INFORMATION:
New Univeristy of Virginia study upends current theories of how mitochondria began
2014-10-16
(Press-News.org) Parasitic bacteria were the first cousins of the mitochondria that power cells in animals and plants – and first acted as energy parasites in those cells before becoming beneficial, according to a new University of Virginia study that used next-generation DNA sequencing technologies to decode the genomes of 18 bacteria that are close relatives of mitochondria.
The study appears this week in the online journal PLOS One, published by the Public Library of Science. It provides an alternative theory to two current theories of how simple bacterial cells were swallowed up by host cells and ultimately became mitochondria, the "powerhouse" organelles within virtually all eukaryotic cells – animal and plant cells that contain a nucleus and other features. Mitochondria power the cells by providing them with adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, considered by biologists to be the energy currency of life.
The origin of mitochondria began about 2 billion years ago and is one of the seminal events in the evolutionary history of life. However, little is known about the circumstances surrounding its origin, and that question is considered an enigma in modern biology.
"We believe this study has the potential to change the way we think about the event that led to mitochondria," said U.Va. biologist Martin Wu, the study's lead author. "We are saying that the current theories – all claiming that the relationship between the bacteria and the host cell at the very beginning of the symbiosis was mutually beneficial – are likely wrong.
"Instead, we believe the relationship likely was antagonistic – that the bacteria were parasitic and only later became beneficial to the host cell by switching the direction of the ATP transport."
The finding, Wu said, is a new insight into an event in the early history of life on Earth that ultimately led to the diverse eukaryotic life we see today. Without mitochondria to provide energy to the rest of a cell, there could not have evolved such amazing biodiversity, he said.
"We reconstructed the gene content of mitochondrial ancestors, by sequencing DNAs of its close relatives, and we predict it to be a parasite that actually stole energy in the form of ATP from its host – completely opposite to the current role of mitochondria," Wu said.
In his study, Wu also identified many human genes that are derived from mitochondria – identification of which has the potential to help understand the genetic basis of human mitochondrial dysfunction that may contribute to several diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and diabetes, as well as aging-related diseases.
In addition to the basic essential role of mitochondria in the functioning of cells, the DNA of mitochondria is used by scientists for DNA forensics, genealogy and tracing human evolutionary history.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Shrinking resource margins in Sahel region of Africa
2014-10-16
The need for food, animal feed and fuel in the Sahel belt is growing year on year, but supply is not increasing at the same rate. New figures from 22 countries indicate falling availability of resources per capita and a continued risk of famine in areas with low 'primary production' from plants. Rising temperatures present an alarming prospect, according to a study from Lund University in Sweden.
The research has investigated developments between the years 2000 and 2010 in the Sahel belt, south of the Sahara Desert. Over this ten-year period, the population of the region ...
How a molecular Superman protects the genome from damage
2014-10-16
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – How many times have we seen Superman swoop down from the heavens and rescue a would-be victim from a rapidly oncoming train?
It's a familiar scenario, played out hundreds of times in the movies. But the dramatic scene is reenacted in real life every time a cell divides. In order for division to occur, our genetic material must be faithfully replicated by a highly complicated machine, whose parts are tiny enough to navigate among the strands of the double helix.
The problem is that our DNA is constantly in use, with other molecular machines ...
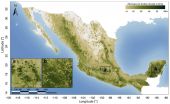
First detailed map of aboveground forest carbon stocks in Mexico unveiled
2014-10-16
Available for download today, the Woods Hole Research Center (WHRC) and Allianza MREDD+ released the first detailed map of aboveground forest carbon stocks of Mexico. This carbon stock inventory is very valuable for Mexico, as one of the first tropical nations to voluntarily pledge to mitigation actions within the context of the United Nation's Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation (REDD+) program.
The hectare-scale map is the result of a collaboration led by WHRC scientists Josef Kellndorfer and Oliver Cartus with Mexico's National Forestry Commission ...
News from Annals of Internal Medicine: Conventional medical centers may be unable to prevent spread of Ebola
2014-10-16
1. Conventional medical centers may be unable to prevent spread of Ebola
A group of infectious disease experts suggests that conventional U.S. medical centers are unprepared and ill equipped to manage Ebola and a national network of specialized containment and treatment facilities may be needed to reduce the virus' spread, according to an article being published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Despite efforts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to prepare hospitals for Ebola, enormous challenges remain. The authors express doubt that conventional ...
Journey to the center of the earth
2014-10-16
A UC Santa Barbara geochemist studying Samoan volcanoes has found evidence of the planet's early formation still trapped inside the Earth. Known as hotspots, volcanic island chains such as Samoa can ancient primordial signatures from the early solar system that have somehow survived billions of years.
Matthew Jackson, an associate professor in UCSB's Department of Earth Science, and colleagues utilized high-precision lead and helium isotope measurements to unravel the chemical composition and geometry of the deep mantle plume feeding Samoa's volcanoes. Their findings ...
Major Hurricane Gonzalo gives an 'eye-opening' performance
2014-10-16
VIDEO:
NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this image of Hurricane Gonzalo off the U.S. East Coast on Oct. 16 at 13:07 UTC (9:07 a.m. EDT).
Click here for more information.
NASA and NOAA satellites have been providing continuous coverage of Hurricane Gonzalo as it moves toward Bermuda. NASA's Terra satellite saw thunderstorms wrapped tightly around the center with large bands of thunderstorms wrapping into it. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided and "eye-opening" view of Gonzalo, ...
Satellites tracking Central Pacific's Tropical Storm Ana
2014-10-16
Tropical Storm Ana continued on a path to the Hawaiian Islands as NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead and gathered data on the storm. NOAA's GOES-West satellite data was compiled into a movie that showed the intensification and movement of Ana. Watches are now in effect for Hawaii.
NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) has issued a Tropical Storm Watch for Hawaii County, Hawaii. A tropical storm watch means that tropical storm conditions are possible within the watch area, in this case within 36 to 48 hours. Life-threatening surf and riptide conditions will ...
Formation and large scale confinement of jets emitted by young stars finally elucidated
2014-10-16
An international team of scientists has succeeded in explaining the formation and propagation over astronomical distances of jets of matter emitted by young stars—one of the most fascinating mysteries of modern astronomy. Using a patented experimental device and large-scale numerical simulations, the team obtained data consistent with astrophysical observations. The results of this research—just published in the prestigious journal Science—open up new opportunities for studying the role of magnetic fields in astrophysics and thermonuclear fusion. Bruno ...
Tiny 'nanoflares' might heat the Sun's corona
2014-10-16
Why is the Sun's million-degree corona, or outermost atmosphere, so much hotter than the Sun's surface? This question has baffled astronomers for decades. Today, a team led by Paola Testa of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) is presenting new clues to the mystery of coronal heating using observations from the recently launched Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS). The team finds that miniature solar flares called "nanoflares" - and the speedy electrons they produce - might partly be the source of that heat, at least in some of the hottest parts ...
Researchers develop personalized ovarian cancer vaccines
2014-10-16
Researchers at the University of Connecticut have found a new way to identify protein mutations in cancer cells. The novel method is being used to develop personalized vaccines to treat patients with ovarian cancer.
"This has the potential to dramatically change how we treat cancer," says Dr. Pramod Srivastava, director of the Carole and Ray Neag Comprehensive Cancer Center at UConn Health and one of the principal investigators on the study. "This research will serve as the basis for the first ever genomics-driven personalized medicine clinical trial in immunotherapy ...