(Press-News.org) Engineers at the University of California, San Diego, have completed the first comprehensive numerical simulation of skeletal muscle tissue using a method that uses the pixels in an image as data points for the computer simulation—a method known as mesh-free simulation.
The researchers, led by J.S. Chen, the William Prager Professor of structural engineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, presented their findings on the development of this method at the CompIMAGE'14 conference in Pittsburgh this month. Chen also gave a keynote speech about the work.
Chen's group has now expanded the use of mesh-free simulation methods to investigate aging and disorders impacting muscle functions, such as muscular dystrophy. "Another area of application for this framework would be the simulation of tissue injuries caused by extreme events such as blasts, car crashes and sport collisions". Chen said. This will require adding the mechanics of tissue damage to the simulation model, including how tissue behaves and functions under high velocity impact.
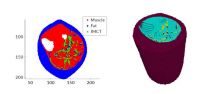
Traditionally, engineers rely on the reconstruction of the geometry captured by from CT scans or MRI images to create simulation models of biological materials, such as muscle tissue. The reconstructed 3D geometry is then used to generate a mesh to describe the material's structure—this is known as the conventional finite element method. This procedure is extremely time consuming and labor intensive.
Using the mesh-free method cuts back on the amount of time for the process of generating the simulation model because researchers don't have to build a mesh for the structure they're trying to simulate, said Ramya Rao Basava, the lead Ph.D. student on the study.
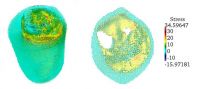
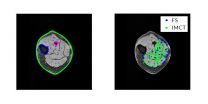
For this study, researchers in Chen's group used Magnetic Resonance and Diffusion Tensor images for the mesh-free simulation. The images were obtained through the Department of Radiology at UC San Diego. The image data acquired was from 10 volunteers between the ages of 20 to 90. The younger subjects were mostly in their 20s and 30s, the older ones mostly in their 80s.
Chen's research group used the simulation techniques they developed to look at how much force is generated from various muscle systems, and more specifically at how loss of force relates to loss of muscle volume due to aging. They found that the loss of force is greater than the loss of volume, which is consistent with prior physiological studies.
Chen is a leader in the field of computational mechanics, particularly mesh-free methods for structures and materials subjected to large deformation and damages.
Chen's research group has advanced mesh-free method research to achieve high accuracy and efficiency in simulating a wide range of engineering and scientific problems that are difficult or impossible to simulate via mesh-based methods, for example, fragment-impact modeling for homeland security applications, landslide simulations in natural disaster predictions, manufacturing processes and contact-impact modeling in the automotive industry, multi-scale materials modeling in material science applications and modeling of DNA-protein interaction, among others. Recently, his research group has started venturing into the field of simulation for biological materials such as muscle tissue.
Chen is also the faculty director of UC San Diego's new Center for Extreme Events Research, which has been established to offer solutions to a wide range of challenges associated with extreme events, such as blasts and landslides, and brings together unique experimental technologies and advances in computational methods.
INFORMATION:
First comprehensive meshfree numerical simulation of skeletal muscle tissue achieved
2014-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low social support linked to poor health in young heart attack survivors
2014-09-30
Having few friends, family and a general lack of social support is associated with poor health and quality of life and depression in young men and women a year after having a heart attack, according to new research in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Social support is the perception of having friends or family who serve as confidants and companions, offer advice and information, show emotional concern, or provide financial or material support, said Emily Bucholz, lead researcher and a student in the School of Medicine and the Department of Chronic Disease ...
Study finds acupuncture does not improve chronic knee pain
2014-09-30
Among patients older than 50 years with moderate to severe chronic knee pain, neither laser nor needle acupuncture provided greater benefit on pain or function compared to sham laser acupuncture, according to a study in the October 1 issue of JAMA.
Chronic knee pain affects many people older than 50 years and is the most common pain concern among older people consulting family physicians. Nonpharmacological approaches are central to managing chronic knee pain, and patients with joint pain frequently use complementary and alternative medicine. Acupuncture is the most ...
Use of a 'virtual ward' model of care does not reduce hospital readmissions, risk of death
2014-09-30
In a trial involving patients at high risk of hospital readmission or death, use of a virtual ward model of care (using some elements of hospital care in the community) after hospital discharge did not significantly reduce the rate of readmission or death up to a year following discharge, according to a study in the October 1 issue of JAMA.
Hospital readmissions are common and costly, and no single intervention or bundle of interventions has reliably reduced readmissions. The virtual ward model of care is a way of providing care to patients with complex needs who are ...
Study compares long-term outcomes for types of aortic valve replacements
2014-09-30
Among patients ages 50 to 69 years who underwent aortic valve replacement with bioprosthetic (made primarily with tissue) compared with mechanical prosthetic valves, there was no significant difference in 15-year survival or stroke, although patients in the bioprosthetic valve group had a greater likelihood of reoperation but a lower likelihood of major bleeding, according to a study in the October 1 issue of JAMA.
Approximately 50,000 patients undergo aortic valve replacement annually in the United States. In older patients, bioprosthetic valves pose a low lifetime ...
Medical professional liability claims and esophageal cancer screening
2014-09-30
An analysis of liability claims related to esophageal cancer screening finds that the risks of claims arising from acts of commission (complications from screening procedure) as well as acts of omission (failure to screen) are similarly low, according to a study in the October 1 issue of JAMA.
Endoscopic screening for esophageal cancer has been recommended for patients with chronic symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease, but only if they have additional risk factors. Surveys of gastroenterologists indicate that concern about litigation for missing a cancer may drive ...
Biodiversity in the Mediterranean is threatened by alien species
2014-09-30
Millions of tourists visit the Mediterranean each year, but its deep-blue waters host the largest invasion currently underway on Earth. Almost 1,000 alien species, including fish, crustaceans, and algae are now established from other seas through human activities. In the open-access journal Frontiers in Marine Science, a multinational team of researchers analyzed data from a new information system developed by the European Commission to show how the introduction of alien species has changed the native biodiversity within the Mediterranean.
A hotspot for marine biodiversity, ...
Clinical trial finds virtual ward does not reduce hospital readmissions
2014-09-30
TORONTO — A virtual ward, a new model of care that provides support to high-risk and complex patients in the community for a few weeks after discharge from hospital, did not prevent hospital readmissions as hoped in a clinical trial in Toronto.
Hospital readmissions are common and costly and no intervention has reliably reduced them. Virtual wards, pioneered in Britain 10 years ago, were thought to have the potential to reduce readmissions, but had not been rigorously evaluated by researchers.
Dr. Irfan Dhalla, a physician at St. Michael's Hospital, led a randomized trial ...
Researchers show EEG's potential to reveal depolarizations following TBI
2014-09-30
CINCINNATI—The potential for doctors to measure damaging "brain tsunamis" in injured patients without opening the skull has moved a step closer to reality, thanks to pioneering research at the University of Cincinnati (UC) Neuroscience Institute.
The research team, led by Jed Hartings, PhD, research associate professor in the department of neurosurgery at the UC College of Medicine, has shown that spreading depolarizations—electrical disturbances that spread through an injured brain like tsunami waves—can be measured by the placement of electroencephalograph (EEG) electrodes ...
NASA's Swift mission observes mega flares from a mini star
2014-09-30
On April 23, NASA's Swift satellite detected the strongest, hottest, and longest-lasting sequence of stellar flares ever seen from a nearby red dwarf star. The initial blast from this record-setting series of explosions was as much as 10,000 times more powerful than the largest solar flare ever recorded.
"We used to think major flaring episodes from red dwarfs lasted no more than a day, but Swift detected at least seven powerful eruptions over a period of about two weeks," said Stephen Drake, an astrophysicist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, ...
NASA's HS3 looks Hurricane Edouard in the eye
2014-09-30
NASA and NOAA scientists participating in NASA's Hurricane and Severe Storms Sentinel (HS3) mission used their expert skills, combined with a bit of serendipity on Sept. 17, 2014, to guide the remotely piloted Global Hawk over the eye of Hurricane Edouard and release a sonde that rotated within the eye as it descended and fell into the eyewall of the storm at low levels.
NASA's HS3 mission has returned to NASA's Wallops Flight Facility on the Eastern Shore of Virginia for the third year to investigate the processes that underlie hurricane formation and intensity change ...