(Press-News.org) Particle physicists have a hard time identifying all the elementary particles created in their particle accelerators. But now researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have designed a material that makes it much easier to distinguish the particles.
To investigate the matter's smallest constituents, physicists have particles colliding with each other at very high speeds, for example in the particle accelerator LHC at Cern. The collisions create bursts of common and rare particles, all invisible to the eye.
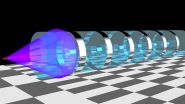
To identify them researchers need to detect the cone of light – known as Cherenkov radiation – formed around a particle that travels faster than light in a transparent material.
Is that possible? Yes, it is. Nothing can travel faster than the speed of light – in vacuum. But in materials light propagates slower and, hence, particles may be moving faster than light without violating the laws of physics. Cherenkov radiation is the optical phenomenon corresponding to the sonic shock wave formed around an object moving faster than the speed of sound. The angle of the Cherenkov light cone, i.e. its sharpness, provides the particle physicists a measure of the velocity of the particle which helps them to identify the particle.
The problem is that the light cone angle has a limit – all particles with high momentum (mass x velocity) generate light cones with the same angle. Hence, these particles are indistinguishable.
Now Chalmers researcher Philippe Tassin and his colleagues at the Free University of Brussels have designed a material that manipulates the Cherenkov cone so that also particles with high momentum get a distinct light cone angle too. The work is on the cover of this week's issue of the journal Physical Review Letters.
"The result is that even particles with large momentum can be efficiently separated and identified," said Philippe Tassin.
The method that they used to design the new material is known as transformation optics. It is a fairly new and very fruitful combination of Einstein's relativity theory – with its curved space-time – and optics.
Carefully calculated variations of the material's refractive index causes the light to experience the material as being curved and, therefore, it behaves differently from what we are used to. In the Chalmers scientists' material, Cherenkov radiation experiences the material as stretched in two different directions, which gives rise to light cones with distinct angles.
Through their work, Philippe Tassin and his colleagues also demonstrated more in-depth opportunities with transformation optics.
"So far, transformation optics has mainly concerned changing the light rays paths through a material. Now, we show that it is also possible to influence the generation of light. As an example, we have solved the problem of Cherenkov light cones for particles of large momentum," explains Philippe Tassin.
Transformation optics may, for example, also be used to design materials that concentrate or absorb light very efficiently, which would be useful for solar energy. Other materials designed via transformation optics are promising for simulating cosmological phenomena such as black holes.
INFORMATION:
The results derive from a collaborative research effort conducted by Chalmers and the Vrije Universiteit Brussel, and the project was funded by the Area of Advance of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology at Chalmers University of Technology and the Research Foundation-Flanders in Belgium.
Link to the article: Controlling Cherenkov Radiation with Transformation-Optical Metamaterials
http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.167402
Light bending material facilitates the search for new particles
2014-10-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cadavers beat computers for learning anatomy
2014-10-16
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Despite the growing popularity of using computer simulation to help teach college anatomy, students learn much better through the traditional use of human cadavers, according to new research that has implications for health care.
Cary Roseth, associate professor of educational psychology at Michigan State University, said the study suggests cadaver-based instruction should continue in undergraduate human anatomy, a gateway course to medical school, nursing and other health and medical fields.
In the United States, most anatomy courses still emphasize ...
S-equol supplements associated with improved measures of reproductive health in postmenopausal women
2014-10-16
Northridge, Calif. (October 16, 2014) – Post-menopausal women experienced improvements in vaginal atrophy, with no significant effect on hormone levels or genital bleeding, after 12 weeks of daily 10 milligram (mg) doses of an investigational fermented soy germ-based nutritional supplement previously shown to help relieve certain menopause symptoms, according to a new peer-reviewed pilot study reported in a poster at the North American Menopause Society (NAMS) annual scientific meeting.
"These data documented improved vaginal epithelium, without significant abnormalities ...
Curious signal hints at dark matter
2014-10-16
Space scientists at the University of Leicester have detected a curious signal in the X-ray sky – one that provides a tantalising insight into the nature of mysterious Dark Matter.
The Leicester team has found what appears to be a signature of 'axions', predicted 'Dark Matter' particle candidates – something that has been a puzzle to science for years.
In a study being published on Monday 20 October in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, the University of Leicester scientists describe their finding of a signal which has no conventional ...
Executive scandal hurts job prospects even for entry-level employees
2014-10-16
October 16, 2014 – There's more bad news for job seekers with a scandal-hit company like Lehman Brothers or Countrywide Mortgage on their résumés. As if it weren't already hard enough to get a new job in this market, people who worked for one of those companies have tarnished reputations to overcome: New research finds that moral suspicion from higher-ups' wrongdoing spills down to people lower in an organization, even if they did not work directly under the moral transgressor.
"We became interested in the plight of people whose career trajectories were ...
Brain's compass relies on geometric relationships, say Penn Researchers
2014-10-16
VIDEO:
The brain has a complex system for keeping track of which direction you are facing as you move about; remembering how to get from one place to another would otherwise...
Click here for more information.
The brain has a complex system for keeping track of which direction you are facing as you move about; remembering how to get from one place to another would otherwise be impossible. Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania have now shown how the brain anchors this ...
How, when, and why industrial ecology is good for business
2014-10-16
Industrial ecology, a rapidly growing field focused on sustainable production and consumption, has contributed numerous important tools to modern environmental management — life cycle assessment; "industrial symbiosis," or the by-product exchange between neighboring facilities; "design for environment"; and the use of material flow analysis to track resource use in supply chains, companies, and economies.
A new special feature of Yale's Journal of Industrial Ecology, titled "Industrial Ecology as a Source of Competitive Advantage," presents new research on how, ...
Study shows inpatient palliative care reduces hospital costs and readmissions
2014-10-16
New Rochelle, NY, October 15, 2014—Palliative care provided in the hospital offers known clinical benefits, and a new study shows that inpatient palliative care can also significantly lower the cost of hospitalization and the rate of readmissions. Further, the study shows the hospital can get the expertise it needs through a collaborative relationship with a community hospice. The results of a comparative study are published in Journal of Palliative Medicine, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal ...
Novel RNAi-based therapy for anemia stimulates liver to produce EPO
2014-10-16
New Rochelle, NY, October 16, 2014—To treat the debilitating anemia associated with reduced erythropoietin (EPO) production by the kidneys in chronic renal disease, patients are often given recombinant human EPO to increase hemoglobin levels. But that treatment has risks. A new approach that uses a small interfering RNA (siRNA) drug to stimulate natural EPO production by the liver has shown promising results in nonhuman primates, as reported in Nucleic Acid Therapeutics, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers. The article is available free ...
Public health in the 21st century
2014-10-16
Ann Arbor, MI, October 16, 2014 – Although disease outbreaks and epidemics drawing worldwide attention emphasize the importance and acute need for public health professionals, the world faces a longer-term challenge—a public health workforce that is truly effective in the 21st century. In a new supplement to the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, experts address critical challenges to public health, from workforce development, capacity building, partnership and collaborations, and changes and needs in workforce composition.
As the U.S. healthcare system ...
New test can help doctors choose best treatment for ovarian cancer
2014-10-16
Researchers have devised a new test to help doctors diagnose ovarian tumours and choose the most appropriate treatment.
Successful treatment depends in part on accurately identifying the type of tumour, but this can be difficult. As a result, many women with cancer are not sent to the right specialist surgeon, or those with a benign cyst may have a more serious operation than they need.
In a study published today in the British Medical Journal, an international team led by Imperial College London and KU Leuven, Belgium describe a new test, called ADNEX, which can discriminate ...