(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) have managed to generate a fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) model that reproduces human colon cancer. With two publications appearing in PLoS One and EMBO Reports, the IRB team also unveil the function of a key gene in the development of the disease.
"The breakthrough is that we have generated cancer in an adult organism and from stem cells, thus reproducing what happens in most types of human cancer. This model has allowed us to identify subtle interactions in the development of cancer that are practically impossible to detect in mice with the current technology available," explains the biologist Andreu Casali, Associate Researcher at IRB Barcelona and leader of the Drosophila project.
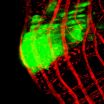
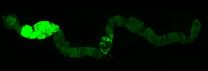
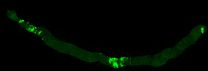
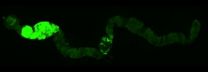
Although the flies do not have a colon, they have an intestine that includes a colon and rectum and that works in the same way as the human colon. The scientists generated mutant flies for two genes that are altered in most human colon tumours, namely APC and Ras. Thanks to the ease with which genetic studies can be performed in Drosophila, the researchers were able to examine the effect of 250 genes that are altered in these types of tumour and found that, of these, 30% affected growth while the others had no significant effects.
"The advantage of the model is that it allows us to explore genetic alterations more quickly, to distinguish between those that are important and those that are not, and to see what role they play," explains Òscar Martorell, first author of the paper that appears in EMBO Reports published today. "Performing these genetic experiments in mice is time-consuming and costly and the Drosophila model allows us to rapidly analyse new pathways that could be relevant for colon cancer," adds the co-author of the study, Francisco Barriga, a postdoctoral fellow working on colon cancer in vertebrate models. Undertaken over five years, the study is the result of collaboration between the Development and Morphogenesis in Drosophila Lab and the Colorectal Cancer Lab, both at IRB Barcelona.
Of all the genes that have a relevant function, the group focused on one called Mirror in Drosophila and lrx in humans. The experiments with flies led to the finding that this gene favours tumour growth in early stages of human cancer. "The problem with human cancer is that we know very little about what happens in the early stages. Our models allows us to better study its development." Also, Casali goes on to speculate that the human gene lrx may become a good drug target "for example, to prevent benign adenomas from developing further." However, first the validity of the gene as a therapeutic target has to be tested in mice.
A good in vivo guinea pig for drugs
The researchers also expound that flies can be used to study candidate drug molecules to combat cancer. Drosophila would serve as an intermediate step between the in vitro phase and testing in vertebrates. On the one hand, this model has the in vitro advantages because many molecules can be tested at a minimum dose, and on the other, it shares the advantage of animals models because, as it is a living organism, toxic molecules or those with poor absorption could be omitted very quickly.
"If there are 2000 promising molecules among a million tested in vitro, instead of testing them in mice, Drosophila could offer a good alternative to identify the two or three that are most appropriate. Both time and costs would be reduced," explains Casali.
With this aim, Casali has start collaborating with the group headed by Ernest Giralt (IRB Barcelona)—an authority on pharmacological chemistry and peptide design—to use flies to test new families of molecules against cancer.
INFORMATION:
Reference articles:
Iro/Irx transcription factors negatively regulate Dpp/TGF-b pathway activity during intestinal tumorigenesis
Òscar Martorell, Francisco M. Barriga, Anna Merlos-Suárez, Camille Stephan-Otto Attolini, Jordi Casanova, Eduard Batlle, Elena Sancho and Andreu Casali
EMBO Reports (2014 Oct 8). 10.15252/embr.201438622
Conserved mechanisms of tumorigenesis in the Drosophila adult midgut
Òscar Martorell, Anna Merlos-Suárez, Kyra Campbell, Francisco M. Barriga, Christo P. Christov,
Irene Miguel-Aliaga, Eduard Batlle, Jordi Casanova, Andreu Casali
PLoS One (2014 Feb) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088413
Flies with colon cancer help to unravel the genetic keys to disease in humans
Researchers generate for the first time Drosophila melanogaster with intestinal cancer and reveal key genetic factors behind human colon cancer
2014-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fruit flies reveal features of human intestinal cancer
2014-10-08
HEIDELBERG, 8 October 2014 – Researchers in Spain have determined how a transcription factor known as Mirror regulates tumour-like growth in the intestines of fruit flies. The scientists believe a related system may be at work in humans during the progression of colorectal cancer due to the observation of similar genes and genetic interactions in cultured colorectal cancer cells. The results are reported in the journal EMBO Reports.
Colorectal cancer leads to more than half a million deaths worldwide each year. The disease originates in the epithelial cells of the ...
Supervisors' abuse, regardless of intent, can make employees behave poorly
2014-10-08
SAN FRANCISCO, Oct. 8, 2014 -- Employees who are verbally abused by supervisors are more likely to "act out" at work, doing everything from taking a too-long lunch break to stealing, according to a new study led by a San Francisco State University organizational psychologist.
Even if the abuse is meant to be motivational -- like when a football coach berates his team or a drill sergeant shames her cadets -- the abused employees are still more likely to engage in counter-productive work behaviors, said Kevin Eschleman, assistant professor of psychology at SF State.
The ...
Large chain restaurants appear to be voluntarily reducing calories in their menu items
2014-10-08
New research from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health finds that large chain restaurants, whose core menu offerings are generally high in calories, fat and sodium, introduced newer food and beverage options that, on average, contain 60 fewer calories than their traditional menu selections in 2012 and 2013.
Researchers say this could herald a trend in calorie reduction in anticipation of expected new federal government rules requiring large chain restaurants – including most fast-food places – to post calorie counts on their menus. The appearance ...
Universal screening for MRSA may be too costly
2014-10-08
PHILADELPHIA – (Oct. 8, 2014) – Numerous experts and policy makers have called for hospitals to screen patients for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections and isolate anyone testing positive to prevent the spread of these so-called "Superbugs" in healthcare settings. Several states have enacted laws requiring patients be screened for MRSA upon admission.
Two new abstracts, scheduled for presentation on Friday at IDWeek, the annual scientific meeting for infectious disease specialists, found universal MRSA screening and isolation of ...
Childhood eating difficulties could be a sign of underlying psychological issues
2014-10-08
This news release is available in French. Researchers at the University of Montreal and its affiliated CHU Sainte-Justine children's hospital are warning parents that difficult eaters could have underlying psychological issues, as they have found that restrictive behaviours can appear before puberty. "Many researchers believe that bulimia only appears at adolescence, but our studies indicate that the problem can arises much earlier. It is possible that it is currently under-diagnosed due to a lack of awareness and investigation," explained clinical psychologist and ...
How dinosaurs divided their meals at the Jurassic dinner table
2014-10-08
How the largest animals to have ever walked the Earth fed, and how this allowed them to live alongside one another in prehistoric ecosystems is the subject of new research from the University of Bristol and the Natural History Museum, London.
The sauropods – large, long-necked plant-eating dinosaurs such as Diplodocus and Brachiosaurus – dominated the land between 210 and 65 million years ago. They were the largest land animals of all time, with the biggest weighing 80 tonnes (more than 11 elephants) and would have needed vast amounts of food.
Despite ...
The Lancet Psychiatry: Schools key to reaching the 1 in 10 children with mental health problems
2014-10-08
Schools are a vital way of reaching the 10–20% of children and young people across the globe who would benefit from some sort of mental health intervention, according to a new Series on mental health interventions in schools published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
The Series highlights that childhood is an important window for intervention because around 75% of adults who access mental health services have had a diagnosable disorder before the age of 18 [1]. What is more, estimates from high-income countries (HICs) indicate that only 25% of children with a mental health ...
Working memory hinders learning in schizophrenia
2014-10-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study pinpoints working memory as a source of learning difficulties in people with schizophrenia.
Working memory is known to be affected in the millions of people – about 1 percent of the population – who have schizophrenia, but it has been unclear whether that has a specific role in making learning more difficult, said study lead author and Brown University postdoctoral researcher Anne Collins.
"We really tend to think of learning as a unitary, single process, but really it is not," said Collins, who along ...
NIST quantum probe enhances electric field measurements
2014-10-08
VIDEO:
This is an animation of NIST's new method for measuring electric field strength based on the quantum properties of atoms. The technique works for abroad range of frequencies, 1-500 gigahertz,...
Click here for more information.
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Michigan have demonstrated a technique based on the quantum properties of atoms that directly links measurements of electric field strength to the International ...
Researchers pump up oil accumulation in plant leaves
2014-10-07
UPTON, NY - Increasing the oil content of plant biomass could help fulfill the nation's increasing demand for renewable energy feedstocks. But many of the details of how plant leaves make and break down oils have remained a mystery. Now a series of detailed genetic studies conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and published in The Plant Cell reveals previously unknown biochemical details about those metabolic pathways-including new ways to increase the accumulation of oil in leaves, an abundant source of biomass for fuel production.
Using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Flies with colon cancer help to unravel the genetic keys to disease in humansResearchers generate for the first time Drosophila melanogaster with intestinal cancer and reveal key genetic factors behind human colon cancer