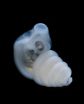
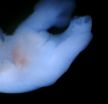
(Press-News.org) When it comes to genitalia, nature enjoys variety. Snakes and lizards have two. Birds and people have one. And while the former group's paired structures are located somewhat at the level of the limbs, ours, and the birds', appear a bit further down. In fact, snake and lizard genitalia are derived from tissue that gives rise to hind legs, while mammalian genitalia are derived from the tail bud. But despite such noteworthy contrasts, these structures are functionally analogous and express similar genes.
How do these equivalent structures arise from different starting tissues?
Reporting in Nature, researchers in Harvard Medical School's Department of Genetics, led by departmental chair Clifford Tabin, have found that the answer is not unlike the real estate axiom Location, location, location.
The embryonic cloaca—which eventually develops into the urinary and gut tracts—issues molecular signals that tell neighboring cells and tissues to form into external genitalia. The cloaca's location determines which tissues receive the signal first. In snakes and lizards, the cloaca is located closer to the lateral plate mesoderm, the same tissue that makes the paired limbs, receives the signal. In mammals, the cloaca is closer to the tail bud.
To further confirm this finding, the researchers grafted cloaca tissue next to the limb buds in one group of chicken embryos, and beside the tail buds in a second group. They found that in both cases, cells closer to the grafted cloaca responded to the signals and partially converted toward a genitalia fate.
This proves that different populations of cells with progenitor potential are able to respond to cloaca signaling and contribute to genitalia outgrowth.
"While mammal and reptile genitalia are not homologous in that they are derived from different tissue, they do share a 'deep homology' in that they are derived from the same genetic program and induced by the same ancestral set of molecular signals," said Tabin, who is also the George Jacob and Jacqueline Hazel Leder Professor of Genetics.
"Here we see that an evolutionary shift in the source of a signal can result in a situation where functionally analogous structures are carved out of nonhomologous substrate," said Patrick Tschopp, an HMS research fellow in genetics in Tabin's lab and first author on the paper. "Moreover, this might help to explain why limbs and genitalia use such similar gene regulatory programs during development."
INFORMATION:
Jerome Gros from the Department of Developmental and Stem Cell Biology at the Institut Pasteur in Paris, is co-senior author on this study.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant R37-HD032443.
Written by David Cameron
Harvard Medical School hms.harvard.edu has more than 9,000 full-time faculty working in 11 academic departments located at the School's Boston campus or in one of 47 hospital-based clinical departments at 16 Harvard-affiliated teaching hospitals and research institutes. Those affiliates include Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston Children's Hospital, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Cambridge Health Alliance, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Pilgrim Health Care, Hebrew SeniorLife, Joslin Diabetes Center, Judge Baker Children's Center, Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Massachusetts General Hospital, McLean Hospital, Mount Auburn Hospital, Schepens Eye Research Institute, Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital and VA Boston Healthcare System.
Scientists from the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the University of California, Los Angeles have shown that a promising technique for accelerating electrons on waves of plasma is efficient enough to power a new generation of shorter, more economical accelerators. This could greatly expand their use in areas such as medicine, national security, industry and high-energy physics research.
This achievement is a milestone in demonstrating the practicality of plasma wakefield acceleration, a technique in which electrons gain energy by essentially ...
AMHERST, Mass. – The surprise discovery of the fossilized skull of a 66- to 70-million-year-old, groundhog-like creature on Madagascar has led to new analyses of the lifestyle of the largest known mammal of its time by a team of specialists including biologist Elizabeth Dumont at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, an expert in jaw structure and bite mechanics.
The skull of this animal, named Vintana sertichi, was found in a geological formation deposited when a great variety of dinosaurs roamed the earth. With a skull that is almost five inches (125 mm) ...
A new study led by the University of California, Berkeley and involving the University of Colorado Boulder indicates the current response to wildfires around the world—aggressively fighting them—is not making society less vulnerable to such events.
The study suggests the key is to treat fires like other natural hazards—including earthquakes, severe storms and flooding—by learning to coexist, adapt and identify vulnerabilities. The new study indicates government-sponsored firefighting and land management policies may actually encourage development ...
Australian researchers have shown why calcium-binding drugs commonly used to treat people with osteoporosis, or with late-stage cancers that have spread to bone, may also benefit patients with tumours outside the skeleton, including breast cancer.
Several clinical trials – where women with breast cancer were given these drugs (bisphosphonates) alongside normal treatment for early-stage disease – showed that they can confer a 'survival advantage' and inhibit cancer spread in some women, although until now no-one has understood why.
A new study by Professor ...
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have identified a class of low-cost, easily-processed semiconducting polymers which, despite their seemingly disorganised internal structure, can transport electrons as efficiently as expensive crystalline inorganic semiconductors.
In this new polymer, about 70% of the electrons are free to travel, whereas in conventional polymers that number can be less than 50%. The materials approach intrinsic disorder-free limits, which would enable faster, more efficient flexible electronics and displays. The results are published today ...
CHICAGO (November 5, 2014) – When wildfire and people intersect, it is often in the wildland-urban interface, or WUI, a geography where homes, roads and trails intermix with fire-prone vegetation. In an article published Thursday in the journal Nature, U.S. Forest Service scientist Sarah McCaffrey and her colleagues advocate for an approach to wildfire management that reflects ecological science as well as research on the human dimensions of wildfire and fire management.
"Learning to Coexist with Wildfire," a research review led by the University of California-Berkley, ...
PHILADELPHIA –A diagnosis of septic shock was once a near death sentence. At best, survivors suffered a substantially reduced quality of life.
Penn Medicine researchers have now shown that while most patients now survive a hospital stay for septic shock, 23 percent will return to the hospital within 30 days, many with another life-threatening condition -- a rate substantially higher than the normal readmission rate at a large academic medical center. The findings are published in the new issue of Critical Care Medicine.
"Half of patients diagnosed with sepsis ...
November 5, 2014 – Insomnia is a "prevalent and persistent" problem for patients in the early phases of recovery from the disease of addiction—and may lead to an increased risk of relapse, according to a report in the November/December Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Treating sleep disturbance in early recovery may have considerable impact on maintenance of sobriety and quality of life," according ...
Despite great advances in understanding how the human brain works, psychiatric conditions, neurodegenerative disorders, and brain injuries are on the rise. Progress in the development of new diagnostic and treatment approaches appears to have stalled. In a special issue of the Cell Press journal Neuron, experts look at the challenges associated with "translational neuroscience," or efforts to bring advances in the lab to the patients who need them.
"A variety of global impact studies have identified brain disorders as a leading contributor to disabilities and morbidity ...
DENVER – A risk stratification model based on lymph node characteristics confirms with a high level of confidence the true lack of lung cancer in lymph nodes adequately sampled with endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration and classified as negative.
Lung cancer treatment and prognosis is critically dependent on accurate staging that takes into account the extent to which cancer has spread from the primary lung tumor to other locations. Examination of lymph nodes containing lung cancer cells that have spread can be done by surgical removal, ...