(Press-News.org) In the early 1900s, Brazil was the world's largest producer of cocoa. Chocolate trees (Theobroma cacao) were cultivated in a 800, 000 ha region of rainforest in the state of Bahia, beneath a dense canopy of native shade trees. Whereas the surrounding rainforest was a biodiversity hotspot, the chocolate trees, which were derived mainly from a handful of seeds introduced in the mid 1700s, had very low levels of genetic variation. According to Brazilian scientist Gonçalo Pereira, "This scenario created a very romantic, but extremely fragile situation". Genetic variation is important for a population's survival, as genetically variable populations are more resistant to pathogens. In 1989, disaster struck in the form of a devastating fungus named Moniliophthora perniciosa. In a ten-year period, the fungus eradicated around 70 percent of Brazil's chocolate trees, resulting in an economic and social catastrophe that affected two million people.
At one stage of its lifecycle, Moniliophthora perniciosa takes on the form of enchanting pink mushrooms that seem to come straight from a fairytale (see picture). For the chocolate tree, however, M. perniciosa spells trouble. These mushrooms are filled with millions of spores that, once released, can enter a susceptible chocolate tree through surface wounds and tiny gaps called stomata and slowly kill the tree. Because infected trees develop bizarre green outgrowths that resemble brooms, the disease is known as witches' broom disease. Two to three months after infection, the brooms turn brown and begin to perish. The fungus then completes its lifecycle by once again giving rise to clusters of spore-producing mushrooms. There is no known cure for this devastating disease.
In 2000, a team of scientists led by Gonçalo Pereira of the Universidade Estadual de Campinas in Brazil initiated the Witches' Broom Genome Project, with the long-term aim of developing a cure for witches' broom disease. A study to be published next week in The Plant Cell represents the culmination of their research to date. The team used a technique known as dual RNA-seq analysis to monitor the interaction between the M. perniciosa fungus and the chocolate tree. This technique allows scientists to reconstruct the battlefield between the chocolate tree and the fungus in unprecedented detail, by providing a readout of genes that are affected in the plant and the fungus during the course of witches' broom disease. "Knowing the molecular and physiological basis of a disease is an important step towards developing effective control strategies," says study author Paulo Teixeira. Using healthy plants as a reference point, the scientists identified 1,967 genes that exhibited unique activities in the green broom structures of infected chocolate trees. An analysis of these genes showed that fungal infection triggers massive changes in the metabolism of the chocolate tree. Additionally, the scientists discovered 8,617 fungal genes that were active in green brooms. Using the Witches' Broom Disease Transcriptome Atlas, a publicly available online tool developed by Pereira's team to support studies of witches' broom disease, the scientists identified 433 fungal genes that were particularly active in green brooms. Many of these genes encoded proteins with presumed functions in the fungal disease mechanism. Study author Daniela Thomazella explains that "The discovery of sets of fungal genes that are most likely involved in pathogenicity paves the way for the development of targeted treatments of the disease". Indeed, the authors are already using the results of this study to develop a novel fungicide that specifically targets M. perniciosa. In addition to increasing our knowledge of a devastating tropical disease, lead scientist Pereira maintains that this work provides an important basis for future studies that aim to improve agricultural sustainability and global food security.
INFORMATION:
Author:
Kathleen L. Farquharson, PhD
kfarquharson@aspb.org
Science Editor, The Plant Cell
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8032-0041
Tel: 206-324-2126
Scientists seek cure for devastating witches' broom disease of the chocolate tree
Transcriptome analysis identifies fungal genes associated with pathogenicity
2014-10-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Decoding the emergence of metastatic cancer stem cells
2014-10-31
In the first study of its kind, Rice University researchers have mapped how information flows through the genetic circuits that cause cancer cells to become metastatic. The research reveals a common pattern in the decision-making that allows cancer cells to both migrate and form new tumors. Researchers say the commonality may open the door to new drugs that interfere with the genetic switches that cancer must flip to form both cancer stem cells and circulating tumor cells -- two of the main players in cancer metastasis.
"Cells have genetic circuits that are used to switch ...
Cell division, minus the cells
2014-10-31
The process of cell division is central to life. The last stage, when two daughter cells split from each other, has fascinated scientists since the dawn of cell biology in the Victorian era. For just as long, it has been notoriously difficult to study this final step, when the dividing cell creates a furrow before cleaving in two.
The name given to this process by those early biologists, cytokinesis, translates as "cell movement" and captures the sense of a highly active and organized series of events. Scientists have now learned much more about the proteins involved ...
Is fleet diversity key to sustainable fisheries?
2014-10-31
Santa Barbara, Calif. — Concern about fisheries is widespread around the world. Over the past several decades, a robust discussion has taken place concerning how to manage fisheries better to benefit ecosystems and humans. Much of the discussion has focused on preserving biological diversity, a critical component of healthy ecosystems. One aspect that gets less attention is the role of fishing fleet diversity.
Fishing fleets can be diverse in many ways, including the gear they use, the fishing grounds they visit and when, and the species they target. A new study ...
Captive rhinos exposed to urban rumbles
2014-10-31
WASHINGTON, D.C., October 31, 2014 -- The soundtrack to a wild rhinoceros's life is wind passing through the savannah grass, birds chirping, and distant animals moving across the plains. But a rhinoceros in a zoo listens to children screaming, cars passing, and the persistent hum of urban life.
A group of researchers from Texas believes that this discrepancy in soundscape may be contributing to rhinos' difficulties thriving and reproducing in captivity. During the 168th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA), which will be held October 27-31, 2014, at the ...
Insomnia increases risk of motor vehicle deaths, other fatal injuries
2014-10-31
DARIEN, IL – New research suggests that insomnia is a major contributor to deaths caused by motor vehicle crashes and other unintentional fatal injuries. The results underscore the importance of the "Sleep Well, Be Well" campaign of the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project.
Results show that the risk of unintentional fatal injury increased in a dose-dependent manner with the number of insomnia symptoms present. People with all three symptoms of insomnia were 2.8 times more likely to die from a fatal injury than those with no insomnia symptoms, even after adjusting ...
Advance directives can benefit patients, families, and health care system
2014-10-31
Nearly one out of four older Americans say that either they or a family member have experienced excessive or unwanted medical treatment, according to the latest issue of The Gerontological Society of America's Public Policy & Aging Report (PP&AR), which goes on to show that Americans strongly support holding doctors accountable when they fail to honor patients' end-of-life health care wishes.
This PP&AR, titled "Advanced Illness Care: Issues and Options," features 12 articles that present new ways of understanding the complexity of securing appropriate advanced illness ...
A new generation of storage -- ring
2014-10-31
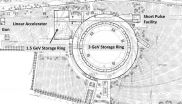
A bright synchrotron source that emits over a wide part of the electromagnetic spectrum from the infrared to hard X-rays is currently being built in Lund, Sweden. The MAX IV facility presents a range of technical challenges for the team putting together its component parts in a storage - ring synchrotron system that will have a circumference of just a few hundred metres. Nevertheless, if these various challenges can be addressed then an entirely new class of experiments that require source brightness and transverse coherence will be possible.
Pedro Tavares and colleagues ...
Viewing cancer on the move: New device yields close-up look at metastasis
2014-10-31
Johns Hopkins engineers have invented a lab device to give cancer researchers an unprecedented microscopic look at metastasis, the complex way that tumor cells spread through the body, causing more than 90 percent of cancer-related deaths. By shedding light on precisely how tumor cells travel, the device could uncover new ways to keep cancer in check.
The inventors, from the university's Whiting School of Engineering and its Institute for NanoBioTechnology (INBT), published details and images from their new system recently in the journal Cancer Research. Their article ...
Lack of oxygen delayed the rise of animals on Earth
2014-10-31
New Haven, Conn. – Geologists are letting the air out of a nagging mystery about the development of animal life on Earth.
Scientists have long speculated as to why animal species didn't flourish sooner, once sufficient oxygen covered the Earth's surface. Animals began to prosper at the end of the Proterozoic period, about 800 million years ago — but what about the billion-year stretch before that, when most researchers think there also was plenty of oxygen?
Well, it seems the air wasn't so great then, after all.
In a study published Oct. 30 in Science, ...
NASA sees remnants of Nilofar go to cyclone graveyard
2014-10-31
Wind shear has caused the demise of former Tropical Cyclone Nilofar in the northern Arabian Sea. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Nilofar on Oct. 31 and captured an image that shows strong wind shear has pushed the bulk of clouds and showers away from Nilofar's center, basically sending the storm to its grave.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of the remnants of Tropical Cyclone Nilofar on Oct. 31 at 08:45 UTC (4:45 a.m. EDT). The image showed that the former tropical cyclone's clouds and showers were pushed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Scientists seek cure for devastating witches' broom disease of the chocolate treeTranscriptome analysis identifies fungal genes associated with pathogenicity