(Press-News.org) LAWRENCE — Scientists have been laboring to detect cancer and a host of other diseases in people using promising new biomarkers called "exosomes." Indeed, Popular Science magazine named exosome-based cancer diagnostics one of the 20 breakthroughs that will shape the world this year. Exosomes could lead to less invasive, earlier detection of cancer, and sharply boost patients' odds of survival.
"Exosomes are minuscule membrane vesicles — or sacs — released from most, if not all, cell types, including cancer cells," said Yong Zeng, assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Kansas. "First described in the mid-'80s, they were once thought to be 'cell dust,' or trash bags containing unwanted cellular contents. However, in the past decade scientists realized that exosomes play important roles in many biological functions through capsuling and delivering molecular messages in the form of nucleic acids and proteins from the donor cells to affect the functions of nearby or distant cells. In other words, this forms a crucial pathway in which cells talk to others."
While the average piece of paper is about 100,000 nanometers thick, exosomes run just 30 to 150 nanometers in size. Because of this, exosomes are hard to separate out and test, requiring multiple-step ultracentrifugation — a tedious and inefficient process requires long stretches in the lab, according to scientists.
"There aren't many technologies out there that are suitable for efficient isolation and sensitive molecular profiling of exosomes," said Zeng. "First, current exosome isolation protocols are time-consuming and difficult to standardize. Second, conventional downstream analyses on collected exosomes are slow and require large samples, which is a key setback in clinical development of exosomal biomarkers."
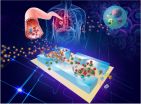
Now, Zeng and colleagues from the University of Kansas Medical Center and KU Cancer Center have just published a breakthrough paper in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal describing their invention of a miniaturized biomedical testing device for exosomes. Dubbed the "lab-on-a-chip," the device promises faster result times, reduced costs, minimal sample demands and better sensitivity of analysis when compared to the conventional bench-top instruments now used to examine the tiny biomarkers.
"A lab-on-a-chip shrinks the pipettes, test tubes and analysis instruments of a modern chemistry lab onto a microchip-sized wafer," Zeng said. "Also referred to as 'microfluidics' technology, it was inspired by revolutionary semiconductor electronics and has been under intensive development since the 1990s. Essentially, it allows precise manipulation of minuscule fluid volumes down to one trillionth of a liter or less to carry out multiple laboratory functions, such as sample purification, running of chemical and biological reactions, and analytical measurement."
Zeng and his fellow researchers have developed the lab-on-a-chip for early detection of lung cancer — the number-one cancer killer in the U.S. Today, lung cancer is detected mostly with an invasive biopsy, after tumors are larger than 3 centimeters in diameter and even metastatic, according to the KU researcher.
Using the lab-on-a-chip, lung cancer could be detected much earlier, using only a small drop of a patient's blood.
"Most lung cancers are first diagnosed based on symptoms, which indicate that the normal lung functions have been already damaged," Zeng said. "Unlike some cancer types such as breast or colon cancer, no widely accepted screening tool has been available for detecting early-stage lung cancers. Diagnosis of lung cancer requires removing a piece of tissue from the lung for molecular examination. Tumor biopsy is often impossible for early cancer diagnosis as the developing tumor is too small to see by the current imaging tools. In contrast, our blood-based test is minimally invasive, inexpensive, and more sensitive, thus suitable for large population screening to detect early-stage tumors."
Zeng said the prototype lab-on-a-chip is made of a widely used silicone rubber called polydimethylsiloxane and uses a technique called "on-chip immunoisolation."
"We used magnetic beads of 3 micrometers in diameter to pull down the exosomes in plasma samples," Zeng said. "In order to avoid other interfering species present in plasma, the bead surface was chemically modified with an antibody that recognizes and binds with a specific target protein — for example, a protein receptor — present on the exosome membrane. The plasma containing magnetic beads then flows through the microchannels on the diagnostic chip in which the beads can be readily collected using a magnet to extract circulating exosomes from the plasma."
Beyond lung cancer, Zeng said the lab-on-a-chip could be used to detect a range of potentially deadly forms of cancer.
"Our technique provides a general platform to detecting tumor-derived exosomes for cancer diagnosis," he said. "In addition to lung cancer, we've also tested for ovarian cancer in this work. In theory, it should be applicable to other types of cancer. Our long-term goal is to translate this technology into clinical investigation of the pathological implication of exosomes in tumor development. Such knowledge would help develop better predictive biomarkers and more efficient targeted therapy to improve the clinical outcome."
INFORMATION:
The research by Zeng and his KU colleagues recently merited a $640,000 grant from the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health, intended to further develop the lab-on-a-chip technology.
You're obese, at risk for diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and so motivated to improve your diet that you've enrolled in an intensive behavioral program. But if you need to travel more than a short distance to a store that offers a good selection of healthy food, your success may be limited.
A new study from UMass Medical School and the Massachusetts Department of Public Health finds that not having close access to healthy foods can deter even the most motivated dieters from improving their diet, suggesting that easy access to healthy food is as important as personal ...
Imagine attempting to trace your genetic history using only information from your mother's side. That's what scientists studying the evolution of the red fox had been doing for decades.
Now, University of California, Davis, researchers have for the first time investigated ancestry across the red fox genome, including the Y chromosome, or paternal line. The data, compiled for over 1,000 individuals from all over the world, expose some surprises about the origins, journey and evolution of the red fox, the world's most widely distributed land carnivore.
"The genome and ...
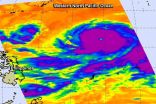
Typhoon Vongfong strengthened into a Super typhoon on Tuesday, October 7 as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead.
On Oct. 7 at 0429 UTC (12:29 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data on Super typhoon Vongfong. AIRS data very strong thunderstorms circling Vongfong's clear 27 nautical-mile wide eye. Those cloud top temperatures were colder than -62F/-53C indicating that they were high in the troposphere and capable of generating heavy rainfall. The bands of thunderstorms circling ...
New Swedish research shows that plasmids containing genes that confer resistance to antibiotics can be enriched by very low concentrations of antibiotics and heavy metals. These results strengthen the suspicion that the antibiotic residues and heavy metals (such as arsenic, silver and copper) that are spread in the environment are contributing to the problems of resistance. These findings have now been published in the highly regarded journal mBio.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing medical problem that threatens human health worldwide. Why and how these resistant bacteria ...
PHILADELPHIA — Nearly 60,000 Americans suffer from myasthenia gravis (MG), a non-inherited autoimmune form of muscle weakness. The disease has no cure, and the primary treatments are nonspecific immunosuppressants and inhibitors of the enzyme cholinesterase.
Now, a pair of researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have developed a fast-acting "vaccine" that can reverse the course of the disease in rats, and, they hope, in humans. Jon Lindstrom, PhD, a Trustee Professor in the department of Neuroscience led the study, published ...
A new review of the way health care professionals emphasise weight to define health and wellbeing suggests the approach could be harmful to patients.
Author of the review article, Dr Rachel Calogero of the School of Psychology at the University of Kent, together with experts from other institutions and organisations, recommends that this approach, known as 'weight-normative', is replaced by health care professionals, public health officials and policy-makers with a 'weight-inclusive' approach.
Weight-inclusive approaches, such as the Health At Every Size initiative, ...
Hamilton, ON (October 7, 2014) – Hospital visitors and staff are greeted with hand sanitizer dispensers in the lobby, by the elevators and outside rooms as reminders to wash their hands to stop infections, but just how clean are patients' hands?
A study led by McMaster University researcher Dr. Jocelyn Srigley has found that hospitalized patients wash their hands infrequently. They wash about 30 per cent of the time while in the washroom, 40 per cent during meal times, and only three per cent of the time when using the kitchens on their units. Hand hygiene rates ...
LONDON, ON – New research shows probiotic yogurt can reduce the uptake of certain heavy metals and environmental toxins by up to 78% in pregnant women. Led by Scientists at Lawson Health Research Institute's Canadian Centre for Human Microbiome and Probiotic Research, this study provides the first clinical evidence that a probiotic yogurt can be used to reduce the deadly health risks associated with mercury and arsenic.
Environmental toxins like mercury and arsenic are commonly found in drinking water and food products, especially fish. These contaminants are particularly ...
Two years ago, Prof. Eshel Ben-Jacob of Tel Aviv University's School of Physics and Astronomy and Rice University's Center for Theoretical Biological Physics made the startling discovery that cancer, like an enemy hacker in cyberspace, targets the body's communication network to inflict widespread damage on the entire system. Cancer, he found, possessed special traits for cooperative behavior and used intricate communication to distribute tasks, share resources, and make decisions.
In research published in the Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of ...
NOAA's GOES-West satellite took a picture of Tropical Storm Simon weakening over Mexico's Baja California.
On Oct. 7, a Tropical Storm Watch was in effect for Punta Abreojos to Punta Eugenia, Mexico. The National Hurricane Center expects Simon to produce storm total rainfall amounts of 3 to 5 inches with isolated amounts around 8 inches through Wednesday, Oct. 8, across northern portions of the Baja California Peninsula and the state of Sonora in northwestern Mexico. Over the next few days, storm total rainfall amounts of 1 to 2 inches with isolated amounts of around ...