(Press-News.org) An active region on the sun – an area of intense and complex magnetic fields – rotated into view on Oct. 18, 2014. Labeled AR 12192, it soon grew into the largest such region in 24 years, and fired off 10 sizable solar flares as it traversed across the face of the sun. The region was so large it could be seen without a telescope for those looking at the sun with eclipse glasses, as many did during a partial eclipse of the sun on Oct. 23.
"Despite all the flares, this region did not produce any significant coronal mass ejections," said Alex Young a solar scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Coronal mass ejections, or CMEs, are giant clouds of solar particles that can affect technology when they reach near-Earth space. "You certainly can have flares without CMEs and vice versa, but most big flares do have CMEs. So we're learning that a big active region doesn't always equal the biggest events."
Such active regions are measured in millionths of a solar hemisphere, where 1 micro-hemisphere, or MH, is about 600,000 square miles. This region topped out at 2,750 MH, making it the 33rd largest region out of approximately 32,000 active regions that have been tracked and measured since 1874. It is the largest sunspot seen since AR 6368, which measured 3,080 MH on Nov. 18, 1990.
The largest five active regions ever observed were between 4,000 and more than 6,000 MH and they all appeared between 1946 and 1951.
On the other hand, the region that produced one of the biggest solar flares of all time on Sep. 1, 1859 – in what's known as the Carrington event – wasn't even one of the top 50 at only 2,300 MH.
During its trip across the front of the sun, AR 12192 produced six X-class flares, which are the largest flares, and four strong M-class flares. M-class flares are one tenth as strong as X-class flares. The number provides more information about its strength. An M2 is twice as intense as an M1, an M3 is three times as intense, etc.
"Having so many similar flares from the same active region will be a nice case study for people who work on predicting solar flares," said Dean Pesnell, project scientist for NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory at Goddard. "This is important for one day improving the nation's ability to forecast space weather and protect technology and astronauts in space."
The dates and peak times in EDT of the large solar flares from AR 12192 are as follows:
Oct. 19, 1:01 am: X1.1
Oct. 21, 9:59 pm: M8.7
Oct. 22, 10:28 am: X1.6
Oct. 24, 5:41 pm: X3.1
Oct. 25, 1:08 pm: X1.0
Oct. 26, 6:56 am: X2.0
Oct. 26, 8:34 pm: M7.1
Oct. 27, 6:09 am: M6.7
Oct. 27, 10:47 am: X2.0
Oct. 28, 11:32 pm: M6.6
AR 12192 rotated onto the far side of the sun on Oct. 30, 2014, however as it evolves, we may see a new version of it rotating back into view in two weeks.
INFORMATION:
Related Links
For more on this gigantic sunspot and its flares:
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/sdo-observes-largest-sunspot-of-the-solar-cycle/
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/sdo-observes-more-flares-erupting-from-giant-sunspot/
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/one-giant-sunspot-6-substantial-flares/
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/oct-22-2014-third-substantial-solar-flare-in-2-days/
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/sdo-observes-an-x-class-solar-flare/
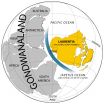
AUSTIN, Texas— A new analysis of geologic history may help solve the riddle of the "Cambrian explosion," the rapid diversification of animal life in the fossil record 530 million years ago that has puzzled scientists since the time of Charles Darwin.
A paper by Ian Dalziel of The University of Texas at Austin's Jackson School of Geosciences, published in the November issue of Geology, a journal of the Geological Society of America, suggests a major tectonic event may have triggered the rise in sea level and other environmental changes that accompanied the apparent ...
Rachel MacTavish is growing salt marsh plants in microcosms that replicate the tide. She assembled them in an outdoor greenhouse at the Sapelo Island National Estuarine Research Reserve in Georgia, USA, with buckets from a hardware store, aquarium tubing, and pumps. Her tidal simulation units could be an important tool for preserving and restoring environmentally important wetlands, because they enable researchers to investigate tidal marsh plant growth in a controlled setting.
"Tidal wetlands are often influenced by many factors, and controlled experiments allow researchers ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- People with muscular dystrophy could one day assess the effectiveness of their medication with the help of a smartphone-linked device, a new study in mice suggests. The study used a new method to process ultrasound imaging information that could lead to hand-held instruments that provide fast, convenient medical information.
In the study presented Oct. 30 at the Acoustical Society of America's annual meeting, researchers determined how well muscles damaged by muscular dystrophy responded to a drug in mice with an animal form of the disease. They did so ...
WASHINGTON — New research points to tau, not amyloid-beta (Abeta) plaque, as the seminal event that spurs neuron death in disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. The finding, which dramatically alters the prevailing theory of Alzheimer's development, also explains why some people with plaque build-up in their brains don't have dementia.
The study is published online today in the journal Molecular Neurodegeneration.
Neuronal death happens when tau, found inside neurons, fails to function. Tau's role is to provide a structure — like a train track —inside ...
Contrary to popular belief, use of the supplement resveratrol (RSV) may not actually enhance the effects of high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Many news outlets and health blogs have long recommended RSV as a complement to exercise and to enhance performance. However, results from a study by Queen's researcher Brendon Gurd suggest that RSV may actually impede the body's response to training.
"The easiest way to experience the benefits of physical activity is to be physically active," says Dr. Gurd, a professor in the School of Kinesiology and Health Studies. "The ...
Where does HIV hide? Antiretroviral drugs can usually control the virus, but can't completely eliminate it. So any strategy to eradicate HIV from the body has to take into account not only the main group of immune cells the virus targets, called CD4 or helper T cells, but other infected cells as well.
New research from Yerkes National Primate Research Center, Emory University, sheds light on the question of which cells support viral replication and persistence, and the answers have implications for future efforts to eliminate HIV from the body in human patients.
The ...
The pathogen Giardia duodenalis is present in mussels from freshwater run-off sites and from areas where California Sea Lions lounge along the coast of California, according to a team of researchers from the University of California, Davis. One of the G. duodenalis strains found is known to infect humans; the two others occur mostly in dogs and other canids. "Thus, the detection of these assemblages implies a potential public health risk if consuming fecally contaminated water or uncooked shellfish," says coauthor Woutrina Smith. The research is published ahead of print ...
Today the leading journal PLOS ONE published research that provides underlying scientific support for a fundamentally new type of natural alternative to the use of antibiotics in livestock feeds for growth promotion and disease prevention. The paper is the result of work by both independent and company scientists. Avivagen Inc. is a wellness company developing and delivering products that support and enhance the health and quality of life for animals and the people who care for them.
The discovery that the product formed by full, spontaneous oxidation of beta-carotene, ...
Drug tests on 517 mothers in English inner city hospitals found that nearly 15% had taken recreational drugs during pregnancy and that mothers of babies with birth defects of the brain were significantly more likely to have taken drugs than mothers with normal babies. The study found no significant links between recreational drug use and any other type of birth defect.
The study was led by a team of UCL researchers co-ordinating data collection from hospitals across London, Bristol and Birmingham and the results are published in the journal PLOS ONE. The study included ...
It is up to 30 centimetres long, it has a green-brown color and is probably known to every beach walker on the North and Baltic Sea: the bladderwrack, a seaweed, which is common on the coasts of the whole North Atlantic area. The bladderwrack provides food and habitat for many other organisms. Its abundance is considered to be an indication of whether a coastal ecosystem is intact or not. Especially in the German Baltic Sea, however, the populations have declined considerably in the past decade. The reasons for this are not yet fully known. "Against this background, it ...