NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Nilofar being affected by wind shear
2014-10-29
(Press-News.org) Wind shear has kicked in and has been pushing clouds and showers away from Tropical Cyclone Nilofar's center. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image that showed the effects of the shear on Oct. 29.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of Tropical Cyclone Nilofar on Oct. 29 at 09:00 UTC (5 a.m. EDT). Tropical Cyclone Nilofar is moving through the Arabian Sea. The image shows that clouds were being pushed to the northeast of the center of the storm, from strong southwesterly wind shear.
On Oct. 29 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Nilofar had maximum sustained winds near 90 knots (103.6 mph/166.7 kph) and slow weakening is expected over the next couple of days. Nilofar was centered near 19.5 north latitude and 62.5 east longitude, about 205 nautical miles (236 miles/380 km) east-southeast of Masirah Island. Nilofar was moving to the north-northeast at 6 knots (6.9 mph/11.1 kph).
India's Regional Specialized Meteorological Service or RSMC forecast said Cyclone Nilofar is expected to move northeastward and cross north Gujarat and the adjoining Pakistan coast around Naliya by the night time hours on Oct. 31, but as it approaches the Gujarat Coast it is expected to weaken to a depression. For the full bulletin, visit: http://www.rsmcnewdelhi.imd.gov.in/images/bulletin/rsmc.pdf. For updated forecasts, visit: http://www.rsmcnewdelhi.imd.gov.in.
Although one of the computer forecast models calls for dry air to move into the system and possible dissipate it over the ocean, the consensus suggests a landfall. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecast calls for Nilofar to weaken to a tropical storm and make landfall near the India/Pakistan border late on Oct. 31 (UTC).
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-29
In the largest study of its kind to date, researchers have used DNA sequencing to uncover dozens of genes that heighten the risk for autism. Joseph Buxbaum, Ph.D., Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, Mark Daly, Ph.D., Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, and their colleagues examined more than 14,000 DNA samples from affected children, parents and unrelated people. They identified changes in 107 genes that are likely to contribute to the risk for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) – a jump from the nine genes implicated in earlier studies using these ...
2014-10-29
Small differences in as many as a thousand genes contribute to risk for autism, according to a study led by Mount Sinai researchers and the Autism Sequencing Consortium (ASC), and published today in the journal Nature.
The new study examined data on several types of rare, genetic differences in more than 14,000 DNA samples from parents, affected children, and unrelated individuals – by far the largest number to date – to dramatically expand the list of genes identified with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Most of the genes that contribute to autism remain ...
2014-10-29
A research group led by Anne Dutrey from the Laboratory of Astrophysics of Bordeaux, France, and the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) observed the distribution of dust and gas in a binary star system called GG Tau-A. It was recently discovered that one of GG Tau-A's components is itself a double star. This object is only a few million years old and lies approximately 460 light-years from Earth in the constellation Taurus.
Like a wheel in a wheel, GG Tau-A contains a large, outer disk encircling the entire system as well as an inner disk around the main central ...
2014-10-29
Mouse lemurs can live at least eight years in the wild – twice as long as some previous estimates, a long-term longitudinal study finds.
PLOS ONE published the research on brown mouse lemurs (Microcebus rufus) led in Madagascar by biologist Sarah Zohdy, a post-doctoral fellow in Emory University's Department of Environmental Sciences and the Rollins School of Public Health. Zohdy conducted the research while she was a doctoral student at the University of Helsinki.
"It's surprising that these tiny, mouse-sized primates, living in a jungle full of predators that ...
2014-10-29
A team led by the Lawrence Livermore scientists has created a new kind of ion channel based on short carbon nanotubes, which can be inserted into synthetic bilayers and live cell membranes to form tiny pores that transport water, protons, small ions and DNA.
These carbon nanotube "porins" have significant implications for future health care and bioengineering applications. Nanotube porins eventually could be used to deliver drugs to the body, serve as a foundation of novel biosensors and DNA sequencing applications, and be used as components of synthetic cells.
Researchers ...
2014-10-29
A study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has identified a potential target for therapies to treat cocaine addiction. In their study receiving advance online publication in Molecular Psychiatry, the investigators find evidence that changing one amino acid in a subunit of an important receptor protein alters whether cocaine-experienced animals will resume drug seeking after a period of cocaine abstinence. Increasing expression of the enzyme responsible for that change within the ...
2014-10-29
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To understand the extent to which human activities are polluting Earth's atmosphere and oceans, it's important to distinguish human-made pollutants from compounds that occur naturally. A recent study co-authored by a Brown University professor does just that for ammonium, a compound that is produced by human activities like agriculture, as well as by natural processes that occur in the ocean.
The research, based on two years of rainwater samples taken in Bermuda, suggests that ammonium deposited over the open ocean comes almost ...
2014-10-29
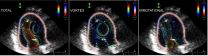
Engineers at the University of California, San Diego have determined for the first time the impact of a ring-shaped vortex on transporting blood flow in normal and abnormal ventricles within the human heart. They worked with cardiologists at the Non-Invasive Cardiology Laboratory at Gregorio Marañon Hospital, in Madrid, Spain.
In order to make the study possible, researchers have developed a novel ultrasound technology that makes screening cheaper and much easier, making it possible to reach a large number of people and even infants. Intra-ventricular flow imaging ...
2014-10-29
VIDEO:
AHCC (Active Hexose Correlated Compound) is a natural immune-modulating compound derived from a unique fraction of specially-cultured medicinal mushroom mycelia which has been clinically shown to strengthen the body's immune...
Click here for more information.
(October 29, 2014, Beaverton, OR) New research presented at the Society for Integrative Oncology (SIO) 11th International Conference in Houston, TX showed for the first time that it is possible to eliminate HPV ...
2014-10-29
Many factors, both genetic and environmental, have been blamed for increasing the risk of a diagnosis of schizophrenia. Some, such as a family history of schizophrenia, are widely accepted. Others, such as infection with Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite transmitted by soil, undercooked meat and cat feces, are still viewed with skepticism.
A new study by Gary Smith, professor of population biology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania's School of Veterinary Medicine, used epidemiological modeling methods to determine the proportion of schizophrenia cases that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Nilofar being affected by wind shear