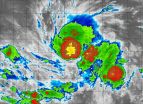
(Press-News.org) Tropical Depression 21E strengthened overnight on Oct. 30 and by Halloween morning, Tropical Storm Vance was haunting the waters of the Eastern Pacific Ocean. In a false-colored infrared image from NASA's Terra satellite on Oct. 31, the strong thunderstorms around the center resemble a pumpkin.
Tropical Depression 21E formed on Oct. 30 after struggling for days as a low pressure area. Just a day later it strengthened into a tropical storm and was renamed Vance.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Vance on October 31 at 4:55 UTC (12:55 a.m. EDT) – the witching hour – and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard Terra captured infrared data. That infrared data was false-colored when the image was created. High, strong thunderstorms with cold cloud top temperatures that circled the center were false-colored in an orange-red color, and resembled the shape of a pumpkin with a stem!
At 5 a.m. EDT, Tropical Storm Vance's maximum sustained winds were near 45 mph (75 kph) and is expected to strengthen gradually. Vance was centered near latitude 10.5 north and longitude 101.0 west. That's about 450 miles (720 km) south of Acapulco, Mexico. Vance is moving toward the west-southwest near 3 mph (6 kph) and is forecast to turn to the west and west-northwest on Nov. 1.
National Hurricane Center Forecaster Dan Brown noted that Vance's center was near the southern edge of the large mass of deep convection due to moderate south-southwesterly shear. The shear and some dry low- to mid-level air are expected to continue to affect the tropical cyclone during the next 12 to 24 hours, and only gradual strengthening is expected during that time.
Most of the intensity guidance shows Vance becoming a hurricane in 2 to 3 days.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Tropical Storm Vance's center looks like a pumpkin to NASA's Terra satellite
2014-10-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Raising cryptography's standards
2014-10-31
Most modern cryptographic schemes rely on computational complexity for their security. In principle, they can be cracked, but that would take a prohibitively long time, even with enormous computational resources.
There is, however, another notion of security — information-theoretic security — which means that even an adversary with unbounded computational power could extract no useful information from an encrypted message. Cryptographic schemes that promise information-theoretical security have been devised, but they're far too complicated to be practical.
In ...
The digital therapist
2014-10-31
WASHINGTON, D.C., October 31, 2014 -- Imagine this scenario: You've been feeling persistently blue lately, so you pull out your phone. Instead of asking Siri to tell you a joke, though, you open an app that records you simply talking about your day. A few hours later, your therapist sends you a message asking if you'd like to meet.
A program like this one that analyzes your speech and uses it to gain information about your mental health could soon be feasible, thanks in part to research from the University of Maryland showing that certain vocal features change as patients' ...
Report examines health care challenges for pregnant women enrolled in covered California
2014-10-31
WASHINGTON, DC (October 31, 2014) — A new report by Milken Institute School of Public Health (Milken Institute SPH) at the George Washington University examines the challenge of maintaining enriched health care for pregnant women who are enrolled in Covered California and who are also eligible for Medi-Cal, which includes the Comprehensive Perinatal Services Program (CPSP). The CPSP, whose roots are in one of the nation's most successful programs ever developed for low-income pregnant women, makes enriched maternity care available to pregnant women facing elevated ...
NYU research: Majority of high school seniors favor more liberal marijuana policies
2014-10-31
The United States is undergoing a drastic change in marijuana policy. Two states legalized recreational use for adults in 2012, and next week, citizens of Oregon, Alaska and the District of Columbia will vote for or against legalization in their area. The majority of the public now favor legalizing or decriminalizing marijuana use, but there is a lack of research examining how marijuana use and demographic characteristics relate to positions toward specific marijuana policies. For example, is it primarily marijuana users who support legalization?
There is a need to examine ...
ESA Frontiers November preview
2014-10-31
Connectivity cost calculations for conservation corridors
Where are conservation dollars best invested to connect fragmented habitats? Sara Torrubia and colleagues test their model balancing restoration costs with connection quality on the threatened Washington ground squirrel in eastern Washington State.
"Getting the most connectivity per conservation dollar," by Sara Torrubia, Brad H McRae, Joshua J Lawler, Sonia A Hall, Meghan Halabisky, Jesse Langdon, and Michael Case.
Agricultural companions: co-planting partner crops improves yields
Soy and cereals, rice and ...
Sexual fantasies: Are you normal?
2014-10-31
This news release is available in French. Hoping for sex with two women is common but fantasizing about golden showers is not. That's just one of the findings from a research project that scientifically defines sexual deviation for the first time ever. It was undertaken by researchers at Institut universitaire en santé mentale de Montréal and Institut Philippe-Pinel de Montréal, affiliated with University of Montreal. Although many theories about deviant sexual fantasies incorporate the concept of atypical fantasies (paraphilias), the scientific literature ...
Synthetic lethality offers a new approach to kill tumor cells, explains Moffitt researcher
2014-10-31
TAMPA, Fla. (Oct. 30, 2014) – The scientific community has made significant strides in recent years in identifying important genetic contributors to malignancy and developing therapeutic agents that target altered genes and proteins. A recent approach to treat cancer called synthetic lethality takes advantage of genetic alterations in cancer cells that make them more susceptible to certain drugs. Alan F. List, MD, president and CEO of Moffitt Cancer Center, co-authored an article on synthetic lethality featured in the October 30 issue of the New England Journal of ...
Novel tinnitus therapy helps patients cope with phantom noise
2014-10-30
Patients with tinnitus hear phantom noise and are sometimes so bothered by the perceived ringing in their ears, they have difficulty concentrating. A new therapy does not lessen perception of the noise but appears to help patients cope better with it in their daily lives, according to new research.
A pilot study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis showed that patients participating in computer-based cognitive training and taking a drug called d-cycloserine reported greater improvements in the ability to go about their daily lives than patients who ...
Himalayan Viagra fuels caterpillar fungus gold rush
2014-10-30
Overwhelmed by speculators trying to cash-in on a prized medicinal fungus known as Himalayan Viagra, two isolated Tibetan communities have managed to do at the local level what world leaders often fail to do on a global scale — implement a successful system for the sustainable harvest of a precious natural resource, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
"There's this mistaken notion that indigenous people are incapable of solving complicated problems on their own, but these communities show that people can be incredibly resourceful when ...
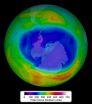
2014 Antarctic ozone hole holds steady
2014-10-30
The Antarctic ozone hole reached its annual peak size on Sept. 11, according to scientists from NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The size of this year's hole was 24.1 million square kilometers (9.3 million square miles) — an area roughly the size of North America.
The single-day maximum area was similar to that in 2013, which reached 24.0 million square kilometers (9.3 million square miles). The largest single-day ozone hole ever recorded by satellite was 29.9 million square kilometers (11.5 million square miles) on Sept. 9, 2000. ...