Scientists develop barcoding tool for stem cells
New technology that tracks the origin of blood cells challenges scientific dogma
2014-10-05
(Press-News.org) A 7-year-project to develop a barcoding and tracking system for tissue stem cells has revealed previously unrecognized features of normal blood production: New data from Harvard Stem Cell Institute scientists at Boston Children's Hospital suggests, surprisingly, that the billions of blood cells that we produce each day are made not by blood stem cells, but rather their less pluripotent descendants, called progenitor cells. The researchers hypothesize that blood comes from stable populations of different long-lived progenitor cells that are responsible for giving rise to specific blood cell types, while blood stem cells likely act as essential reserves.
The work, supported by a National Institutes of Health Director's New Innovator Award and published in Nature, suggests that progenitor cells could potentially be just as valuable as blood stem cells for blood regeneration therapies.
This new research challenges what textbooks have long read: That blood stem cells maintain the day-to-day renewal of blood, a conclusion drawn from their importance in re-establishing blood cell populations after bone marrow transplants—a fact that still remains true. But because of a lack of tools to study how blood forms in a normal context, nobody had been able to track the origin of blood cells without doing a transplant.
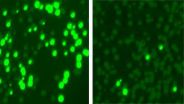
Boston Children's Hospital scientist Fernando Camargo, PhD, and his postdoctoral fellow Jianlong Sun, PhD, addressed this problem with a tool that generates a unique barcode in the DNA of all blood stem cells and their progenitor cells in a mouse. When a tagged cell divides, all of its descendant cells possess the same barcode. This biological inventory system makes it possible to determine the number of stem cells/progenitors being used to make blood and how long they live, as well as answer fundamental questions about where individual blood cells come from.
"There's never been such a robust experimental method that could allow people to look at lineage relationships between mature cell types in the body without doing transplantation," Sun said. "One of the major directions we can now go is to revisit the entire blood cell hierarchy and see how the current knowledge holds true when we use this internal labeling system."
"People have tried using viruses to tag blood cells in the past, but the cells needed to be taken out of the body, infected, and re-transplanted, which raised a number of issues," said Camargo, who is a member of Children's Stem Cell Program and an associate professor in Harvard University's Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology. "I wanted to figure out a way to label blood cells inside of the body, and the best idea I had was to use mobile genetic elements called transposons."
A transposon is a piece of genetic code that can jump to a random point in DNA when exposed to an enzyme called transposase. Camargo's approach works using transgenic mice that possess a single fish-derived transposon in all of their blood cells. When one of these mice is exposed to transposase, each of its blood cells' transposons changes location. The location in the DNA where a transposon moves acts as an individual cell's barcode, so that if the mouse's blood is taken a few months later, any cells with the same transposon location can be linked back to its parent cell.
The transposon barcode system took Camargo and Sun seven years to develop, and was one of Camargo's first projects when he opened his own lab at the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research directly out of grad school. Sun joined the project after three years of setbacks, and accomplished an experimental tour de force to reach the conclusions in the Nature paper, which includes data on how many stem cells or progenitor cells contribute to the formation of immune cells in mouse blood.
With the original question of how blood arises in a non-transplant context answered, the researchers are now planning to explore many more applications for their barcode tool.
"We are also tremendously excited to use this tool to barcode and track descendants of different stem cells or progenitor cells for a range of conditions, from aging, to the normal immune response," Sun said. "We first used this technology for blood analysis, however, this system can also help address basic questions about cell populations in solid tissue. You can imagine being able to look at tumor progression or identify the precise origins of cancer cells that have broken off from a tumor and are now circulating in the blood."
"I think that not only for the blood field, this can change the way people look at stem cell and progenitor relationships," Camargo added. "The feedback that we have received from other experts in the field has been fantastic. This can truly be a groundbreaking technology."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by an NIH Director's New Innovator Award (DP2OD006472) and the Harvard Stem Cell Institute.
Cited: Sun, J, et. al., Clonal dynamics of native haematopoiesis. Nature. October 16, 2014. DOI: 10.1038/nature13824
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-05
This news release is available in French and German. Physicians and researchers at CHU Sainte-Justine, Université de Montréal, CHU de Québec, Université Laval, and Hubrecht Institute have discovered a rare disease affecting both heart rate and intestinal movements. The disease, which has been named "Chronic Atrial Intestinal Dysrhythmia syndrome" (CAID), is a serious condition caused by a rare genetic mutation. This finding demonstrates that heart and guts rhythmic contractions are closely linked by a single gene in the human body, as shown in a study published on October ...
2014-10-05
A new crystallographic technique developed at the University of Leeds is set to transform scientists' ability to observe how molecules work.
A research paper, published in the journal Nature Methods on October 5, describes a new way of doing time-resolved crystallography, a method that researchers use to observe changes within the structure of molecules.
Although fast time-resolved crystallography (Laue crystallography) has previously been possible, it has required advanced instrumentation that is only available at three sites worldwide. Only a handful of proteins ...
2014-10-05
A study published in Nature Geoscience shows that air pollution has had a significant impact on the amount of water flowing through many rivers in the northern hemisphere.
The paper shows how such pollution, known as aerosols, can have an impact on the natural environment and highlights the importance of considering these factors in assessments of future climate change.
The research resulted from a collaboration between scientists at the Met Office, Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, University of Reading, Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique in France, and the University ...
2014-10-05
The multitude of microbes scientists have found populating the human body have good, bad and mostly mysterious implications for our health. But when something goes wrong, we defend ourselves with the undiscriminating brute force of traditional antibiotics, which wipe out everything at once, regardless of the consequences.
Researchers at Rockefeller University and their collaborators are working on a smarter antibiotic. And in research to be published October 5 in Nature Biotechnology, the team describes a 'programmable' antibiotic technique that selectively targets the ...
2014-10-05
Type 2 diabetes affects an estimated 28 million Americans according to the American Diabetes Association, but medications now available only treat symptoms, not the root cause of the disease. New research from Rutgers shows promising evidence that a modified form of a different drug, niclosamide – now used to eliminate intestinal parasites – may hold the key to battling the disease at its source.
The study, led by Victor Shengkan Jin, an associate professor of pharmacology at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, has been published online by the journal Nature ...
2014-10-03
Montréal, October 2, 2014 – Scientists at the IRCM discovered a mechanism that promotes the progression of medulloblastoma, the most common brain tumour found in children. The team, led by Frédéric Charron, PhD, found that a protein known as Sonic Hedgehog induces DNA damage, which causes the cancer to develop. This important breakthrough will be published in the October 13 issue of the prestigious scientific journal Developmental Cell. The editors also selected the article to be featured on the journal's cover.
Sonic Hedgehog belongs to a family of proteins that gives ...
2014-10-03
Despite the legalization of same-sex marriage in 19 states and the District of Columbia and an executive order to prohibit federal contractors from discrimination against lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender employees, LGBT individuals face tremendous hurdles in access to health care and basic human rights. A special report published by The Hastings Center, LGBT Bioethics: Visibility, Disparities, and Dialogue, is a call to action for the bioethics field to help right the wrongs in the ways that law, medicine, and society have treated LGBT people.
The editors are Tia ...
2014-10-03
FALLS CHURCH, Va. (October 3, 2014) — A new National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) study, published online in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, found that recommended safe handling practices for workers who administer antineoplastic drugs in healthcare settings are not always followed.
Results are derived from the 2011 Health and Safety Practices Survey of Healthcare Workers, the largest federally-sponsored survey of healthcare workers in the U.S., which addresses safety and health practices relative to use of hazardous chemicals. ...
2014-10-03
Men who consume more alcohol have a greater risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, according to a recent study by Moffitt Cancer Center researchers.
HPV is a common sexually transmitted virus, with more than six million new infections in the United States each year. HPV causes genital warts in both men and women and is a contributing factor to a number of different cancers in women, including cervical, vaginal and anal cancers. More recent studies have shown that HPV can also cause penile, anal and oropharyngeal cancer in men. However, there is limited data regarding ...
2014-10-03
A snaking, extended filament of solar material currently lies on the front of the sun-- some 1 million miles across from end to end. Filaments are clouds of solar material suspended above the sun by powerful magnetic forces. Though notoriously unstable, filaments can last for days or even weeks.
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which watches the sun 24 hours a day, has observed this gigantic filament for several days as it rotated around with the sun. If straightened out, the filament would reach almost across the whole sun, about 1 million miles or 100 times ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists develop barcoding tool for stem cells
New technology that tracks the origin of blood cells challenges scientific dogma