administration of high-dose vitamin D3 compared with placebo did not reduce hospital length of stay, intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay, hospital mortality, or the risk of death at 6 months among patients with vitamin D deficiency who were critically ill, according to a study published in JAMA. The study is being posted early online to coincide with its presentation at the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine annual congress.
A high prevalence of low vitamin D levels has been confirmed in patients who are critically ill. Many studies suggest that a low vitamin D status is a significant factor associated with disease severity, mortality, or a shorter survival time in the ICU. However, it is unknown whether a low vitamin D status is an independent contributor to the risk of illness or death for these patients, according to background information in the article.
Karin Amrein, M.D., M.Sc., of the Medical University of Graz, Austria, and colleagues randomly assigned 492 adult ICU patients with vitamin D deficiency to receive either high-dose vitamin D3 (n = 249) or a placebo (n = 243).
For the primary study outcome, length of hospital stay, the vitamin D3 group was not significantly different from the placebo group: 20.1 days vs 19.3 days. There was also no significant difference for length of ICU stay: 9.6 days for the vitamin D3 group vs 10.7 days for the placebo group.
Among the patients in the vitamin D3 group, 28.3 percent died in the hospital compared with 35.3 percent in the placebo group. After 6 months, 35.0 percent of the patients had died in the vitamin D3 group and 42.9 percent in the placebo group.
Lower hospital mortality was observed in a subgroup of patients with severe vitamin D deficiency, but this finding should be considered hypothesis generating and requires further study, the authors write.
"Among patients with vitamin D deficiency who are critically ill, administration of high-dose vitamin D3 compared with placebo did not improve hospital length of stay, hospital mortality, or 6-month mortality."INFORMATION:
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.13204; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
High-dose vitamin D for ICU patients who are vitamin D deficient does not improve outcomes
2014-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gut bacteria promote obesity in mice
2014-09-30
A species of gut bacteria called Clostridium ramosum, coupled with a high-fat diet, may cause animals to gain weight. The work is published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
A research team from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke in Nuthetal observed that mice harboring human gut bacteria including C. ramosum gained weight when fed a high-fat diet. Mice that did not have C. ramosum were less obese even when consuming a high-fat diet, and mice that had C. ramosum but consumed a low-fat ...
Endoscopists recommend frequent colonoscopies, leading to its overuse
2014-09-30
Boston, MA – A retrospective study led by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), has found an overuse of colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening and surveillance. The study demonstrated that endoscopists commonly recommended shorter follow-up intervals than established guidelines support, and these recommendations were strongly correlated with subsequent colonoscopy overuse.
"Our study shows that a high percentage of follow-up colonoscopies are being performed too early, resulting in use of scarce health care resources with potentially limited clinical ...
Chinese scientists unveil liquid phase 3-D printing method using low melting metal alloy ink
2014-09-30
Three-dimensional metal printing technology is an expanding field that has enormous potential applications in areas ranging from supporting structures, functional electronics to medical devices. Conventional 3D metal printing is generally restricted to metals with a high melting point, and the process is rather time consuming.
Now scientists at the Beijing Key Laboratory of CryoBiomedical Engineering, part of the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a new conceptual 3D printing method with "ink" consisting of ...
First dark matter search results from Chinese underground lab hosting PandaX-I experiment
2014-09-30
Scientists across China and the United States collaborating on the PandaX search for dark matter from an underground lab in southwestern China report results from the first stage of the experiment in a new study published in the Beijing-based journal SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy.
PandaX is the first dark matter experiment in China that deploys more than one hundred kilograms of xenon as a detector; the project is designed to monitor potential collisions between xenon nucleons and weakly interactive massive particles, hypothesized candidates for dark matter.
In ...
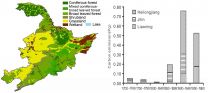
New estimates on carbon emissions triggered by 300 years of cropland expansion in Northeast China
2014-09-30
The conversion of forests, grasslands, shrublands and wetlands to cropland over the course of three centuries profoundly changed the surface of the Earth and the carbon cycle of the terrestrial ecosystem in Northeast China.
In a new study published in the Beijing-based journal SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences, a team of researchers from Beijing Normal University, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, and the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, present new calculations on carbon emissions triggered ...
Alcohol makes smiles more 'contagious,' but only for men
2014-09-30
Consuming an alcoholic beverage may make men more responsive to the smiles of others in their social group, according to new research in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The findings suggest that, for men, alcohol increases sensitivity to rewarding social behaviors like smiling, and may shed light on risk factors that contribute to problem drinking among men.
"This experimental alcohol study, which included a social context, finds the clearest evidence yet of greater alcohol reinforcement for men than women," says ...
Slim cigarette smokers not exposed to more harmful chemicals
2014-09-30
A new study confirms that the exposure to tar tended to be lower for smokers of slim cigarettes than of regular cigarettes. Similarly, exposure to nicotine tended to be lower.
Slim cigarettes are an increasingly popular type of cigarette in several countries around the world. Previous studies have shown that the levels of certain toxic chemicals in the smoke of these cigarettes are lower than those in regular cigarettes. However, because lower levels of chemicals in the smoke are not necessarily linked to a reduced exposure to harmful chemicals, concerns had been raised ...
Genomic data could help doctors know whether to prescribe statins
2014-09-30
Genomic data could predict whether statins will benefit a patient or not, according to an article in the open access journal Genome Biology. The research suggests that genomic data alone can explain around 15% of patients' responses to a cholesterol-lowering statin, and further studies could increase the accuracy of these predictions.
The study looked at data from 372 participants in an American clinical trial for the statin, Simvastatin, and found that certain genetic signatures were more common in patients whose cholesterol was effectively lowered by the treatment, ...
Half of global wildlife lost, says new WWF report
2014-09-30
Washington, DC – Monday, September 29: Between 1970 and 2010 populations of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish around the globe dropped 52 percent, says the 2014 Living Planet Report released today by World Wildlife Fund (WWF). This biodiversity loss occurs disproportionately in low-income countries—and correlates with the increasing resource use of high-income countries.
In addition to the precipitous decline in wildlife populations the report's data point to other warning signs about the overall health of the planet. The amount of carbon in our atmosphere ...
Association of physical activity with diabetes is weakest among women at high genetic risk
2014-09-30
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) suggests that the protective effect of physical activity against diabetes is weakest among those at high genetic risk. The research is by Dr Yann Klimentidis, an Assistant Professor at the University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health, in Tucson, AZ, USA, and colleagues.
It is well established that physical activity reduces type 2 diabetes risk. However, the extent of protection afforded by physical activity may differ according to genetic ...