(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR—An unexpectedly high amount of the climate-changing gas methane, the main component of natural gas, is escaping from the Four Corners region in the U.S. Southwest, according to a new study by the University of Michigan and NASA.
The researchers mapped satellite data to uncover the nation's largest methane signal seen from space. They measured levels of the gas emitted from all sources, and found more than half a teragram per year coming from the area where Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado and Utah meet. That's about as much methane as the entire coal, oil, and gas industries of the United Kingdom give off each year.
Four Corners sits on North America's most productive coalbed methane basin. Coalbed methane is a variety of the gas that's stuck to the surface of coal. It is dangerous to miners (not to mention canaries), but in recent decades, it's been tapped as a resource.
"There's so much coalbed methane in the Four Corners area, it doesn't need to be that crazy of a leak rate to produce the emissions that we see. A lot of the infrastructure is likely contributing," said Eric Kort, assistant professor of atmospheric, oceanic and space sciences at the U-M College of Engineering.
Kort, first author of a paper on the findings published in Geophysical Research Letters, says the controversial natural gas extraction technique of hydraulic fracturing is not the main culprit.
"We see this large signal and it's persistent since 2003," Kort said. "That's a pre- fracking timeframe in this region. While fracking has become a focal point in conversations about methane emissions, it certainly appears from this and other studies that in the U.S., fossil fuel extraction activities across the board likely emit higher than inventory estimates."
While the signal represents the highest concentration of methane seen from space, the researchers caution that Four Corners isn't necessarily the highest emitting region.
"One has to be somewhat careful in equating abundances with emissions," said study contributor Christian Frankenberg at Jet Propulsion Laboratory. "The Four Corners methane source is in a relatively isolated area with little other methane emissions, hence causing a well distinguishable hot-spot in methane abundances. Local or more diffuse emissions in other areas, such as the eastern U.S., may be convoluted with other nearby sources."
Natural gas is often touted as more sustainable than coal and oil because it releases fewer pollutants when it burns. But when it leaks into the air before it gets to the pilot light, methane has 30 times the short-term heat-trapping effects of carbon dioxide. Policymakers, energy companies and environmentalists alike are aiming to reduce methane emissions as a way to curb climate change. But pinpointing plumes—a first step to stopping them—has been a difficult task with today's tools.
The research team demonstrated a new approach to finding leaks. They used a satellite instrument—the European Space Agency's SCIAMACHY—to get regional methane measurements over the entire United States. They ran the data through a mathematical model to account for mountains and valleys, which can trap methane. That's how they identified the anomaly at Four Corners. Then they zoomed in on that region and ran another mathematical model to control for wind, to make sure that didn't negate the original signal. It didn't.
"We didn't know this was a region we should look at. We found it from space," Kort said. "We've demonstrated that satellite measurements can help identify, locate and quantify anomalous methane emissions in regions that are unexpected."
Methane gets into the atmosphere from both natural and human-made sources. Wetlands and landfills release it, as do certain bacteria. Agriculture is a big contributor. So are gas and oil drilling and distribution. Inventories such as those the EPA compiles make estimates based on measurements from a sampling of these sources. In previous work, air measurements from planes and a sparse network of monitoring towers have revealed that the inventory-based numbers are coming in low—roughly 50 percent low. But towers and planes can't see everywhere to figure out exactly where all the methane is coming from. With limited observations there can be blind spots, the researchers say.
This study used satellite data from 2003 to 2009. In later years, they were able to validate the satellite measurements with a year of ground-based data.
SCIAMACHY is no longer operating, so there aren't equivalent satellites to provide this information for other parts of the world. For the Four Corners region, Kort will be taking readings from an airplane next year, to get even closer to identifying the leaks.
INFORMATION:
The study is titled "Four Corners: the largest US methane anomaly viewed from space." The research was funded by NASA and Los Alamos National Lab.
Eric Kort: http://aoss.engin.umich.edu/people/eakort
Abstract: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2014GL061503/abstract
An international research team comprised of German, Israeli and American ecologists, including Dr. Claus Holzapfel, Dept. of Biological Sciences, Rutgers University-Newark, has conducted unique long-term experiments in Israel to test predictions of climate change, and has concluded that plant communities in the Holy Land can cope with climate change of "biblical" dimensions. Their findings appear in the current issue of Nature Communications at http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2014/141006/ncomms6102/pdf/ncomms6102.pdf.
When taking global climate change into account, many ...
A team of scientists using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has made the most detailed global map yet of the glow from a turbulent planet outside our solar system, revealing its secrets of air temperatures and water vapor.
Hubble observations show the exoplanet, called WASP-43b, is no place to call home. It is a world of extremes, where seething winds howl at the speed of sound from a 3,000-degree-Fahrenheit "day" side, hot enough to melt steel, to a pitch-black "night" side with plunging temperatures below 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit.
Astronomers have mapped the temperatures ...
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have unveiled a new method to form tiny 3D metal nanoparticles in prescribed shapes and dimensions using DNA, Nature's building block, as a construction mold.
The ability to mold inorganic nanoparticles out of materials such as gold and silver in precisely designed 3D shapes is a significant breakthrough that has the potential to advance laser technology, microscopy, solar cells, electronics, environmental testing, disease detection and more.
"We built tiny foundries made ...
MADISON, Wis. – In Wisconsin, bioenergy is for the birds. Really.
In a study published today in the journal PLOS ONE, University of Wisconsin-Madison and Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) scientists examined whether corn and perennial grassland fields in southern Wisconsin could provide both biomass for bioenergy production and bountiful bird habitat.
The research team found that where there are grasslands, there are birds. Grass-and-wildflower-dominated fields supported more than three times as many bird species as cornfields, including 10 imperiled ...
Three new species of leafhoppers from China in the genus Futasujinus were recently identified during a review of leafhoppers in museum collections in China, the UK, and Illinois. One of them, Futasujinus dietrichi, was "named after Dr. Chris Dietrich, University of Illinois, USA, in recognition of his good work on leafhoppers." The new species are described in an article in Annals of the Entomological Society of America.
The other two species are Futasujinus truncatus and Futasujinus hastatus. Both species epithets allude to processes on their aedeagal shafts.
All three ...
Tempe, Ariz. (Oct. 9, 2014) - New Ebola research demonstrates that quick and forceful implementation of control interventions are necessary to control outbreaks and avoid far worse scenarios.
Researchers analyzed up-to-date epidemiological data of Ebola cases in Nigeria as of Oct. 1, 2014, in order to estimate the case fatality rate, proportion of health care workers infected, transmission progression and impact of control interventions on the size of the epidemic.
"Rapid and forceful control measures are necessary as is demonstrated by the Nigerian success story. This ...
A Greek and international team of divers and archaeologists has retrieved stunning new finds from an ancient Greek ship that sank more than 2,000 years ago off the remote island of Antikythera. The rescued antiquities include tableware, ship components, and a giant bronze spear that would have belonged to a life-sized warrior statue.
The Antikythera wreck was first discovered in 1900 by sponge divers who were blown off course by a storm. They subsequently recovered a spectacular haul of ancient treasure including bronze and marble statues, jewellery, furniture, luxury ...
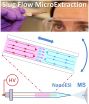
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new technique makes it possible to quickly detect the presence of drugs or to monitor certain medical conditions using only a single drop of blood or urine, representing a potential tool for clinicians and law enforcement.
The technique works by extracting minute quantities of target molecules contained in specimens of blood, urine or other biological fluids, and then testing the sample with a mass spectrometer.
Testing carried out with the technology takes minutes, whereas conventional laboratory methods take hours or days to yield results ...
SAN FRANCISCO -- The information that interprets the genetic code in a new embryo differs depending on whether it comes from the father or mother, researchers at San Francisco State University have found.
The research, detailed in an article published today in the journal PLOS Genetics, sheds light on the multilayered process of how a sperm and egg pass along information needed for successful reproduction. Though one layer is the DNA code that is transferred, the new study identifies information not encoded by DNA, a so-called "epigenetic" layer of information that helps ...
Most women are infected with HIV through vaginal intercourse, and without effective vaccines or microbicides, women who cannot negotiate condom use by their partners remain vulnerable. How exactly the virus establishes infection in the female reproductive tract (FRT) remains poorly understood. A study published on October 9th in PLOS Pathogens reports surprising results from a study of HIV transmission in the FRT of rhesus macaques.
Most studies of HIV transmission after vaginal exposure to date have been done in rhesus macaques and focused on the cervix, the lower part ...