(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – Majorities of media researchers, parents and pediatricians agree that exposure to violent media can increase aggression in children, according to a new national study.
The study found that 66 percent of researchers, 67 percent of parents and 90 percent of pediatricians agree or strongly agree that violent video games can increase aggressive behavior among children.
Majorities of these groups also believed that children's aggressive behavior can be fueled by viewing violent video games, movies, TV programs, and Internet sites. However, fewer than half agreed that violent comic books or literature would have such harmful effects on children.
"Some people claim there is no consensus about whether violent media can increase aggression in children, but this study shows that there is consensus," said Brad Bushman, lead author of the study and professor of communication and psychology at The Ohio State University.
"As in most areas of research, there is not complete agreement. But we found the overwhelming majority of media researchers, parents and pediatricians agree that violent media is harmful to children."
Bushman conducted the study with Carlos Cruz, a doctoral student at Ohio State, and Mario Gollwitzer, a professor at Philipps University Marburg in Germany. Their study appears online in the journal Psychology of Popular Media Culture.
Bushman noted that while 66 percent of researchers agreed or strongly agreed that violent video games increased aggression, only 17 percent disagreed or strongly disagreed. The remaining 17 percent were undecided.
"That means that among researchers who have an opinion, eight out of 10 agree that violent games increase aggression," Bushman said. "That's hardly a controversy."
For the study, the researchers surveyed 371 media psychologists and communication scientists from three professional organizations; 92 members of the Council on Communication and Media of the American Academy of Pediatrics; and a nationally representative sample of 268 American parents.
In addition to the other findings, the study revealed that majorities of researchers, pediatricians and parents agreed that there is a causal relationship between exposure to violent media and aggressive behavior.
There was considerable disagreement among the three groups as to whether media violence was a major factor in real-life violence. That finding is not surprising, Bushman said, but it underscores one of the important implications of this study.
"With the general consensus about the harmful effects of media violence, it may seem surprising that some people still question the effects of violent media on aggression," Bushman said. "One important reason is that people don't distinguish between aggression and violence."
Violent acts are rare, he said, and are caused by many factors acting together.
"You cannot predict a shooting rampage just based on exposure to violent media or any other single factor," Bushman said.
But the evidence is clear, he said, that exposure to violent media can predict less-serious forms of aggression.
Bushman said other forces driving the continued public debate on violent media effects include: journalists reporting violent media research in a way that increases uncertainty; media industries having a vested interest in keeping the public uncertain about the link between violent media and aggression; the motivation of violent media consumers to deny they are affected; and a few media researchers who repeatedly claim that violent media do not increase aggression.
INFORMATION:
Written by Jeff Grabmeier
Imagine being able to tune the properties of a solid material just by flashing pulses of light on it, for example turning an insulator into a superconductor. That is just one potential payoff down-the-road from the physical phenomenon of electrons and atoms interacting with ultrashort pulses of light. The technology of ultrafast spectroscopy is a key to understanding this phenomenon and now a new wrinkle to that technology has been introduced by Berkeley Lab researchers.
In a study led by Alessandra Lanzara of Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division, time- and angle-resolved ...
Rabies causes acute inflammation of the brain, producing psychosis and violent aggression. The virus, which paralyzes the body's internal organs, is always deadly for those unable to obtain vaccines in time. Some 55,000 people die from rabies every year.
For the first time, Tel Aviv University scientists have discovered the exact mechanism this killer virus uses to efficiently enter the central nervous system, where it erupts in a toxic explosion of symptoms. The study, published in PLOS Pathogens, was conducted by Dr. Eran Perlson and Shani Gluska of TAU's Sackler Faculty ...
Obesity is a risk factor for many health problems, but a new Penn Medicine study published this month in the journal Sleep suggests having a larger tongue with increased levels of fat may be a sign of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in obese adults.
The researchers examined tongue fat in 31 obese adults who had OSA and 90 obese adults without the condition. All subjects underwent magnetic resonance imaging and the size and distribution of upper airway fat deposits in their tongue and upper airway muscles measured.
"Previous studies showed that the human tongue has a high ...
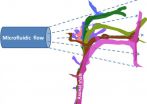
A University of Texas at Arlington team exploring how neuron growth can be controlled in the lab and, possibly, in the human body has published a new paper in Nature Scientific Reports on how fluid flow could play a significant role.
In a new study co-authored by Samarendra Mohanty, leader of the Biophysics and Physiology Lab in the College of Science, the researchers were able to use microfluidic stimulations to change the path of an axon at an angle of up to 90 degrees. Axons are the shafts of neurons, on the tips of which connections are made with other neurons or cells. ...
URBANA, Ill. – Hardly a day passes without pundits crying for leadership in the NFL commissioner and team owners, among high-ranking government officials, and in other public figures. If University of Illinois experts didn't have evidence that this valuable trait can be taught, they might join the collective swoon that's engulfing much of the country.
But a new U of I study supports the idea that leaders are made, not born, and that leadership development follows a specific progression.
Past research suggests that leadership is 30 percent genetic and 70 percent a result ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue researchers have identified a set of genes that can be used to naturally boost the provitamin A content of corn kernels, a finding that could help combat vitamin A deficiency in developing countries and macular degeneration in the elderly.
Professor of agronomy Torbert Rocheford and fellow researchers found gene variations that can be selected to change nutritionally poor white corn into biofortified orange corn with high levels of provitamin A carotenoids - substances that the human body can convert into vitamin A. Vitamin A plays key roles ...
NEW YORK (October 6, 2014) – Investigators at The Children's Hospital at Montefiore (CHAM) and Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University will present their latest research on neonatal lung disease, reducing wrong-patient errors in the NICU, hormonal contraception and more at the AAP Experience, the National Conference & Exhibition of the American Academy of Pediatrics. The AAP Experience will take place October 11-14 in San Diego, California.
Judy Aschner, M.D., F.A.A.P., physician-in-chief, CHAM, professor of pediatrics and Michael I. Cohen, M.D., University ...
Hamilton, ON (October 6, 2014) – A research study out of McMaster University has found that only 40 per cent of Canadians exercise to cope with stress.
The researchers analyzed data from Statistics Canada's Canadian Community Health Survey of nearly 40,000 Canadians 15 and older. Of 13 coping behaviours or strategies polled, exercise was ranked eighth, meaning people were more likely to cope with stress by problem-solving; looking on the bright side, trying to relax, talking to others, blaming oneself, ignoring stress or praying, rather than being active.
"We know ...
AUGUSTA, Ga. - The initial motivation was to estimate the age structure of a fruit fly population, the result a fundamental theorem that can help determine the age distribution of essentially any group.
This emerging theorem on stationary populations shows that you can determine the age distribution of a population by looking at how long they still have to live.
The mathematical discovery can help produce data with a wide range of implications, from predicting rates of infectious diseases, such as West Nile virus spread by mosquitoes, to anticipating the health care ...
WASHINGTON, Oct. 6, 2014— Melanoma is the fifth most common cancer type in the United States, and it's also the deadliest form of skin cancer, causing more than 75 percent of skin-cancer deaths. If caught early enough though, it is almost always curable. Now a camera, capable of taking snapshots of the entire human body and rendering high-resolution images of a patient's skin may help doctors spot cancer early and save lives.
Developed by a team of researchers at Duke University in North Carolina, USA, the "gigapixel whole-body photographic camera" is essentially three ...