(Press-News.org) Many fire scientists have tried to get Smokey the Bear to hang up his "prevention" motto in favor of tools like thinning and prescribed burns, which can manage the severity of wildfires while allowing them to play their natural role in certain ecosystems.
But a new international research review led by the University of California, Berkeley, says the debate over fuel-reduction techniques is only a small part of a much larger fire problem that will make society increasingly vulnerable to catastrophic losses unless it changes its fundamental approach from fighting fire to coexisting with fire as a natural process.
The paper, "Learning to Coexist with Wildfire," to be published in the Nov. 6 issue of the journal Nature, examines research findings from three continents and from both the natural and social sciences. The authors conclude that government-sponsored firefighting and land-use policies actually encourage development on inherently hazardous landscapes, amplifying human losses over time.
"We don't try to 'fight' earthquakes – we anticipate them in the way we plan communities, build buildings and prepare for emergencies. We don't think that way about fire, but our review indicates that we should," said lead author Max Moritz, Cooperative Extension specialist in fire at UC Berkeley's College of Natural Resources. "Human losses will only be mitigated when land-use planning takes fire hazards into account in the same manner as other natural hazards, like floods, hurricanes and earthquakes."
The analysis looked at different kinds of natural fires, what drives them in various ecosystems, the ways public response to fire can differ, and the critical interface zones between built communities and natural landscapes. The authors found infinite variations on how these factors can come together.
"It quickly became clear that generic one-size-fits-all solutions to wildfire problems do not exist," Moritz said. "Fuel reduction may be a useful strategy for specific places, like California's dry conifer forests, but when we zoomed out and looked at fire-prone regions throughout the Western United States, Australia and the Mediterranean Basin, we realized that over vast parts of the world, a much more nuanced strategy of planning for coexistence with fire is needed."
Planning for co-existence
If humans choose to live in fire-prone regions, fire must be managed on par with other naturally occurring hazards, the authors argue, and research must seek to understand what factors and outcomes we can and cannot affect.
One common tool is applicable to the vast array of ecological and social science interactions at the critical wildfire/urban interface: more effective land-use planning, along with the regulations that guide it.
The authors recommend prioritizing location-specific approaches to improve development and safety in fire-prone areas, including:
Adopting new land-use regulations and zoning guidelines that restrict development in the most fire-prone areas;
Updating building codes, such as requiring fire-resistant construction to match local hazard levels and encouraging retrofits to existing ignition-prone homes;
Implementing locally appropriate vegetation management strategies around structures and neighborhoods;
Evaluating evacuation planning and warning systems, including understanding situations in which mandatory evacuations are or are not effective;
Developing household and community plans for how to survive stay-and-defend situations; and
Developing better maps of fire hazards, ecosystem services and climate change effects to assess trade-offs between development and hazard.
As an example of positive steps, the report cites new fire danger mapping efforts, including an existing fire hazard severity zone map that guides building codes in California. Produced by the state's Department of Forestry and Fire Protection, the current map does not explicitly incorporate locally varying wind patterns, which influence the worst fire-related losses of homes and lives, but future iterations will include these data.
Fire ecology and climate
The authors underscore that wildfires are a natural part of many ecosystems and can have a positive long-term influence on the landscape, despite people labeling them as "disasters." They can stimulate vegetation regeneration, promote a diversity of vegetation types, provide habitat for many species and sustain other ecosystem services, such as nutrient cycling.
Around the world, the numbers, sizes, and intensities of fires vary greatly. In some ecosystems, big, severe wildfires are natural events and more climate-driven – by drought or high winds – so fuel reduction is not a very effective tool in these locations. By contrast, many ecosystems that would naturally experience frequent lower-severity fires may respond to vegetation management aimed at both reducing fire hazard to humans and restoring crucial ecosystem processes. But, the authors agree, where fuel reduction is an appropriate goal, it would ideally be achieved by letting wildfires do their job.
A changing climate will complicate management strategies.
"How should future fire patterns compare to this historical variability? That's the big question," Moritz said.
Describing wildfire as "one of the most basic and ongoing natural processes on Earth," the authors call for a paradigm shift in the way society interacts with it, changing to an approach that achieves long-term, sustainable coexistence that benefits the planet's ecosystems on the landscape scale, while minimizing catastrophic losses on the human scale.
"A different view of wildfire is urgently needed," said Moritz. "We must accept wildfire as a crucial and inevitable natural process on many landscapes. There is no alternative. The path we are on will lead to a deepening of our fire-related problems worldwide, which will only become worse as the climate changes."
INFORMATION:
BOSTON – Each year nearly two million Americans suffer osteoporosis-related fractures, and as the population ages that number is expected to increase dramatically, placing a major burden on the health care system. While osteoporosis prevention and treatment efforts have historically been focused on post-menopausal women, a new study from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) suggests that critical opportunities are being lost by not focusing more attention on bone loss and fracture risk in older men.
"Given that the prevalence of fragility fractures among ...
When it comes to genitalia, nature enjoys variety. Snakes and lizards have two. Birds and people have one. And while the former group's paired structures are located somewhat at the level of the limbs, ours, and the birds', appear a bit further down. In fact, snake and lizard genitalia are derived from tissue that gives rise to hind legs, while mammalian genitalia are derived from the tail bud. But despite such noteworthy contrasts, these structures are functionally analogous and express similar genes.
How do these equivalent structures arise from different starting ...
Scientists from the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the University of California, Los Angeles have shown that a promising technique for accelerating electrons on waves of plasma is efficient enough to power a new generation of shorter, more economical accelerators. This could greatly expand their use in areas such as medicine, national security, industry and high-energy physics research.
This achievement is a milestone in demonstrating the practicality of plasma wakefield acceleration, a technique in which electrons gain energy by essentially ...
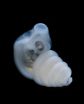
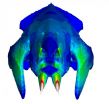
AMHERST, Mass. – The surprise discovery of the fossilized skull of a 66- to 70-million-year-old, groundhog-like creature on Madagascar has led to new analyses of the lifestyle of the largest known mammal of its time by a team of specialists including biologist Elizabeth Dumont at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, an expert in jaw structure and bite mechanics.
The skull of this animal, named Vintana sertichi, was found in a geological formation deposited when a great variety of dinosaurs roamed the earth. With a skull that is almost five inches (125 mm) ...
A new study led by the University of California, Berkeley and involving the University of Colorado Boulder indicates the current response to wildfires around the world—aggressively fighting them—is not making society less vulnerable to such events.
The study suggests the key is to treat fires like other natural hazards—including earthquakes, severe storms and flooding—by learning to coexist, adapt and identify vulnerabilities. The new study indicates government-sponsored firefighting and land management policies may actually encourage development ...
Australian researchers have shown why calcium-binding drugs commonly used to treat people with osteoporosis, or with late-stage cancers that have spread to bone, may also benefit patients with tumours outside the skeleton, including breast cancer.
Several clinical trials – where women with breast cancer were given these drugs (bisphosphonates) alongside normal treatment for early-stage disease – showed that they can confer a 'survival advantage' and inhibit cancer spread in some women, although until now no-one has understood why.
A new study by Professor ...
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have identified a class of low-cost, easily-processed semiconducting polymers which, despite their seemingly disorganised internal structure, can transport electrons as efficiently as expensive crystalline inorganic semiconductors.
In this new polymer, about 70% of the electrons are free to travel, whereas in conventional polymers that number can be less than 50%. The materials approach intrinsic disorder-free limits, which would enable faster, more efficient flexible electronics and displays. The results are published today ...
CHICAGO (November 5, 2014) – When wildfire and people intersect, it is often in the wildland-urban interface, or WUI, a geography where homes, roads and trails intermix with fire-prone vegetation. In an article published Thursday in the journal Nature, U.S. Forest Service scientist Sarah McCaffrey and her colleagues advocate for an approach to wildfire management that reflects ecological science as well as research on the human dimensions of wildfire and fire management.
"Learning to Coexist with Wildfire," a research review led by the University of California-Berkley, ...
PHILADELPHIA –A diagnosis of septic shock was once a near death sentence. At best, survivors suffered a substantially reduced quality of life.
Penn Medicine researchers have now shown that while most patients now survive a hospital stay for septic shock, 23 percent will return to the hospital within 30 days, many with another life-threatening condition -- a rate substantially higher than the normal readmission rate at a large academic medical center. The findings are published in the new issue of Critical Care Medicine.
"Half of patients diagnosed with sepsis ...
November 5, 2014 – Insomnia is a "prevalent and persistent" problem for patients in the early phases of recovery from the disease of addiction—and may lead to an increased risk of relapse, according to a report in the November/December Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Treating sleep disturbance in early recovery may have considerable impact on maintenance of sobriety and quality of life," according ...