(Press-News.org) In a trial involving patients at high risk of hospital readmission or death, use of a virtual ward model of care (using some elements of hospital care in the community) after hospital discharge did not significantly reduce the rate of readmission or death up to a year following discharge, according to a study in the October 1 issue of JAMA.
Hospital readmissions are common and costly, and no single intervention or bundle of interventions has reliably reduced readmissions. The virtual ward model of care is a way of providing care to patients with complex needs who are not hospitalized. This model takes many elements of hospital care that are appreciated by patients or clinicians (e.g., an interprofessional team, a daily team meeting, a single point of contact for patients, etc.) and incorporates them into community-based care, with a goal of improving health outcomes and patient experience while also providing better value for money. Despite the virtual ward's conceptual appeal and its increasingly common implementation, it has not been rigorously evaluated, according to background information in the article.
Irfan A. Dhalla, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Toronto and St. Michael's Hospital, Toronto, and colleagues randomly assigned 1,923 high-risk adult hospital discharge patients in Toronto to either the virtual ward (n = 963) or usual care (n = 960). Patients assigned to the virtual ward received care coordination plus direct care provision (via a combination of telephone, home visits, or clinic visits) from an interprofessional team for several weeks after hospital discharge. The interprofessional team met daily at a central site to design and implement individualized management plans. Patients assigned to usual care typically received a structured discharge summary, prescription for new medications if indicated, counseling from the resident physician, arrangements for home care as needed, and recommendations, appointments, or both for follow-up care with physicians as indicated.
The researchers found no significant between-group difference for the primary measured outcome for the study: within the 30-day period following discharge, 24.6 percent of patients assigned to usual care and 21.2 percent of patients assigned to the virtual ward had been readmitted to hospital or died. There were 47 deaths in the usual care group and 40 deaths in the virtual ward group (4.9 percent vs 4.2 percent).
By 90 days after discharge, 38.0 percent of patients assigned to usual care and 37.1 percent of patients assigned to the virtual ward had been readmitted to a hospital or died. There were no significant between-group differences in any of the outcomes (including nursing home admission and emergency department visits) at 6 months or 1 year.
The authors write that although their data are not inconsistent with a small absolute benefit at 30 days, outcome data at 90 days suggest that any benefits were not sustained. "As a consequence, given the per-patient costs of our intervention, it is highly unlikely that a virtual ward model of care structured similarly to ours would represent an efficient use of health care resources."
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.11492; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Editorial: Managing Posthospital Care Transitions for Older Adults
"The rigorously conducted trial by Dhalla et al adds important data that contribute to advancing the understanding of determining optimal approaches to improve postdischarge transitions for high-risk patients," writes Peter A. Boling, M.D., of Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, in an accompanying editorial.
"An important aspect of their report, however, was that the authors identified real-world obstacles including incompatible electronic health records, clinician discontinuity, difficulties integrating with primary care, and lack of contact with patients in hospital. These observations may be useful in the development of future trials designed to improve care transitions and reduce readmissions. Moreover, it is still likely that in this era of exponential development of technologically supported solutions to complex problems, elements of the 'virtual ward' may have a place, perhaps linked with more robust in-home care delivery."
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.12360; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
INFORMATION: END
Use of a 'virtual ward' model of care does not reduce hospital readmissions, risk of death
2014-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study compares long-term outcomes for types of aortic valve replacements
2014-09-30
Among patients ages 50 to 69 years who underwent aortic valve replacement with bioprosthetic (made primarily with tissue) compared with mechanical prosthetic valves, there was no significant difference in 15-year survival or stroke, although patients in the bioprosthetic valve group had a greater likelihood of reoperation but a lower likelihood of major bleeding, according to a study in the October 1 issue of JAMA.
Approximately 50,000 patients undergo aortic valve replacement annually in the United States. In older patients, bioprosthetic valves pose a low lifetime ...
Medical professional liability claims and esophageal cancer screening
2014-09-30
An analysis of liability claims related to esophageal cancer screening finds that the risks of claims arising from acts of commission (complications from screening procedure) as well as acts of omission (failure to screen) are similarly low, according to a study in the October 1 issue of JAMA.
Endoscopic screening for esophageal cancer has been recommended for patients with chronic symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease, but only if they have additional risk factors. Surveys of gastroenterologists indicate that concern about litigation for missing a cancer may drive ...
Biodiversity in the Mediterranean is threatened by alien species
2014-09-30
Millions of tourists visit the Mediterranean each year, but its deep-blue waters host the largest invasion currently underway on Earth. Almost 1,000 alien species, including fish, crustaceans, and algae are now established from other seas through human activities. In the open-access journal Frontiers in Marine Science, a multinational team of researchers analyzed data from a new information system developed by the European Commission to show how the introduction of alien species has changed the native biodiversity within the Mediterranean.
A hotspot for marine biodiversity, ...
Clinical trial finds virtual ward does not reduce hospital readmissions
2014-09-30
TORONTO — A virtual ward, a new model of care that provides support to high-risk and complex patients in the community for a few weeks after discharge from hospital, did not prevent hospital readmissions as hoped in a clinical trial in Toronto.
Hospital readmissions are common and costly and no intervention has reliably reduced them. Virtual wards, pioneered in Britain 10 years ago, were thought to have the potential to reduce readmissions, but had not been rigorously evaluated by researchers.
Dr. Irfan Dhalla, a physician at St. Michael's Hospital, led a randomized trial ...
Researchers show EEG's potential to reveal depolarizations following TBI
2014-09-30
CINCINNATI—The potential for doctors to measure damaging "brain tsunamis" in injured patients without opening the skull has moved a step closer to reality, thanks to pioneering research at the University of Cincinnati (UC) Neuroscience Institute.
The research team, led by Jed Hartings, PhD, research associate professor in the department of neurosurgery at the UC College of Medicine, has shown that spreading depolarizations—electrical disturbances that spread through an injured brain like tsunami waves—can be measured by the placement of electroencephalograph (EEG) electrodes ...
NASA's Swift mission observes mega flares from a mini star
2014-09-30
On April 23, NASA's Swift satellite detected the strongest, hottest, and longest-lasting sequence of stellar flares ever seen from a nearby red dwarf star. The initial blast from this record-setting series of explosions was as much as 10,000 times more powerful than the largest solar flare ever recorded.
"We used to think major flaring episodes from red dwarfs lasted no more than a day, but Swift detected at least seven powerful eruptions over a period of about two weeks," said Stephen Drake, an astrophysicist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, ...
NASA's HS3 looks Hurricane Edouard in the eye
2014-09-30
NASA and NOAA scientists participating in NASA's Hurricane and Severe Storms Sentinel (HS3) mission used their expert skills, combined with a bit of serendipity on Sept. 17, 2014, to guide the remotely piloted Global Hawk over the eye of Hurricane Edouard and release a sonde that rotated within the eye as it descended and fell into the eyewall of the storm at low levels.
NASA's HS3 mission has returned to NASA's Wallops Flight Facility on the Eastern Shore of Virginia for the third year to investigate the processes that underlie hurricane formation and intensity change ...
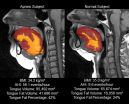
Study shows that tongue size and fat may predict sleep apnea risk in obese adults
2014-09-30
DARIEN, IL – A new study of obese adults is the first to show that those who have obstructive sleep apnea have a significantly larger tongue with a higher percentage of fat than obese controls. This may provide a mechanistic explanation for the relationship between obesity and sleep apnea.
Results show that obese participants with sleep apnea had significantly greater tongue volumes, tongue fat and percentage of tongue fat than obese controls without sleep apnea, after adjusting for potential confounders such as age, body mass index (BMI), gender and race. Further analysis ...
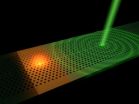
Ultrafast remote switching of light emission
2014-09-30
This news release is available in German.
The researchers etched a photonic crystal around several quantum dots in a semiconductor layer. Quantum dots are small structures that spontaneously emit light as a consequence of atomic processes. If a short laser pulse is fired at the photonic crystal, its refractive index is modified and the quantum dot experiences a change in the electromagnetic field around it. This change can speed up or slow down the emission of light by the dot. As soon as the refractive index recovers its usual value, the dot emits light again ...
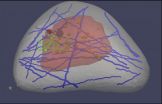
'Virtual breast' could improve cancer detection
2014-09-30
Next to lung cancer, breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in women, according to the American Cancer Society. That's why so many medical professionals encourage women to get mammograms, even though the tests are imperfect at best: only a minority of suspicious mammograms actually leads to a cancer diagnosis.
That results in lots of needless worry for women and their families—not to mention the time, discomfort and expense of additional tests, including ultrasounds and biopsies.
Recently, a different type of test, ultrasound elastography, has been used ...