(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C., October 31, 2014 -- Imagine this scenario: You've been feeling persistently blue lately, so you pull out your phone. Instead of asking Siri to tell you a joke, though, you open an app that records you simply talking about your day. A few hours later, your therapist sends you a message asking if you'd like to meet.
A program like this one that analyzes your speech and uses it to gain information about your mental health could soon be feasible, thanks in part to research from the University of Maryland showing that certain vocal features change as patients' feelings of depression worsen. The team behind the work will present their findings at the 168th meeting of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA), held October 27-31 at the Indianapolis Marriott Downtown Hotel.
The research is part of an interdisciplinary initiative at the University of Maryland to engineer patient-focused mental health monitoring systems. Rather than relying solely on patients' self-reports, these systems could monitor both physical and psychological symptoms of mental illness on a regular basis and provide both patients and their mental health providers with feedback about their status.
To conduct a quantitative experiment on the vocal characteristics of depression acoustician Carol Espy-Wilson and her colleagues repurposed a dataset collected from a 2007 study from an unaffiliated lab also investigating the relationship between depression and speech patterns. The earlier study assessed patients' depression levels each week using the Hamilton Depression Scale (a standard clinical evaluation tool to measure the severity of depression) and then recorded them speaking freely about their day.
The University of Maryland researchers used data from six patients who, over the six-week course of the previous study, had registered as depressed some weeks and not depressed other weeks. They compared these patients' Hamilton scores with their speech patterns each week, and found a correlation between depression and certain acoustic properties.
When patients' feelings of depression were worst, their speech tended to be breathier and slower. The team also found increases in jitter and shimmer, two measures of acoustic disturbance that measure the frequency and amplitude variation of the sound, respectively. Speech high in jitter and shimmer tends to sound hoarse or rough.
The researchers plan to repeat the study in a larger population, this time comparing speech patterns in individuals with no history of mental illness to those with depression to create an acoustic profile of depression-typical speech. A phone app could use this information to analyze patients' speech, identify acoustic signatures of depression and provide feedback and support.
Espy-Wilson hopes the interactive technology will appeal to teens and young adults, a particularly vulnerable group for mental health problems. "Their emotions are all over the place during this time, and that's when they're really at risk for depression. We have to reach out and figure out a way to help kids in that stage," she said.
Sometimes, patients might not recognize or be willing to admit that they are depressed. By receiving regular feedback based on acoustical and other measurements, they might learn to self-monitor their mental states and recognize when they should seek help. The technology could also promote communication between therapists and patients, allowing for continuous, responsive care in addition to regular in-person appointments.
The researchers acknowledge that developing an effective app requires a larger scope than just the underlying science—a challenge they plan to address. "We definitely need human factors to develop something that people will use," said Espy-Wilson. "There's a lot that has to go into making this a useful tool."
Presentation #5aSC12, "Effects of depression on speech," by Saurabh Sahu and Carol Espy-Wilson will be presented during a poster session on Friday, October 31, 2014, from 8:00 AM to noon in Marriott 5. The abstract can be found by searching for the presentation number here: https://asa2014fall.abstractcentral.com/planner.jsp
INFORMATION:
ABOUT THE MEETING
The 168th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA) will be held October 27-31, 2014, at the Indianapolis Marriott Downtown Hotel. It will feature more than 1,100 presentations on sound and its applications in physics, engineering, and medicine. Reporters are invited to cover the meeting remotely or attend in person for free.
PRESS REGISTRATION
We will grant free registration to credentialed journalists and professional freelance journalists. If you are a reporter and would like to attend, contact Jason Bardi (jbardi@aip.org, 240-535-4954), who can also help with setting up interviews and obtaining images, sound clips, or background information.
USEFUL LINKS
Main meeting website: http://acousticalsociety.org/content/fall-2014-meeting
Program and Abstracts: https://asa2014fall.abstractcentral.com/planner.jsp
Live Webcast Oct. 29: http://www.aipwebcasting.com/webcast/registration/oct2014.php
ASA's World Wide Press Room https://acoustics.org/?page_id=165
WORLD WIDE PRESS ROOM
ASA's World Wide Press Room is being updated with additional tips on dozens of newsworthy stories and with lay-language papers, which are 300-1,200 word summaries of presentations written by scientists for a general audience and accompanied by photos, audio, and video.
LIVE MEDIA WEBCAST
A press briefing featuring a selection of newsworthy research will be webcast live from the conference the afternoon of Wednesday, October 29. A separate announcement, which includes topics and times, will be sent later this week. Register at: http://www.aipwebcasting.com/webcast/registration/oct2014.php
ABOUT THE ACOUSTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7,000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America (the world's leading journal on acoustics), Acoustics Today magazine, books, and standards on acoustics. The society also holds two major scientific meetings each year. For more information about ASA, visit our website at http://www.acousticalsociety.org
WASHINGTON, DC (October 31, 2014) — A new report by Milken Institute School of Public Health (Milken Institute SPH) at the George Washington University examines the challenge of maintaining enriched health care for pregnant women who are enrolled in Covered California and who are also eligible for Medi-Cal, which includes the Comprehensive Perinatal Services Program (CPSP). The CPSP, whose roots are in one of the nation's most successful programs ever developed for low-income pregnant women, makes enriched maternity care available to pregnant women facing elevated ...
The United States is undergoing a drastic change in marijuana policy. Two states legalized recreational use for adults in 2012, and next week, citizens of Oregon, Alaska and the District of Columbia will vote for or against legalization in their area. The majority of the public now favor legalizing or decriminalizing marijuana use, but there is a lack of research examining how marijuana use and demographic characteristics relate to positions toward specific marijuana policies. For example, is it primarily marijuana users who support legalization?
There is a need to examine ...
Connectivity cost calculations for conservation corridors
Where are conservation dollars best invested to connect fragmented habitats? Sara Torrubia and colleagues test their model balancing restoration costs with connection quality on the threatened Washington ground squirrel in eastern Washington State.
"Getting the most connectivity per conservation dollar," by Sara Torrubia, Brad H McRae, Joshua J Lawler, Sonia A Hall, Meghan Halabisky, Jesse Langdon, and Michael Case.
Agricultural companions: co-planting partner crops improves yields
Soy and cereals, rice and ...
This news release is available in French. Hoping for sex with two women is common but fantasizing about golden showers is not. That's just one of the findings from a research project that scientifically defines sexual deviation for the first time ever. It was undertaken by researchers at Institut universitaire en santé mentale de Montréal and Institut Philippe-Pinel de Montréal, affiliated with University of Montreal. Although many theories about deviant sexual fantasies incorporate the concept of atypical fantasies (paraphilias), the scientific literature ...
TAMPA, Fla. (Oct. 30, 2014) – The scientific community has made significant strides in recent years in identifying important genetic contributors to malignancy and developing therapeutic agents that target altered genes and proteins. A recent approach to treat cancer called synthetic lethality takes advantage of genetic alterations in cancer cells that make them more susceptible to certain drugs. Alan F. List, MD, president and CEO of Moffitt Cancer Center, co-authored an article on synthetic lethality featured in the October 30 issue of the New England Journal of ...
Patients with tinnitus hear phantom noise and are sometimes so bothered by the perceived ringing in their ears, they have difficulty concentrating. A new therapy does not lessen perception of the noise but appears to help patients cope better with it in their daily lives, according to new research.
A pilot study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis showed that patients participating in computer-based cognitive training and taking a drug called d-cycloserine reported greater improvements in the ability to go about their daily lives than patients who ...
Overwhelmed by speculators trying to cash-in on a prized medicinal fungus known as Himalayan Viagra, two isolated Tibetan communities have managed to do at the local level what world leaders often fail to do on a global scale — implement a successful system for the sustainable harvest of a precious natural resource, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
"There's this mistaken notion that indigenous people are incapable of solving complicated problems on their own, but these communities show that people can be incredibly resourceful when ...
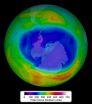
The Antarctic ozone hole reached its annual peak size on Sept. 11, according to scientists from NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The size of this year's hole was 24.1 million square kilometers (9.3 million square miles) — an area roughly the size of North America.
The single-day maximum area was similar to that in 2013, which reached 24.0 million square kilometers (9.3 million square miles). The largest single-day ozone hole ever recorded by satellite was 29.9 million square kilometers (11.5 million square miles) on Sept. 9, 2000. ...
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has picked up the faint, ghostly glow of stars ejected from ancient galaxies that were gravitationally ripped apart several billion years ago. The mayhem happened 4 billion light-years away, inside an immense collection of nearly 500 galaxies nicknamed "Pandora's Cluster," also known as Abell 2744.
The scattered stars are no longer bound to any one galaxy, and drift freely between galaxies in the cluster. By observing the light from the orphaned stars, Hubble astronomers have assembled forensic evidence that suggests as many as six galaxies ...
A UAlberta team has discovered that a protein that plays a critical role in metabolism, the process by which the cell generates energy from foods, is important for the development of pulmonary hypertension, a deadly disease.
Pulmonary hypertension is caused by the narrowing of the blood vessels in the lung, due to excessive growth of cells in the blood vessel wall. The cells grow in number until they obstruct the vessels, causing the heart to struggle pushing blood through the lungs to the point where the heart fails and the patient dies.
Evangelos Michelakis, a professor ...