Researchers redefine hypothesis on holes in the brain
2014-10-06
(Press-News.org) Over the years, researchers have described how some of the body's cells have giant channels – a kind of holes that completely uncritically allow both small and large molecules to penetrate into and out of the cell. The hypothesis is that these normally closed gatekeeper proteins in the cell membrane allow unrestricted access in the event of diseases such as myocardial infarction, stroke or Alzheimer's. If the hypothesis was correct, the obvious choice would be to look for novel drugs to block the relevant membrane proteins and in this way cure or prevent disease.
New research findings published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry unfortunately show that the hypothesis is a bit too optimistic. A new study conducted by researchers from the Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine and the Department of Biomedical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen indicates a more complicated picture. The holes apparently do not act as unrestricted pathways.
Nanna MacAulay, the researcher behind the new results that disprove an existing paradigm within cell biology:
– If there are huge channels in the cells that open, e.g. in response to hypoxia or inflammation of the brain, it would be very interesting to focus on these channels as targets for new drugs. Over the years, many researchers have formulated how such channels could open in the cell membrane in connection with various diseases. Laboratory tests now show that the channels in question behave differently than previously described, being far more restrictive and behaving differently depending on the type of channel.
The researchers have studied the membrane proteins connexin and pannexin and their ability to lead various chemical compounds into and out of the cells.
INFORMATION:
Read the scientific article in the Journal of Biological Chemistry
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-06
A specialist group of European researchers are studying the remains of prehistoric human settlements which are now submerged beneath our coastal seas. Some of these drowned sites are tens of thousands of years old. From the progressive discovery and analysis of these prehistoric remains, a new scientific field has emerged, combining the expertise from many disciplines including archaeology, oceanography and the geosciences. The new field is called Continental Shelf Prehistoric Research.
This rapidly evolving research field is the focus of a new European Marine Board ...
2014-10-06
Since the first human fetal surgery was reported in 1965, several different fetal surgical procedures have been developed and perfected, resulting in significantly improved outcomes for many fetuses. However, the significant investments associated with this highly specialized service and quality metrics must be considered as more fetal treatment programs are developed.
Katharine D. Wenstrom, MD, director of the Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island, co-director of the hospital's Integrated Program for High-Risk Pregnancy, and ...
2014-10-06
WASHINGTON, Oct. 6, 2014 — It's happened to many of us: Half asleep in the morning, you finish brushing your teeth and reach for your daily glass of orange juice. After taking a big swig, you spit it back out, making a face like you've just chewed on a lemon. Turns out, a specific chemical in your toothpaste is responsible for that nasty taste. This week, Reactions explains why toothpaste and orange juice don't mix. Learn all about it at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9X5_gtel-c0.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to ...
2014-10-06
Quantum computing will allow for the creation of powerful computers, but also much smarter and more creative robots than conventional ones. This was the conclusion arrived at by researchers from Spain and Austria, who have confirmed that quantum tools help robots learn and respond much faster to the stimuli around them.
Quantum mechanics has revolutionised the world of communications and computers by introducing algorithms which are much quicker and more secure in transferring information. Now researchers from the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM) and the University ...
2014-10-06
The way neurons are interconnected in the brain is very complicated. This holds especially true for the cells of the hippocampus. It is one of the oldest brain regions and its form resembles a see horse (hippocampus in Latin). The hippocampus enables us to navigate space securely and to form personal memories. So far, the anatomic knowledge of the networks inside the hippocampus and its connection to the rest of the brain has left scientists guessing which information arrived where and when.
Signals spread through the brain
Accordingly, Dr Martin Pyka and his colleagues ...
2014-10-06
New research by scientists at the University of Bristol has challenged one of the key axioms in biology - that enzymes need water to function. The breakthrough could eventually lead to the development of new industrial catalysts for processing biodiesel.
Enzymes are large biological molecules that catalyse thousands of different chemical reactions that are essential for all life, from converting food into energy, to controlling how our cells replicate DNA.
Throughout this diverse range of biological environments in which enzymes perform their various roles, the only ...
2014-10-06
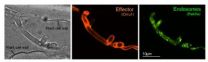
Plants that come under attack from pathogens have an automatic immune response. Fungi get around this plant immunity by injecting proteins into the host plant cells. These 'effector proteins' enable the fungi to escape the plant's immune system and allow the fungal cells to enter the plant unrecognised.
Exeter scientists have now shown that signalling organelles, known as 'early endosomes' act as long distance messengers in the fungi. They travel rapidly along long tube-like cells between the plant-invading fungal cell tip and the fungal cell nucleus. This rapid communication ...
2014-10-06
PITTSBURGH—One way to combat the rising level of errors and fraud in life sciences research is through massive online laboratories, which use videogames to engage large numbers of non-professional investigators and prevent scientists from manually testing their own hypotheses, researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Stanford University say.
Though unconventional, CMU's Adrien Treuille and Stanford's Rhiju Das argue that this online, game-like approach actually is more scientifically rigorous than the standard practice of scientists proposing an explanation for ...
2014-10-06
This news release is available in Spanish. [Gondar, Ethiopia and Geneva, Switzerland – October 6, 2014] - The international research & development (R&D) consortium, AfriCoLeish, formed by six research organizations from East Africa and Europe, has launched a Phase III clinical study to address the extreme difficulty in treating visceral leishmaniasis (VL) in patients who also are HIV-positive. The study will assess the efficacy and the safety of two treatments: a combination treatment of AmBisome® and miltefosine, and AmBisome® alone. This is the first randomized clinical ...
2014-10-06
New research confirms that sleep disturbances are linked to pain and depression, but not disability, among patients with osteoarthritis (OA). Study results published in Arthritis Care & Research, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), found that poor sleep increases depression and disability, but does not worsen pain over time.
Arthritis is one of the top three health concerns that cause disability in the U.S., with OA being the most common form of arthritis. Medical evidence reports that nearly 30 million Americans are affected by OA, which has increased ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers redefine hypothesis on holes in the brain