(Press-News.org) Berlin, Germany (November, 2014) – Reconstructing ancient life has long required a certain degree of imagination. This is especially true when considering the coloration of long-extinct organisms. However, new methods of investigation are being incorporated into paleontology that may shed light (and color) on fossils. Research presented at the recent Society of Vertebrate Paleontology meeting shows the importance of using new imaging technologies in reconstructing the color of Archaeopteryx, one of the most famous and important fossils species.
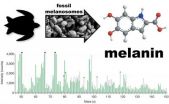
Ryan Carney of Brown University incorporated scanning electron microscopy in a 2012 study to identify melanosomes (melanin-containing pigment structures) in modern feathers to reconstruct the feather color of the iconic Archaeopteryx, the so-called "missing link" -- or more appropriately, evolutionary intermediate -- between non-avian dinosaurs and birds. Archaeopteryx has also been referred to as the "Mona Lisa of paleontology," a fossil taxon with great scientific, historical, and cultural importance.
However, after Carney's original publication, there has been some recent controversy with respect to two competing papers that offer alternative interpretations. The first was that the Archaeopteryx feather was both black and white, based on the distribution of organic sulfur imaged via synchrotron. The second was that the fossilized microbodies in the feather represent bacteria instead of melanosomes, given their similarities in size and shape.
The results of Carney's new research address these alternative interpretations and provide new insights into the Archaeopteryx feather. "The inner vane of the Archaeopteryx feather, which they claimed was white, we instead found to be packed with black melanosomes," said Carney. "This is critical because white feather color is only produced in the absence of melanosomes."
Furthermore, Carney and his Swedish colleagues have investigated the preservation of melanosomes in a variety of other fossils, utilizing additional new analytical methods such as Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToF-SIMS). Carney added, "We are not contending that every fossilized microbody is a melanosome. However, this new chemical method has allowed us to detect actual melanin molecules, which are associated with the melanosome-like microbodies in fossilized feathers and skin, from both terrestrial and marine environments. This integrated structural and direct chemical evidence provides the definitive proof that melanosomes can indeed be preserved in the fossil record."
Together, this new research paints the final picture of the famous wing feather as matte black with a darker tip, coloration that would have provided structural advantages to the plumage during this early evolutionary stage of dinosaur flight.
The application of such high-sensitivity analytical techniques is ushering in a new age of paleontological investigations. What once was artistic license, such as the appearance of ancient organisms, is now revealing itself in living color. As analytical methods in paleontology keep a pulse on technological advancements, we will continue to gain understanding of how fossil animals once lived and looked.
INFORMATION:
About the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology
Founded in 1940 by thirty-four paleontologists, the Society now has more than 2,300 members representing professionals, students, artists, preparators, and others interested in VP. It is organized exclusively for educational and scientific purposes, with the object of advancing the science of vertebrate paleontology.
Society of Vertebrate Paleontology website: http://www.vertpaleo.org
Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology
The Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology (JVP) is the leading journal of professional vertebrate paleontology and the flagship publication of the Society. It was founded in 1980 by Dr. Jiri Zidek and publishes contributions on all aspects of vertebrate paleontology.
Journal Web site: http://vertpaleo.org/Publications/Journal-of-Vertebrate-Paleontology.aspx
AUTHOR CONTACT INFORMATION
RYAN CARNEY
Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology
Brown University
Providence, RI
United States
ryan_carney@brown.edu
http://www.ryancarney.com
OTHER EXPERTS NOT ASSOCIATED WITH THIS STUDY
MIKE BENTON
School of Earth Sciences
University of Bristol
mike.benton@bristol.ac.uk
JULIA CLARKE
Department of Geological Sciences
University of Texas at Austin
julia_clarke@jsg.utexas.edu
Taking a deeper look at 'ancient wing'
2014-11-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
African diamond mine reveals dinosaur and large mammal tracks
2014-11-05
Berlin, Germany (November, 2014) – Unexpectedly one of the largest diamond mines in Africa, Catoca in Angola, holds 118 million year old dinosaur, crocodile and large mammal tracks. The mammal tracks show a raccoon-sized animal, during a time when most were no larger than a rat.
Nearly 70 distinct tracks were recovered in the Catoca mine in Angola. All the tracks were found in a small sedimentary basin, formed about 118 Ma, during the Early Cretaceous, in the crater of a kimberlite pipe.
The most important of these finds are those whose morphology is attributable ...
Jet-fueled electricity at room temperature
2014-11-05
SALT LAKE CITY, Nov. 5, 2014 – University of Utah engineers developed the first room-temperature fuel cell that uses enzymes to help jet fuel produce electricity without needing to ignite the fuel. These new fuel cells can be used to power portable electronics, off-grid power and sensors.
A study of the new cells appears online today in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Catalysis.
Fuel cells convert energy into electricity through a chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxygen-rich source such as air. If a continuous flow of fuel is provided, a fuel ...
Turning pretty penstemon flowers from blue to red
2014-11-05
While roses are red, and violets are blue, how exactly do flower colors change?
In the case of penstemons, with over 200 species to choose from, scientists Carolyn Wessinger and Mark Rausher have now shown that turning their flowers from blue to red involves knocking out the activity of just a single enzyme involved in the production of blue floral pigments.
A genetically conserved biochemical pathway produces the vivid blue pigments that they found to mutate over time to produce red. To shift into red pigment production, the enzyme flavonoid 3', 5' –hydroxylase ...
Patients with emergency-diagnosed lung cancer report barriers to seeing their GP
2014-11-05
MANY patients whose lung cancer is diagnosed as an emergency in hospital reported difficulties in previously seeing their GP, according to research presented at the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference in Liverpool today (Tuesday).
The study, carried out by researchers from the London Cancer Alliance (LCA) and King's College London, investigated around 130 patients who were diagnosed with lung cancer after attending as an emergency at one of seven hospitals in south and west London.
Overall, nearly half of the patients reported that something ...
Scientists uncover potential drug to tackle 'undruggable' fault in third of cancers
2014-11-05
SCIENTISTS have found a possible way to halt one of the most common faults in many types of cancer, according to research presented at the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference in Liverpool today (Wednesday).
A team of scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology in Germany has
uncovered a new strategy and new potential drug to target an important signalling protein in cells called Ras, which is faulty in a third of cancers.
When the Ras protein travels from the centre of a cell to the cell membrane, it becomes 'switched on' ...
Trial results reveal first targeted treatment to boost survival for oesophageal cancer
2014-11-05
PATIENTS with a specific type of oesophageal cancer survived longer when they were given the latest lung cancer drug, according to trial results being presented at the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference today (Wednesday).
Up to one in six patients with oesophageal cancer were found to have EGFR duplication in their tumour cells and taking the drug gefitinib, which targets this fault, boosted their survival by up to six months, and sometimes beyond.
This is the first treatment for advanced oesophageal cancer shown to improve survival in patients ...
Gene 'switches' could predict when breast cancers will spread to the brain
2014-11-05
SCIENTISTS have found a pattern of genetic 'switches' – chemical marks that turn genes on or off - that are linked to breast cancer's spread to the brain, according to research* presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Cancer Conference in Liverpool today (Wednesday).
The researchers, based at the University of Wolverhampton, studied 24 breast cancers that had spread to the brain, along with samples from the original breast tumour, and found a handful of genes with faulty switches.
Crucially, two of the genetic switches became faulty early on in the ...
New insight into the neuroscience of choking under pressure
2014-11-05
Everyone knows the scene: a basketball player at the free throw line, bouncing the ball as he concentrates on the basket. It's a tight game, and his team needs this point. He regularly makes baskets from much farther away while avoiding defenders, but now, when all is calm, he chokes and misses the basket, and his team loses. Recent research from The Johns Hopkins University suggests that in situations like this, performance depends on two factors: the framing of the incentive in terms of a loss or a gain, and a person's aversion to loss.
"We can measure someone's loss ...
Oxytocin levels in blood, cerebrospinal fluid are linked, Stanford study finds
2014-11-04
For years, scientists have debated how best to assess brain levels of oxytocin, a hormone implicated in social behaviors. Now, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have found the first direct evidence in children that blood oxytocin measurements are tightly linked to levels of oxytocin in cerebrospinal fluid, which bathes the brain.
Low oxytocin levels in blood and CSF are both correlated to high anxiety levels, the research also showed. The findings will be published online Nov. 4 in Molecular Psychiatry.
"So many psychiatric disorders involve ...
Digital dinosaurs: New research employs high-end technology to restore dinosaur fossil
2014-11-04
Fossils are usually deformed or incompletely preserved when they are found, after sometimes millions of years of fossilization processes. Consequently, fossils have to be studied very carefully to avoid damage, and are sometimes they are difficult to access, as they might be located in remote museum collections. An international team of scientists, led by Dr. Stephan Lautenschlager from the University of Bristol now solved some of these problems by using modern computer technology, as described in a recent issue of the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
The team consisting ...