(Press-News.org) Parkinson's disease is strongly linked to the degeneration of the brain's movement center. In the last decade, the question of where the disease begins has led researchers to a different part of the human anatomy. In 2003, the German neuropathologist Heiko Braak presented a theory suggesting that the disease begins in the gut and spreads to the brain. The idea has since, despite vocal critics, gained a lot of ground. Researchers at Lund University in Sweden now present the first direct evidence that the disease can actually migrate from the gut to the brain.
The so-called Braak's hypothesis proposes that the disease process begins in the digestive tract and in the brain's center of smell. The theory is supported by the fact that symptoms associated with digestion and smell occur very early on in the disease.
Researchers at Lund University have previously mapped the spread of Parkinson's in the brain. The disease progression is believed to be driven by a misfolded protein that clumps together and "infects" neighboring cells. Professor Jia-Yi Li's research team has now been able to track this process further, from the gut to the brain in rat models. The experiment shows how the toxic protein, alpha-synuclein, is transported from one cell to another before ultimately reaching the brain's movement center, giving rise to the characteristic movement disorders in Parkinson's disease.
"We have now been able to prove that the disease process actually can travel from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system, in this case from the wall of the gut to the brain. In the longer term, this may give us new therapeutic targets to try to slow or stop the disease at an earlier stage", says Professor Jia-Yi Li, research group leader for Neural Plasticity and Repair at Lund University.
The research team will now carry out further studies in which the mechanisms behind the transport of the harmful protein will be examined in detail. The current study suggests that the protein is transferred during nerve cell communication. It is at this point of interaction that the researchers want to intervene in order to put a stop to the further spread of the disease.
INFORMATION:
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00401-014-1343-6 END
Disputed theory on Parkinson's origin strengthened
2014-10-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Magnetic superconductor: Strange bedfellows
2014-10-14
Chemists at Ludwig-Maximilias-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have synthesized a ferromagnetic superconducting compound that is amenable to chemical modification, opening the route to detailed studies of this rare combination of physical properties.
Superconductivity and ferromagnetism – the "normal" form of magnetism, such as that found in the familiar horseshoe magnet – are like chalk and cheese: They generally don't go together. Ferromagnets are magnetic because the parallel alignment of adjacent electron spins in the iron atoms generates a strong internal ...
Rising sea levels of 1.8 meters in worst-case scenario
2014-10-14
The climate is getting warmer, the ice sheets are melting and sea levels are rising – but how much? The report of the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2013 was based on the best available estimates of future sea levels, but the panel was not able to come up with an upper limit for sea level rise within this century. Now researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute and their colleagues have calculated the risk for a worst-case scenario. The results indicate that at worst, the sea level would rise a maximum of 1.8 meters. The results are published ...
The chemistry of pizza (video)
2014-10-14
WASHINGTON, Oct. 13, 2014 — Whether it's a plain cheese, a deep-dish stacked with meats or a thin-crust veggie delight, there's just something about pizza that makes it delicious. There's a lot of chemistry that goes into everything from dough to sauce to toppings to, of course, cheese. There's also a very specific chemical reaction at work on every single slice, no matter what toppings you choose. Check out the latest episode here: http://youtu.be/tOkCgAwhh9U.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to ...
Oral drug reduces formation of precancerous polyps in the colon, UB researchers find
2014-10-14
BUFFALO, N.Y. — An oral biologic medication has successfully treated chronic, precancerous inflammation in the intestine, according to results of an animal study authored by an MD/PhD student in the University at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences.
The study is featured on the cover of the current issue of Cancer Research; it was published online ahead of print in September. The journal's editors characterized the study's findings as "striking."
Inflammatory cells in the colon, or polyps, are very common after the age of 50. The average 60-year-old ...
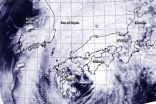
NASA satellite sees wind shear affecting Tropical Storm Vongfong
2014-10-14
Tropical Storm Vongfong continues to weaken as it tracks across the big islands of Japan, and NASA satellite data showed that westerly wind shear is taking its toll on the storm's structure.
On Oct. 12 at 0500 UTC (1 a.m. EDT), the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of Tropical Storm Vongfong approaching Japan. Despite weakening to a tropical storm, Vongfong still appeared to have an eye as its northeastern quadrant blanketed the large island of Kyushu, Japan. By 11 a.m. EDT, Maximum sustained winds had dropped to 55 knots (63 mph/102 kph). ...
Tropical Storm Gonzalo triggered many warnings in Eastern Caribbean
2014-10-14
The Eastern Caribbean islands were getting the brunt of Tropical Storm Gonzalo as the storm slowly moved through on Oct. 13. NASA's Terra satellite and NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided data on the storm. Gonzalo is the sixth named storm in the Atlantic Ocean Hurricane Season.
On Oct. 12 at 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT), NASA's Terra satellite flew over Tropical Storm Gonzalo while it moved over the Lesser Antilles. The MODIS instrument captured a visible image of the storm that showed a concentration of strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation and in a thick ...
Satellites confirm Fay weakened to a Tropical Storm
2014-10-14
The fifth named Atlantic storm didn't maintain hurricane status long. Fay became a hurricane late on Oct. 12 and by early on Oct. 13, had weakened back to a tropical storm.
A visible image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on Oct. 13 at 1145 UTC (7:45 a.m. EDT) showed Tropical Storm Fay northeast of Bermuda and Tropical Storm Gonzalo over the Lesser Antilles. Fay appeared circular, but didn't have the signature shape of a tropical storm like Gonzalo, with bands of thunderstorms spiraling into the center. The image was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard ...
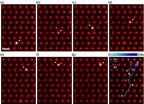
ORNL researchers make first observation of atoms moving inside bulk material
2014-10-14
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Oct. 13, 2014 -- Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have obtained the first direct observations of atomic diffusion inside a bulk material. The research, which could be used to give unprecedented insight into the lifespan and properties of new materials, is published in the journal Physical Review Letters (06 October 2014, DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.155501).
"This is the first time that anyone has directly imaged single dopant atoms moving around inside a material," said Rohan Mishra of Vanderbilt University who ...
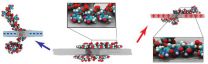
Charged graphene gives DNA a stage to perform molecular gymnastics
2014-10-14
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — When Illinois researchers set out to investigate a method to control how DNA moves through a tiny sequencing device, they did not know they were about to witness a display of molecular gymnastics.
Fast, accurate and affordable DNA sequencing is the first step toward personalized medicine. Threading a DNA molecule through a tiny hole, called a nanopore, in a sheet of graphene allows researchers to read the DNA sequence; however, they have limited control over how fast the DNA moves through the pore. In a new study published in the journal Nature ...
Scientists sniff out unexpected role for stem cells in the brain
2014-10-14
For decades, scientists thought that neurons in the brain were born only during the early development period and could not be replenished. More recently, however, they discovered cells with the ability to divide and turn into new neurons in specific brain regions. The function of these neuroprogenitor cells remains an intense area of research. Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) report that newly formed brain cells in the mouse olfactory system — the area that processes smells — play a critical role in maintaining proper connections. The results ...