(Press-News.org) Studying mice with a genetic change similar to what is found in Kabuki syndrome, a inherited disease of humans, Johns Hopkins researchers report they have used an anticancer drug to "open up" DNA and improve mental function.
Along with a potential treatment for the intellectual disability seen in Kabuki syndrome, the study's findings also suggest a new way of thinking about a category of genetic diseases known as Mendelian disorders of the epigenetic machinery, the researchers say. In these disorders, a genetic mutation causes errors in the way proteins and chemicals bind to DNA, which in turn affects the rate at which DNA make proteins. In the case of a Kabuki syndrome-like condition in mice, the researchers found that those errors lead to a persistent but treatable decrease in new cell growth in one part of the brain. Their study adds to the growing evidence that intellectual disability may not always be irreversible.
A report on the research appears online Oct. 1 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
"Mendelian disorders of the epigenetic machinery affect how cells 'package' and use DNA, so they tend to have complicated and far-reaching effects," says Hans Bjornsson, M.D., Ph.D., an assistant professor of pediatrics and genetics in the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine's McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine. "Finding that a drug can ease some of the symptoms in this group of disorders suggests that other Mendelian disorders of the histone machinery may be treated in a similar manner." Bjornsson led the study in collaboration with Harry "Hal" Dietz, M.D., the Victor A. McKusick Professor of Medicine and Genetics and director of the William S. Smilow Center for Marfan Syndrome Research.
Bjornsson heads the McKusick-Nathans Epigenetics and Chromatin Clinic. His research focuses on Kabuki syndrome, which is caused by mutations in one of two genes that govern proteins that DNA wrap around. DNA wound around the packaging proteins is known as chromatin; only by forming chromatin can several feet of DNA fit inside the tiny command centers of each cell. But in order for a cell to read the DNA and put it to use making new proteins of its own, the chromatin must temporarily open up.
Specialized enzymes, often called "writers" and "erasers," add or subtract chemical groups to the packaging proteins to help induce the chromatin to open or close. In recent years, other researchers have found that Kabuki syndrome can be caused by mutations to one of two genes — one for a writer, one for an eraser — with the same net effect on chromatin opening. That finding led Bjornsson and his collaborators to suspect that Kabuki syndrome and similar conditions might be caused by an imbalance between chromatin's open and closed states.
If true, that would mean that disorders of the histone machinery could be treated by altering the balance between open and closed states, Bjornsson says. To test the idea, Joel Benjamin, a graduate student in Bjornsson's lab, used mice with a mutation in one of the Kabuki syndrome genes and a condition similar to Kabuki syndrome.
When the mice were at their young adult phase, the team treated them with AR-42, a drug developed for cancers of the blood that was already known to open up compacted chromatin. After two weeks of treatment, they put the mice through a drill called the Morris water maze, which tests their ability to form memories in a region of the brain called the hippocampus. The treated mice performed better than the untreated mice with the Kabuki-like condition — about as well as healthy mice.
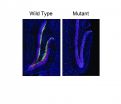
Studying the brains of the treated mice, the researchers saw that compared to untreated peers, they had more newly formed neurons in a part of the hippocampus called the dentate gyrus. "The dentate gyrus is important for memory formation, and it's also one of the few places in adult brains where we see new neurons," Bjornsson says. "We think that when DNA's chromatin open up, the cells are able to 'turn up' one or more genes needed for that new growth."
Physicians generally consider the intellectual disability that accompanies disorders like Kabuki syndrome to be irreversible, Bjornsson notes. "But we now know that new brain cells continue to form throughout our lives. If Kabuki syndrome and related disorders cause fewer neurons to be made in adulthood, stimulating neuron growth may be an effective strategy for treating intellectual disability," he says. A Scottish research group has reported a way to reverse neurological dysfunction in mice with a condition similar to Rett syndrome, an inherited disorder that also causes intellectual disability.
A treatment for any inborn intellectual disability in people — including Kabuki syndrome — could still take a decade or more to develop, Bjornsson cautions. His next steps will be to home in on the dentate gyrus to see whether it really is the main source of the memory defect found in the Kabuki mice and to explore whether there are other potential drugs that have a similar effect.
INFORMATION:
Other authors on the paper were Li Zhang, Elizabeth E. Gerber, Yi-Chun Chen, Michelle C. Potter and Kasper D. Hansen of The Johns Hopkins University; and Jacqueline Weissman and Rebecca Vaurio of the Kennedy Krieger Institute.
This work was supported by the William S. Smilow Center for Marfan Syndrome Research, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Institutes of Health's Director's Early Independence Award (grant number DP5OD017877) and the American Academy of Pediatrics' Section on Genetics and Birth Defects.
Drug treats inherited form of intellectual disability in mice
Study suggests some symptoms in human version of the disorder could be eased
2014-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds potential new target to treat asthma attacks brought on by colds
2014-10-01
Researchers have identified a molecular mechanism that could explain why the common cold can bring on life-threatening asthma attacks.
Published today in Science Translational Medicine, the findings indicate this may be a potential target for new drugs that could be more effective than existing treatments.
Viruses that infect the airways are the most common cause of asthma attacks, accounting for 80-90 per cent of cases. The great majority of these are rhinoviruses, which are the predominant cause of the common cold.
Although illnesses caused by rhinoviruses are ...
Stem cell discovery could lead to better treatments for blindness
2014-10-01
Scientists at the University of Southampton have discovered that a region on the front surface of the eye harbours special stem cells that could treat blinding eye conditions.
This part of the eye is called the 'corneal limbus' and is a narrow gap lying between the transparent cornea and white sclera.
The research, published in PLOS ONE, showed that stem cells can be cultured from the corneal limbus in vitro. Under the correct culture conditions, these cells could be directed to behave like the cells needed to see light - photoreceptor cells.
The loss of photoreceptors ...
Predictor of tissue injury in kidney transplant recipients found
2014-10-01
Researchers at UC San Francisco and Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, may have found a predictor for a disorder affecting kidney transplant recipients that can accelerate organ failure, a discovery that eventually could allow for customized therapies and improved patient selection for transplant.
The study of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), a devastating form of kidney disease, is in the Oct. 1 issue of Science Translational Medicine. Research was conducted by an international study team, with Necker Hospital in Paris and UCSF joint lead authors and ...
Researchers find promise in new treatments for GBM
2014-10-01
(Boston) — Glioblastma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most lethal primary brain tumors, with median survival for these patients only slightly over one year. Researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM), in collaboration with researchers from the City of Hope, are looking toward novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of GBM in the form of targeted therapies against a unique receptor, the interleukin-13 receptor α chain variant 2 (IL13Rα2).
In a review paper published in the October issue of Neuro-Oncology, the researchers discuss various ...
Team advances understanding of the Greenland Ice Sheet's meltwater channels
2014-10-01
An international research team's field work, drilling and measuring melt rates and ice sheet movement in Greenland is showing that things are, in fact, more complicated than we thought.
"Although the Greenland Ice Sheet initially speeds up each summer in its slow-motion race to the sea, the network of meltwater channels beneath the sheet is not necessarily forming the slushy racetrack that had been previously considered," said Matthew Hoffman, a Los Alamos National Laboratory scientist on the project.
A high-profile paper appearing in Nature this week notes that observations ...
NASA sees intensifying typhoon Phanfone heading toward Japan
2014-10-01
VIDEO:
NASA's TRMM satellite saw Phanfone was producing rainfall over a very large area on Oct. 1. Some storms in these bands were dropping rain at a rate of over 76...
Click here for more information.
An intensifying typhoon called Phanfone that originated east of Guam on September 28, 2014 is headed toward southern Japan. The TRMM satellite crossed above Typhoon Phanfone on October 1, 2014 at 1039 UTC and gathered data about rainfall rates occurring in the storm.
TRMM, ...
Genetic secrets of the monarch butterfly revealed
2014-10-01
The monarch butterfly is one of the most iconic insects in the world, best known for its distinct orange and black wings and a spectacular annual mass migration across North America. However, little has been known about the genes that underlie these famous traits, even as the insect's storied migration appears to be in peril.
Sequencing the genomes of monarch butterflies from around the world, a team of scientists has now made surprising new insights into the monarch's genetics. They identified a single gene that appears central to migration – a behavior generally regarded ...
Gut bacteria are protected by host during illness
2014-10-01
To protect their gut microbes during illness, sick mice produce specialized sugars in the gut that feed their microbiota and maintain a healthy microbial balance. This protective mechanism also appears to help resist or tolerate additional harmful pathogens, and its disruption may play a role in human diseases such as Crohn's disease, report scientists from the University of Chicago in Nature on Oct 1.
"Both hosts and their gut microbiota can suffer in the case of sickness, but this mutually beneficial relationship is guarded by the host," said study senior author Alexander ...
New study explains wintertime ozone pollution in Utah oil and gas fields
2014-10-01
Chemicals released into the air by oil and gas exploration, extraction and related activities can spark reactions that lead to high levels of ozone in wintertime, high enough to exceed federal health standards, according to new NOAA-led research, published today in Nature.
The study comes at a time when new technologies are helping to accelerate oil and gas development in Utah's Uintah Basin, elsewhere in the United States and in many other countries, and its findings may help air quality managers determine how to best minimize the impact of ozone pollution.
When ozone ...
Evolving plumbing system beneath Greenland slows ice sheet as summer progresses
2014-10-01
AUSTIN, Texas—A team led by scientists at the University of Texas at Austin's Institute for Geophysics has for the first time directly observed multiple parts of Greenland's subglacial plumbing system and how that system evolves each summer to slow down the ice sheet's movement toward the sea.
These new observations could be important in accurately modeling Greenland's future response to climate change.
"Everyone wants to know what's happening under Greenland as it experiences more and more melt," said study coauthor Ginny Catania, a research scientist at the institute ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study confirms that people with ADHD can be more creative. The reason may be that they let their mind wander
Research gives insight into effect of neurodegenerative diseases on speech rhythm
Biochar and plants join forces to clean up polluted soils and boost ecosystem recovery
Salk scientist Joseph Ecker awarded McClintock Prize for Plant Genetics and Genome Studies
ADHD: Women are diagnosed five years later than men, despite symptoms appearing at the same age.
Power plants may emit more pollution during government shutdowns
Increasing pressures for conformity de-skilling and demotivating teachers, study warns
Researchers develop smarter menstrual product with potential for wearable health monitoring
Microwaves for energy-efficient chemical reactions
MXene current collectors could reduce size, improve recyclability of Li-ion batteries
Living near toxic sites linked to aggressive breast cancer
New discovery could open door to male birth control
Wirth elected Fellow of American Physical Society
The Journal of Nuclear Medicine Ahead-of-Print Tip Sheet: October 10, 2025
Destined to melt
Attitudes, not income, drive energy savings at home
The playbook for perfect polaritons
‘Disease in a dish’ study of progressive MS finds critical role for unusual type of brain cell
Solar-powered method lights the way to a ‘de-fossilized’ chemical industry
Screen time linked to lower academic achievement among Ontario elementary students
One-year outcomes after traumatic brain injury and early extracranial surgery in the TRACK-TBI Study
Enduring outcomes of COVID-19 work absences on the US labor market
Affirmative action repeal and racial and ethnic diversity in us medical school admissions
Cancer progression illuminated by new multi-omics tool
Screen time and standardized academic achievement tests in elementary school
GLP-1RA order fills and out-of-pocket costs by race, ethnicity, and indication
Study finds HEPA purifiers alone may not be enough to reduce viral exposure in schools
UVA Health developing way to ID people at risk of dangerous lung scarring even before symptoms appear
How can we know when curing cancer causes myocarditis?
Male infertility in Indian men linked to lifestyle choices and hormonal imbalances
[Press-News.org] Drug treats inherited form of intellectual disability in miceStudy suggests some symptoms in human version of the disorder could be eased