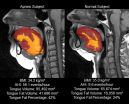
(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL – A new study of obese adults is the first to show that those who have obstructive sleep apnea have a significantly larger tongue with a higher percentage of fat than obese controls. This may provide a mechanistic explanation for the relationship between obesity and sleep apnea.
Results show that obese participants with sleep apnea had significantly greater tongue volumes, tongue fat and percentage of tongue fat than obese controls without sleep apnea, after adjusting for potential confounders such as age, body mass index (BMI), gender and race. Further analysis found that tongue fat percentage in participants with sleep apnea was site specific, with increased fat toward the base of the tongue in the retroglossal region.
"This is the first study to show that fat deposits are increased in the tongue of obese patients with obstructive sleep apnea," said principal investigator and senior author Dr. Richard J. Schwab, Professor in the Department of Medicine and co-director of the Penn Sleep Center at the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. "This work provides evidence of a novel pathogenic mechanism explaining the relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and obesity."
Study results are published in the Oct. 1 issue of the journal Sleep.
"Tongue size is one of the physical features that should be evaluated by a physician when screening obese patients to determine their risk for obstructive sleep apnea," said American Academy of Sleep Medicine President Dr. Timothy Morgenthaler. "Effective identification and treatment of sleep apnea is essential to optimally manage other conditions associated with this chronic disease, including high blood pressure, heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, stroke and depression."
The study involved 90 obese adults with sleep apnea and 31 obese controls without sleep apnea. All subjects underwent high resolution upper airway magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Sophisticated volumetric reconstruction algorithms were used to study the size and distribution of upper airway fat deposits in the tongue.
The authors proposed that in addition to enlarging the size of the tongue, increased tongue fat may impair the functioning of the muscles that attach the tongue to bone, preventing these muscles from positioning the tongue away from the airway. According to the authors, future studies should examine the effectiveness of removing tongue fat through weight loss, upper airway exercises or surgery as a potential treatment for sleep apnea.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine reports that excess body weight is the major predisposing factor for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Common warning signs for sleep apnea include snoring and choking, gasping, or silent breathing pauses during sleep. The AASM and other partners in the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project urge anyone with signs or symptoms of sleep apnea to visit http://www.stopsnoringpledge.org to pledge to "Stop the Snore" and talk to a doctor about sleep apnea.
Adults who have a BMI of 30 or higher are considered to be obese. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 34.9 percent of U.S. adults – 78.6 million people - are obese, based on nationally representative survey data from 2011 – 2012.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
To request a copy of the study, "Tongue Fat and its Relationship to Obstructive Sleep Apnea," and the commentary, "Does My Tongue Look Fat?", or to arrange an interview with the study author or an AASM spokesperson, please contact Communications Coordinator Lynn Celmer at 630-737-9700, ext. 9364, or lcelmer@aasmnet.org.
The monthly, peer-reviewed, scientific journal Sleep is published online by the Associated Professional Sleep Societies LLC, a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society. The AASM is a professional membership society that improves sleep health and promotes high quality patient centered care through advocacy, education, strategic research, and practice standards (http://www.aasmnet.org). A searchable directory of AASM accredited sleep centers is available at http://www.sleepeducation.org.
Study shows that tongue size and fat may predict sleep apnea risk in obese adults
Tongue is large and has a high percentage of fat in obese adults who have obstructive sleep apnea
2014-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ultrafast remote switching of light emission
2014-09-30
This news release is available in German.
The researchers etched a photonic crystal around several quantum dots in a semiconductor layer. Quantum dots are small structures that spontaneously emit light as a consequence of atomic processes. If a short laser pulse is fired at the photonic crystal, its refractive index is modified and the quantum dot experiences a change in the electromagnetic field around it. This change can speed up or slow down the emission of light by the dot. As soon as the refractive index recovers its usual value, the dot emits light again ...
'Virtual breast' could improve cancer detection
2014-09-30
Next to lung cancer, breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in women, according to the American Cancer Society. That's why so many medical professionals encourage women to get mammograms, even though the tests are imperfect at best: only a minority of suspicious mammograms actually leads to a cancer diagnosis.
That results in lots of needless worry for women and their families—not to mention the time, discomfort and expense of additional tests, including ultrasounds and biopsies.
Recently, a different type of test, ultrasound elastography, has been used ...
Rehospitalization in younger patients
2014-09-30
Older adults often are readmitted after hospitalization for heart failure, pneumonia, and acute myocardial infarction, a significant issue that has caused Medicare to target hospitals with high 30-day readmission rates for financial penalties. Older adults are also often admitted for reasons other than the original hospitalization. This vulnerability to readmission has been referred to as "post-hospital syndrome." However, whether younger patients also experience a similar pattern of readmission has not been well studied.
In a large cohort study, Isuru Ranasinghe and ...
Diuretics in proton pump inhibitor-associated hypomagnesemia
2014-09-30
Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is associated with hospitalization for hypomagnesemia, particularly among patients also receiving diuretics, according to research published this week in PLOS Medicine. The study, conducted by David Juurlink of the University of Toronto and colleagues, suggests that physicians reconsider long-term PPI therapy for patients with a diagnosis of hypomagnesemia or concurrent use of diuretics.
Roughly 145 million prescriptions for PPI are dispensed in the United States annually for acid-related disorders such as dyspepsia and gastroesophageal ...
At dusk and dawn: Scientists pinpoint biological clock's synchronicity
2014-09-30
Scientists have uncovered how pacemaker neurons are synchronized at dusk and dawn in order to maintain the proper functioning of their biological clocks. Their findings, which appear in the journal PLOS Biology, enhance our understanding of how sleep-wake cycles are regulated and offer promise for addressing related afflictions.
"We've known for some time that the time-keeping of our biological clocks is a complex enterprise," says New York University's Justin Blau, a professor of biology and neural science and one of the study's co-authors. "But our results offer new ...
How dinosaur arms turned into bird wings
2014-09-30
Although we now appreciate that birds evolved from a branch of the dinosaur family tree, a crucial adaptation for flight has continued to puzzle evolutionary biologists. During the millions of years that elapsed, wrists went from straight to bent and hyperflexible, allowing birds to fold their wings neatly against their bodies when not flying.
How this happened has been the subject of much debate, with substantial disagreement between developmental biologists, who study how the wings of modern birds develop in the growing embryo, and palaeontologists who study the bones ...
Study shows how chimpanzees share skills
2014-09-30
Evidence of new behaviour being adopted and transmitted socially from one individual to another within a wild chimpanzee community is publishing on September 30 in the open access journal PLOS Biology. This is the first instance of social learning recorded in the wild.
Scientists from University of St Andrews, University of Neuchâtel, Anglia Ruskin University, and Université du Quebec studied the spread of two novel tool-use behaviours among the Sonso chimpanzee community living in Uganda's Budongo Forest. Dr Catherine Hobaiter, Lecturer in Psychology at the University ...
Boys and girls who've had a traumatic brain injury differ in rates of harmful behavior
2014-09-30
TORONTO, Sept. 30, 2014 – Teenagers who said they had a traumatic brain injury in their lifetime, especially girls, also reported significantly higher rates of harmful behavior, according to new research.
The study looked at 13 harmful health behaviours –such as contemplating suicide, smoking marijuana or binge drinking– among 9,288 Ontario students between Grades 7 and 12.
"Both boys and girls were more likely to engage in a variety of harmful behaviours if they reported a history of TBI, but girls engaged in all 13 harmful behaviours we looked for, whereas boys were ...
Blades of grass inspire advance in organic solar cells
2014-09-30
AMHERST, Mass. – Using a bio-mimicking analog of one of nature's most efficient light-harvesting structures, blades of grass, an international research team led by Alejandro Briseno of the University of Massachusetts Amherst has taken a major step in developing long-sought polymer architecture to boost power-conversion efficiency of light to electricity for use in electronic devices.
Briseno, with colleagues and graduate students at UMass Amherst and others at Stanford University and Dresden University of Technology, Germany, report in the current issue of Nano Letters ...
Comprehensive Study of allergic deaths in US finds medications are main culprit
2014-09-30
September 30, 2014—(BRONX, NY)—Medications are the leading cause of allergy-related sudden deaths in the U.S., according to an analysis of death certificates from 1999 to 2010, conducted by researchers at Montefiore Medical Center and Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University. The study, published online today in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, also found that the risk of fatal drug-induced allergic reactions was particularly high among older people and African-Americans and that such deaths increased significantly in the U.S. in recent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Study shows that tongue size and fat may predict sleep apnea risk in obese adultsTongue is large and has a high percentage of fat in obese adults who have obstructive sleep apnea