Making oxygen before life
2014-10-03
(Press-News.org) About one-fifth of the Earth's atmosphere is oxygen, pumped out by green plants as a result of photosynthesis and used by most living things on the planet to keep our metabolisms running. But before the first photosynthesizing organisms appeared about 2.4 billion years ago, the atmosphere likely contained mostly carbon dioxide, as is the case today on Mars and Venus.
Over the past 40 years, researchers have thought that there must have been a small amount of oxygen in the early atmosphere. Where did this abiotic ("non-life") oxygen come from? Oxygen reacts quite aggressively with other compounds, so it would not persist for long without some continuous source.
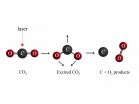
Now UC Davis graduate student Zhou Lu, working with professors in the Departments of Chemistry and of Earth and Planetary Sciences, has shown that oxygen can be formed in one step by using a high energy vacuum ultraviolet laser to excite carbon dioxide. (The work is published Oct. 3 in the journal Science).
"Previously, people believed that the abiotic (no green plants involved) source of molecular oxygen is by CO2 + solar light — > CO + O, then O + O + M — > O2 + M (where M represents a third body carrying off the energy released in forming the oxygen bond)," Zhou said in an email. "Our results indicate that O2 can be formed by carbon dioxide dissociation in a one step process. The same process can be applied in other carbon dioxide dominated atmospheres such as Mars and Venus."
Zhou used a vacuum ultraviolet laser to irradiate CO2 in the laboratory. Vacuum ultraviolet light is so-called because it has a wavelength below 200 nanometers and is typically absorbed by air. The experiments were performed by using a unique ion imaging apparatus developed at UC Davis.
Such one-step oxygen formation could be happening now as carbon dioxide increases in the region of the upper atmosphere, where high energy vacuum ultraviolet light from the Sun hits Earth or other planets. It is the first time that such a reaction has been shown in the laboratory. According to one of the scientists who reviewed the paper for Science, Zhou's work means that models of the evolution of planetary atmospheres will now have to be adjusted to take this into account.
INFORMATION:
Coauthors on the paper are, in the UC Davis Department of Chemistry, postdoctoral researcher Yih Chung Chang, Distinguished Professor Cheuk-Yiu Ng and Distinguished Professor emeritus William M. Jackson; and Professor Qing-Zhu Yin, Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences. The work was principally funded by NASA, NSF, and the U.S. Department of Energy.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-03
Curiosity helps us learn about a topic, and being in a curious state also helps the brain memorize unrelated information, according to researchers at the UC Davis Center for Neuroscience. Work published Oct. 2 in the journal Neuron provides insight into how piquing our curiosity changes our brains, and could help scientists find ways to enhance overall learning and memory in both healthy individuals and those with neurological conditions.
"Our findings potentially have far-reaching implications for the public because they reveal insights into how a form of intrinsic motivation ...
2014-10-03
White Americans may view diversity and multiculturalism more negatively as the U.S. moves toward becoming a minority-majority nation, UCLA psychologists report.
As part of their study, the researchers divided 98 white Americans from all regions of the country — half male, half female, with an average age of 37 — randomly into two groups. One group was told that whites will no longer be the majority in the U.S. by 2050; in fact, this is likely to be true as soon as 2043, according to some projections. The second group was told that whites would retain their majority status ...
2014-10-03
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA -- New applications of structures and materials that replicate complex yet efficient arrangements that have evolved in nature over millennia are featured in a special section on biomimetic and bioinspired materials for applications in biophotonics in the October issue of the Journal of Biomedical Optics. The journal is published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, in the SPIE Digital Library. Several of the peer-reviewed articles are accessible via open access.
"Biomimetic and bioinspired materials present an emerging ...
2014-10-03
VIDEO:
The video compares the two sliding states of the C60 flake attached to the tip of the microscope: a) commensurate state at low temperature where the C60 do not rotate...
Click here for more information.
About 3500 years ago, man invented the wheel to make life easier. Then, thanks to Leonardo Da Vinci's genius, the wheel was made smaller to obtain ball bearings. And today? "Today we are trying to get even smaller: scientists are thinking about nano-bearings", comments ...
2014-10-03
PULLMAN, Wash.—A Washington State University undergraduate has helped develop a new method for detecting water on Mars. Her findings appear in Nature Communications, one of the most influential general science journals.
Kellie Wall, 21, of Port Orchard, Wash., looked for evidence that water influenced crystal formation in basalt, the dark volcanic rock that covers most of eastern Washington and Oregon. She then compared this with volcanic rock observations made by the rover Curiosity on Mars' Gale Crater.
"This is really cool because it could potentially be useful for ...
2014-10-03
COLUMBUS, Ohio—Is it a solar cell? Or a rechargeable battery?
Actually, the patent-pending device invented at The Ohio State University is both: the world's first solar battery.
In the October 3, 2014 issue of the journal Nature Communications, the researchers report that they've succeeded in combining a battery and a solar cell into one hybrid device.
Key to the innovation is a mesh solar panel, which allows air to enter the battery, and a special process for transferring electrons between the solar panel and the battery electrode. Inside the device, light and oxygen ...
2014-10-03
Too many stroke patients in Canada are not getting the rehabilitation they need to return to a healthy, active life, according to a new study which will be presented at the Canadian Stroke Congress in Vancouver tomorrow. The research findings strongly suggest that such decisions are being made based on what services are available in the health system rather than what patients really need.
It found that overall just 16 per cent of patients with stroke were discharged to inpatient rehabilitation but that the rates varied widely by province (1% to 26%) and hospital (0% to ...
2014-10-03
They base their findings on 1221 Danish men between the ages of 18 and 28, all of whom underwent a medical examination to assess their fitness for military service, which is compulsory in Denmark, between 2008 and 2012.
As part of their assessment, the military recruits were asked how much alcohol they drank in the week before their medical exam (recent drinking); whether this was typical (habitual); and how often they binge drank, defined as more than 5 units in one sitting, and had been drunk in the preceding month.
They were also invited to provide a semen sample ...
2014-10-03
There is some evidence to suggest that alcohol impairs the workings of the immune system, both in terms of the initial protective inflammatory response to infection and the development of subsequent immunity.
And habitual drinking is known to increase susceptibility to bacterial pneumonia, septicaemia, tuberculosis and viral hepatitis. The researchers therefore wanted to find out if there was any association between drinking patterns and susceptibility to HPV infection.
They included 1313 men who were already taking part in the US arm of the HPV in Men (HIM) study, ...
2014-10-03
Previous research has suggested that gout might be associated with diabetes, but the findings were restricted to one study of men at high risk of heart disease and stroke. The researchers wanted to know if the link existed in the general population, and also applied to women.
They searched the Health Improvement Network (THIN), an electronic database of the anonymised health records of almost 7.5 million patients registered with 477 general practices across the UK.
They included adults who were at least 20 years old, and whose details had been entered into the database ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Making oxygen before life