(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC – OCTOBER 10, 2014 - A robust, broad spectrum antibiotic, and a gene that confers immunity to that antibiotic are both found in the bacterium Staphylococcus epidermidis Strain 115. The antibiotic, a member of the thiopeptide family of antibiotics, is not in widespread use, partly due to its complex structure, but the investigators, from Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, now report that the mechanism of synthesis is surprisingly simple. "We hope to come up with innovative processes for large-scale production and derivitization so that new, and possibly more potent versions of the antibiotic can become available, says co-corresponding author Joel S. Griffitts. The research is published ahead of print in Journal of Bacteriology.
Strain 115 was originally discovered on turkeys that appeared to have enhanced immunity to bacterial infections. "The motivation behind our current work was a desire to understand the connection between Strain 115 and immunity to disease-causing bacteria," says Griffitts.
It quickly became clear to the investigators that Strain 115 could produce a potent antibiotic that targets a large number of medically relevant bacteria, including those that cause staph infections, strep throat, and severe gastrointestinal diseases. "We wanted to know the identity of this antibiotic and the means by which Strain 115 protects itself from its own antibiotic's deadly effects," says Griffitts.
"We found that the genes for both antibiotic synthesis and self protection in Strain 115 are conveniently clustered on a compact DNA molecule [a plasmid] that replicates itself as a small circle within the cells of Strain 115," says Griffitts. Among experiments they conducted to prove this, they engineered a version of Strain 115 that was missing the plasmid. That version failed to produce both the antibiotic and the immunity to the antibiotic.
The investigators then analyzed the mechanism of immunity. "Thiopeptide antibiotics kill cells by blocking a part of the ribosome," Griffitts explains. Ribosomes, common to all living organisms, are the machines that read the genetic code, producing proteins based on the instructions therein. The plasmid, which directs the production of the thiopeptide antibiotic, also directs production of a spare part for the ribosome, a replacement for the part that is blocked by the antibiotic, which renders the ribosome insensitive to the antibiotic.
The investigation of Strain 115 began as an undergraduate project, after the bacteria had sat in a laboratory freezer for decades, says Griffitts. "It quickly grew into an effort involving two Ph.D. microbiologists, a talented graduate student, and several analytical biochemists." Hopefully, he says, the research will ultimately enable production of a valuable antibiotic, in quantities sufficient to make a dent in the antibiotic crisis.
INFORMATION:
The article will be published ahead of print on Monday, October 13. Please email ghogan@asmusa.org for a copy of the manuscript.
Journal of Bacteriology is a publication of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM). The ASM is the largest single life science society, composed of over 39,000 scientists and health professionals. Its mission is to advance the microbiological sciences as a vehicle for understanding life processes and to apply and communicate this knowledge for the improvement of health and environmental and economic well-being worldwide.
Developing the cloak of invisibility would be wonderful, but sometimes simply making an object appear to be something else will do the trick, according to Penn State electrical engineers.
"Previous attempts at cloaking using a single metasurface layer were restricted to very small-sized objects," said Zhi Hao Jiang, postdoctoral fellow in electrical engineering, Penn State. "Also, the act of cloaking would prevent an enclosed antenna or sensor from communicating with the outside world."
Jiang and Douglas H. Werner, John L. and Genevieve H. McCain Chair Professor of ...
Stanford University scientists have developed a "smart" lithium-ion battery that gives ample warning before it overheats and bursts into flames.
The new technology is designed for conventional lithium-ion batteries now used in billions of cellphones, laptops and other electronic devices, as well as a growing number of cars and airplanes.
"Our goal is to create an early-warning system that saves lives and property," said Yi Cui, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford. "The system can detect problems that occur during the normal operation ...
SAN DIEGO – When the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) published its policy statement in 1999 discouraging electronic media use by children under 2, the focus was on television programs, videos and DVDs.
Over the past 15 years, the technology landscape has changed dramatically. Toddlers now have access to a dizzying array of touchscreen devices that are available anywhere and everywhere. Although the AAP has revised its media use policy over the years based on the latest research, the message regarding toddlers' exposure to screens is the same.
Given the ...
WASHINGTON (Oct. 13, 2014) — Men and women have different cardiovascular and psychological reactions to mental stress, according to a study of men and women who were already being treated for heart disease. The study, published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, looked at 56 women and 254 men diagnosed with heart disease enrolled in a larger REMIT study of the impact of the medication escitalopram on heart disease induced by mental stress.
After undergoing baseline testing, participants carried out three mentally stressful tasks — ...
Five of the most high-risk freshwater invaders from the Ponto-Caspian region around Turkey and Ukraine are now in Britain - including the quagga mussel, confirmed just two weeks ago on 1 October in the Wraysbury River near Heathrow airport.
Researchers say that, with at least ten more of these high-risk species established just across the channel in Dutch ports, Britain could be on the brink of what they describe as an 'invasional meltdown': as positive interactions between invading species cause booming populations that colonise ecosystems - with devastating consequences ...
SAN DIEGO – Former Secretary of State Hillary Rodham Clinton will discuss the role that pediatricians and parents can play in promoting young children's early learning during her remarks on Sunday Oct. 12 at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition in San Diego. Secretary Clinton will announce the launch of the Academy's updated early literacy toolkit for pediatricians and parents, Books Build Connections, which will be shared with its 62,000 pediatrician members immediately following Secretary Clinton's remarks.
In June 2014, the ...
Spintronics is an emerging field of technology where devices work by manipulating the spin of electrons rather than their charge. The field can bring significant advantages to computer technology, combining higher speeds with lower energy consumption. Spintronic circuits need ways to control electron spin without interference from electron charge. Scientists at EPFL, working with Université Paris-Sud and Paul Scherrer Institut, have discovered that a common insulating material behaves as a perfect spintronic conductor because it is not affected by background electron ...
An innovative laboratory culture system has succeeded, for the first time, in reproducing the full course of events underlying the development of Alzheimer's disease. Using the system they developed, investigators from the Genetics and Aging Research Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) now provide the first clear evidence supporting the hypothesis that deposition of beta-amyloid plaques in the brain is the first step in a cascade leading to the devastating neurodegenerative disease. They also identify the essential role in that process of an enzyme, inhibition ...
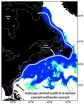
AMHERST, Mass. – Using a first-of-its-kind, high-resolution numerical model to describe ocean circulation during the last ice age about 21,000 year ago, oceanographer Alan Condron of the University of Massachusetts Amherst has shown that icebergs and meltwater from the North American ice sheet would have regularly reached South Carolina and even southern Florida. The models are supported by the discovery of iceberg scour marks on the sea floor along the entire continental shelf.
Such a view of past meltwater and iceberg movement implies that the mechanisms of abrupt ...
VIDEO:
Researchers have developed a technique to jump-start the body's systems for creating blood vessels, opening the door for potential new treatments for diseases whose impacts include amputation and blindness....
Click here for more information.
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers have developed a technique to jump-start the body's systems for creating blood vessels, opening the door for potential new treatments for diseases whose impacts include amputation and blindness.
The ...