Turning pretty penstemon flowers from blue to red
2014-11-05
(Press-News.org) While roses are red, and violets are blue, how exactly do flower colors change?
In the case of penstemons, with over 200 species to choose from, scientists Carolyn Wessinger and Mark Rausher have now shown that turning their flowers from blue to red involves knocking out the activity of just a single enzyme involved in the production of blue floral pigments.
A genetically conserved biochemical pathway produces the vivid blue pigments that they found to mutate over time to produce red. To shift into red pigment production, the enzyme flavonoid 3', 5' –hydroxylase (F3'5'h) is functionally inactivated in the 13 red-flowered species they examined by mutations that abolish enzyme activity. This occurred by independent evolutionary events, showing a relatively simple, predictable genetic change behind the evolution from blue to red penstemons.
While blue can change to red, in this case, evolution always drives down a one-way street, as reverse changes of red to blue are not observed.
"Evolutionary shifts from blue to red flowers in Penstemon predictably involves degeneration of the same particular flower pigment gene, suggesting there are limited genetic 'options' for evolving red flowers in this group," said Wessinger. "However, it is lot easier for evolution to break a gene than to fix one, so we suspect that reversals from red to blue flowers would be highly unlikely."
The study was published in the advanced online edition of Molecular Biology and Evolution.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-05
MANY patients whose lung cancer is diagnosed as an emergency in hospital reported difficulties in previously seeing their GP, according to research presented at the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference in Liverpool today (Tuesday).
The study, carried out by researchers from the London Cancer Alliance (LCA) and King's College London, investigated around 130 patients who were diagnosed with lung cancer after attending as an emergency at one of seven hospitals in south and west London.
Overall, nearly half of the patients reported that something ...
2014-11-05
SCIENTISTS have found a possible way to halt one of the most common faults in many types of cancer, according to research presented at the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference in Liverpool today (Wednesday).
A team of scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology in Germany has
uncovered a new strategy and new potential drug to target an important signalling protein in cells called Ras, which is faulty in a third of cancers.
When the Ras protein travels from the centre of a cell to the cell membrane, it becomes 'switched on' ...
2014-11-05
PATIENTS with a specific type of oesophageal cancer survived longer when they were given the latest lung cancer drug, according to trial results being presented at the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference today (Wednesday).
Up to one in six patients with oesophageal cancer were found to have EGFR duplication in their tumour cells and taking the drug gefitinib, which targets this fault, boosted their survival by up to six months, and sometimes beyond.
This is the first treatment for advanced oesophageal cancer shown to improve survival in patients ...
2014-11-05
SCIENTISTS have found a pattern of genetic 'switches' – chemical marks that turn genes on or off - that are linked to breast cancer's spread to the brain, according to research* presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Cancer Conference in Liverpool today (Wednesday).
The researchers, based at the University of Wolverhampton, studied 24 breast cancers that had spread to the brain, along with samples from the original breast tumour, and found a handful of genes with faulty switches.
Crucially, two of the genetic switches became faulty early on in the ...
2014-11-05
Everyone knows the scene: a basketball player at the free throw line, bouncing the ball as he concentrates on the basket. It's a tight game, and his team needs this point. He regularly makes baskets from much farther away while avoiding defenders, but now, when all is calm, he chokes and misses the basket, and his team loses. Recent research from The Johns Hopkins University suggests that in situations like this, performance depends on two factors: the framing of the incentive in terms of a loss or a gain, and a person's aversion to loss.
"We can measure someone's loss ...
2014-11-04
For years, scientists have debated how best to assess brain levels of oxytocin, a hormone implicated in social behaviors. Now, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have found the first direct evidence in children that blood oxytocin measurements are tightly linked to levels of oxytocin in cerebrospinal fluid, which bathes the brain.
Low oxytocin levels in blood and CSF are both correlated to high anxiety levels, the research also showed. The findings will be published online Nov. 4 in Molecular Psychiatry.
"So many psychiatric disorders involve ...
2014-11-04
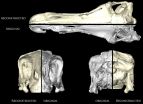
Fossils are usually deformed or incompletely preserved when they are found, after sometimes millions of years of fossilization processes. Consequently, fossils have to be studied very carefully to avoid damage, and are sometimes they are difficult to access, as they might be located in remote museum collections. An international team of scientists, led by Dr. Stephan Lautenschlager from the University of Bristol now solved some of these problems by using modern computer technology, as described in a recent issue of the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
The team consisting ...
2014-11-04
In a study that included nearly 38,000 patients, those diagnosed with nonobstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) had a significantly increased risk of heart attack or death one year after diagnosis, according to a study in the November 5 issue of JAMA.
Nonobstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) is atherosclerotic plaque that would not be expected to obstruct blood flow or result in anginal symptoms (such as chest pain). Although such lesions are relatively common, occurring in 10 percent to 25 percent of patients undergoing coronary angiography, their presence has ...
2014-11-04
Among patients with metastatic melanoma, treatment with a combination of the drugs sargramostim plus ipilimumab, compared with ipilimumab alone, resulted in longer overall survival and lower toxicity, but no difference in progression-free survival, according to a study in the November 5 issue of JAMA.
F. Stephen Hodi, M.D., of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues conducted a phase 2 clinical trial in which 245 patients with unresectable (unable to be removed by surgery) stage Ill or IV melanoma were randomly assigned to receive ipilimumab (intravenously) ...
2014-11-04
Testing of study participants who wore head-mounted display systems (Google glasses) found that the glasses created a partial peripheral vision obstruction, according to a study in the November 5 issue of JAMA.
Interest in wearable head-mounted display systems for general consumers is increasing, with multiple models in production. However, their effect on vision is largely unknown. Peripheral visual field is a main component of vision and essential for daily activities such as driving, pedestrian safety, and sports. Conventional spectacle frames can reduce visual field, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Turning pretty penstemon flowers from blue to red