Fine-tuning of bitter taste receptors may be key to animal survival
This week in Molecular Biology and Evolution
2014-10-08
(Press-News.org) One key to animal survival is bitter taste----the better to avoid ingesting potentially harmful poisons or foods. The evolution of bitter taste has been a hot topic amongst evolutionary biologists, and with more and more DNA data available, a rich area of exploration.
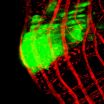
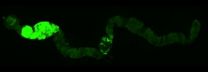
Now, professor Maik Behrens, et. al. examined the genetic repertoire of bitter taste receptor genes in chickens and frogs, which represent two extremes. Chickens only have 3 bitter taste receptor genes (Tas2rs), while frogs have more than 50 (humans are somewhere in the middle). They studied the different molecular properties of cloned Tas2r genes and measured their responses when exposed to a panel of 46 natural or synthetic bitter compounds.
First, they constructed a gene tree for a selection of Tas2r genes of various vertebrate species and showed that all avian genes come from the same 3 ancestral genes. Frogs were found to have 5 ancestral genes, indicating that their expanded repertoire was due to later gene duplication events.
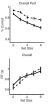
They showed that all the three chicken Tas2rs are "broadly tuned" for bitter taste, whereas six frog Tas2rs tested are mixed consisting of broadly as well as narrowly tuned receptors. Interestingly, both chicken and frog receptor repertoires responded to about half of the compounds, showing that the tuning range rather the number of Tas2r genes was a critical factor. In general, individual substances activated different receptors in clearly separated concentration ranges, which may also provide a clue to the role of bitter taste diversity in enhancing the chance of survival.
The authors conclude that a low number of functional Tas2r genes found in chickens can be compensated by an increased average tuning width. They speculate that the environmental duality of amphibian life, living on both land and water, may account for the increased Tas2r gene diversity in frogs. In mixed aquatic and terrestrial environments amphibians such as frogs may have encountered a larger number of bitter compounds, causing the evolutionary pressure to provide a larger taste receptor repertoire.
The findings appear in the advanced online edition of Molecular Biology and Evolution.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-08
This news release is available in French. The association between saturated fat and cardiovascular risk has become a hot topic in nutrition. Researchers at the Institute of nutrition and functional foods (INAF) of Université Laval are calling for a review of dietary recommendations on saturated fat (SFA) in relation to cardiovascular disease (CVD).
In a Comment paper, published today in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism the authors provide a number of arguments for the urgency to re-assess the association between dietary saturated fat ...
2014-10-08
Researchers at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) have managed to generate a fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) model that reproduces human colon cancer. With two publications appearing in PLoS One and EMBO Reports, the IRB team also unveil the function of a key gene in the development of the disease.
"The breakthrough is that we have generated cancer in an adult organism and from stem cells, thus reproducing what happens in most types of human cancer. This model has allowed us to identify subtle interactions in the development of cancer that are ...
2014-10-08
HEIDELBERG, 8 October 2014 – Researchers in Spain have determined how a transcription factor known as Mirror regulates tumour-like growth in the intestines of fruit flies. The scientists believe a related system may be at work in humans during the progression of colorectal cancer due to the observation of similar genes and genetic interactions in cultured colorectal cancer cells. The results are reported in the journal EMBO Reports.
Colorectal cancer leads to more than half a million deaths worldwide each year. The disease originates in the epithelial cells of the ...
2014-10-08
SAN FRANCISCO, Oct. 8, 2014 -- Employees who are verbally abused by supervisors are more likely to "act out" at work, doing everything from taking a too-long lunch break to stealing, according to a new study led by a San Francisco State University organizational psychologist.
Even if the abuse is meant to be motivational -- like when a football coach berates his team or a drill sergeant shames her cadets -- the abused employees are still more likely to engage in counter-productive work behaviors, said Kevin Eschleman, assistant professor of psychology at SF State.
The ...
2014-10-08
New research from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health finds that large chain restaurants, whose core menu offerings are generally high in calories, fat and sodium, introduced newer food and beverage options that, on average, contain 60 fewer calories than their traditional menu selections in 2012 and 2013.
Researchers say this could herald a trend in calorie reduction in anticipation of expected new federal government rules requiring large chain restaurants – including most fast-food places – to post calorie counts on their menus. The appearance ...
2014-10-08
PHILADELPHIA – (Oct. 8, 2014) – Numerous experts and policy makers have called for hospitals to screen patients for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections and isolate anyone testing positive to prevent the spread of these so-called "Superbugs" in healthcare settings. Several states have enacted laws requiring patients be screened for MRSA upon admission.
Two new abstracts, scheduled for presentation on Friday at IDWeek, the annual scientific meeting for infectious disease specialists, found universal MRSA screening and isolation of ...
2014-10-08
This news release is available in French. Researchers at the University of Montreal and its affiliated CHU Sainte-Justine children's hospital are warning parents that difficult eaters could have underlying psychological issues, as they have found that restrictive behaviours can appear before puberty. "Many researchers believe that bulimia only appears at adolescence, but our studies indicate that the problem can arises much earlier. It is possible that it is currently under-diagnosed due to a lack of awareness and investigation," explained clinical psychologist and ...
2014-10-08
How the largest animals to have ever walked the Earth fed, and how this allowed them to live alongside one another in prehistoric ecosystems is the subject of new research from the University of Bristol and the Natural History Museum, London.
The sauropods – large, long-necked plant-eating dinosaurs such as Diplodocus and Brachiosaurus – dominated the land between 210 and 65 million years ago. They were the largest land animals of all time, with the biggest weighing 80 tonnes (more than 11 elephants) and would have needed vast amounts of food.
Despite ...
2014-10-08
Schools are a vital way of reaching the 10–20% of children and young people across the globe who would benefit from some sort of mental health intervention, according to a new Series on mental health interventions in schools published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
The Series highlights that childhood is an important window for intervention because around 75% of adults who access mental health services have had a diagnosable disorder before the age of 18 [1]. What is more, estimates from high-income countries (HICs) indicate that only 25% of children with a mental health ...
2014-10-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study pinpoints working memory as a source of learning difficulties in people with schizophrenia.
Working memory is known to be affected in the millions of people – about 1 percent of the population – who have schizophrenia, but it has been unclear whether that has a specific role in making learning more difficult, said study lead author and Brown University postdoctoral researcher Anne Collins.
"We really tend to think of learning as a unitary, single process, but really it is not," said Collins, who along ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fine-tuning of bitter taste receptors may be key to animal survival
This week in Molecular Biology and Evolution