(Press-News.org) NASA and NOAA scientists participating in NASA's Hurricane and Severe Storms Sentinel (HS3) mission used their expert skills, combined with a bit of serendipity on Sept. 17, 2014, to guide the remotely piloted Global Hawk over the eye of Hurricane Edouard and release a sonde that rotated within the eye as it descended and fell into the eyewall of the storm at low levels.
NASA's HS3 mission has returned to NASA's Wallops Flight Facility on the Eastern Shore of Virginia for the third year to investigate the processes that underlie hurricane formation and intensity change in the Atlantic Ocean basin.
NOAA's Advanced Vertical Atmospheric Profiling System (AVAPS) aboard Global Hawk No. 872 released 88 dropsondes into the hurricane that measured temperature, humidity and winds throughout the depth of the troposphere, the region of the atmosphere where humans and aircraft experience weather.
During the Global Hawk's seventh science flight on Sept. 17, "the remotely piloted aircraft released a dropsonde from 62,000 feet along the inner edge of the eyewall on a south to north pass," said Michael L. Black, research meteorologist at the Hurricane Research Division, NOAA's Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research - Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory in Florida.
Black said, "The sonde started out on the south side of the eye and rotated around to the eastern eyewall. The sonde reported a sea-level pressure of 963 millibars, surface winds of 90 knots [103.6 mph, or 166.7 kph], and average low-level winds of 95 knots."
The data showed that Eduoard was indeed still at least a strong Category 2 hurricane, possibly Category 3, as the strong winds continued to be observed near the ocean surface.
Basically, the dropsonde, along with 87 others during this flight, provided readings from top to bottom of the critical region of the atmosphere, giving scientists a perfect view of winds, temperature and pressure throughout the whole depth of the storm.
On Sept. 18, Global Hawk No. 872 took off at 7:15 a.m. EDT to return to investigate Eduoard as it moved over cooler Atlantic waters and was expected to weaken. This mission was the eighth science flight during the current campaign for the Global Hawk. During the flight, the Global Hawk ejected 50 dropsondes and observed the decay of Hurricane Edouard to tropical storm strength and recorded the beginning of the demise of the storm that included the decoupling from the mid- and low-level centers of the storm.
Overall, the Global Hawk flights into Edouard documented its formation into a tropical storm, its rapid increase in intensity into a major, Category 3 storm, and its decay back to a tropical depression thereby capturing the life cycle of a classic hurricane with roots from a tropical wave from Africa.
The HS3 mission is funded by NASA Headquarters and overseen by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. It is one of five large airborne campaigns operating under the Earth Venture program.
The HS3 mission also involves collaborations with partners including the National Centers for Environmental Prediction, Naval Postgraduate School, Naval Research Laboratory, NOAA's Unmanned Aircraft System Program, Hurricane Research Division and Earth System Research Laboratory, Northrop Grumman Space Technology, National Center for Atmospheric Research, State University of New York at Albany, University of Maryland - Baltimore County, University of Wisconsin, and University of Utah. The HS3 mission is managed by the Earth Science Project Office at NASA Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. The aircraft are maintained and based at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
INFORMATION:
For more information about NASA's HS3 mission, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/hs3
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland
NASA's HS3 looks Hurricane Edouard in the eye
NASA's HS3 Hurricane mission examines Hurricane Edouard
2014-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
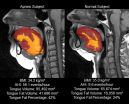
Study shows that tongue size and fat may predict sleep apnea risk in obese adults
2014-09-30
DARIEN, IL – A new study of obese adults is the first to show that those who have obstructive sleep apnea have a significantly larger tongue with a higher percentage of fat than obese controls. This may provide a mechanistic explanation for the relationship between obesity and sleep apnea.
Results show that obese participants with sleep apnea had significantly greater tongue volumes, tongue fat and percentage of tongue fat than obese controls without sleep apnea, after adjusting for potential confounders such as age, body mass index (BMI), gender and race. Further analysis ...
Ultrafast remote switching of light emission
2014-09-30
This news release is available in German.
The researchers etched a photonic crystal around several quantum dots in a semiconductor layer. Quantum dots are small structures that spontaneously emit light as a consequence of atomic processes. If a short laser pulse is fired at the photonic crystal, its refractive index is modified and the quantum dot experiences a change in the electromagnetic field around it. This change can speed up or slow down the emission of light by the dot. As soon as the refractive index recovers its usual value, the dot emits light again ...
'Virtual breast' could improve cancer detection
2014-09-30
Next to lung cancer, breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in women, according to the American Cancer Society. That's why so many medical professionals encourage women to get mammograms, even though the tests are imperfect at best: only a minority of suspicious mammograms actually leads to a cancer diagnosis.
That results in lots of needless worry for women and their families—not to mention the time, discomfort and expense of additional tests, including ultrasounds and biopsies.
Recently, a different type of test, ultrasound elastography, has been used ...
Rehospitalization in younger patients
2014-09-30
Older adults often are readmitted after hospitalization for heart failure, pneumonia, and acute myocardial infarction, a significant issue that has caused Medicare to target hospitals with high 30-day readmission rates for financial penalties. Older adults are also often admitted for reasons other than the original hospitalization. This vulnerability to readmission has been referred to as "post-hospital syndrome." However, whether younger patients also experience a similar pattern of readmission has not been well studied.
In a large cohort study, Isuru Ranasinghe and ...
Diuretics in proton pump inhibitor-associated hypomagnesemia
2014-09-30
Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is associated with hospitalization for hypomagnesemia, particularly among patients also receiving diuretics, according to research published this week in PLOS Medicine. The study, conducted by David Juurlink of the University of Toronto and colleagues, suggests that physicians reconsider long-term PPI therapy for patients with a diagnosis of hypomagnesemia or concurrent use of diuretics.
Roughly 145 million prescriptions for PPI are dispensed in the United States annually for acid-related disorders such as dyspepsia and gastroesophageal ...
At dusk and dawn: Scientists pinpoint biological clock's synchronicity
2014-09-30
Scientists have uncovered how pacemaker neurons are synchronized at dusk and dawn in order to maintain the proper functioning of their biological clocks. Their findings, which appear in the journal PLOS Biology, enhance our understanding of how sleep-wake cycles are regulated and offer promise for addressing related afflictions.
"We've known for some time that the time-keeping of our biological clocks is a complex enterprise," says New York University's Justin Blau, a professor of biology and neural science and one of the study's co-authors. "But our results offer new ...
How dinosaur arms turned into bird wings
2014-09-30
Although we now appreciate that birds evolved from a branch of the dinosaur family tree, a crucial adaptation for flight has continued to puzzle evolutionary biologists. During the millions of years that elapsed, wrists went from straight to bent and hyperflexible, allowing birds to fold their wings neatly against their bodies when not flying.
How this happened has been the subject of much debate, with substantial disagreement between developmental biologists, who study how the wings of modern birds develop in the growing embryo, and palaeontologists who study the bones ...
Study shows how chimpanzees share skills
2014-09-30
Evidence of new behaviour being adopted and transmitted socially from one individual to another within a wild chimpanzee community is publishing on September 30 in the open access journal PLOS Biology. This is the first instance of social learning recorded in the wild.
Scientists from University of St Andrews, University of Neuchâtel, Anglia Ruskin University, and Université du Quebec studied the spread of two novel tool-use behaviours among the Sonso chimpanzee community living in Uganda's Budongo Forest. Dr Catherine Hobaiter, Lecturer in Psychology at the University ...
Boys and girls who've had a traumatic brain injury differ in rates of harmful behavior
2014-09-30
TORONTO, Sept. 30, 2014 – Teenagers who said they had a traumatic brain injury in their lifetime, especially girls, also reported significantly higher rates of harmful behavior, according to new research.
The study looked at 13 harmful health behaviours –such as contemplating suicide, smoking marijuana or binge drinking– among 9,288 Ontario students between Grades 7 and 12.
"Both boys and girls were more likely to engage in a variety of harmful behaviours if they reported a history of TBI, but girls engaged in all 13 harmful behaviours we looked for, whereas boys were ...
Blades of grass inspire advance in organic solar cells
2014-09-30
AMHERST, Mass. – Using a bio-mimicking analog of one of nature's most efficient light-harvesting structures, blades of grass, an international research team led by Alejandro Briseno of the University of Massachusetts Amherst has taken a major step in developing long-sought polymer architecture to boost power-conversion efficiency of light to electricity for use in electronic devices.
Briseno, with colleagues and graduate students at UMass Amherst and others at Stanford University and Dresden University of Technology, Germany, report in the current issue of Nano Letters ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] NASA's HS3 looks Hurricane Edouard in the eyeNASA's HS3 Hurricane mission examines Hurricane Edouard