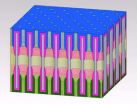
(Press-News.org) COLLEGE PARK, Md. -- Researchers at the University of Maryland have invented a single tiny structure that includes all the components of a battery that they say could bring about the ultimate miniaturization of energy storage components.
The structure is called a nanopore: a tiny hole in a ceramic sheet that holds electrolyte to carry the electrical charge between nanotube electrodes at either end. The existing device is a test, but the bitsy battery performs well. First author Chanyuan Liu, a graduate student in materials science & engineering, says that it can be fully charged in 12 minutes, and it can be recharged thousands of time.
A team of UMD chemists and materials scientists collaborated on the project: Gary Rubloff , director of the Maryland NanoCenter and a professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and in the Institute for Systems Research; Sang Bok Lee, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemisty and the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; and seven of their Ph.D. students (two now graduated).
Many millions of these nanopores can be crammed into one larger battery the size of a postage stamp. One of the reasons the researchers think this unit is so successful is because each nanopore is shaped just like the others, which allows them to pack the tiny thin batteries together efficiently. Coauthor Eleanor Gillette's modeling shows that the unique design of the nanopore battery is responsible for its success.
The space inside the holes is so small that the space they take up, all added together, would be no more than a grain of sand.
Now that the scientists have the battery working and have demonstrated the concept, they have also identified improvements that could make the next version 10 times more powerful. The next step to commercialization: the inventors have conceived strategies for manufacturing the battery in large batches.
INFORMATION:
Note to Editors: A YouTube video for this story is available after embargo ends. The url for this video is: http://youtu.be/vJ1JeFtU-Xw
It is live, but hidden (the title etc. is non-searchable until after the embargo lifts).
The research was funded by the Department of Energy. It will be published on November 10 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
"An all-in-one nanopore battery array," Nature Nanotechnology (2014), Chanyuan Liu, Eleanor I. Gillette, Xinyi Chen, Alexander J. Pearse, Alexander C. Kozen, Marshall A. Schroeder, Keith E. Gregorczyk, Sang Bok Lee and Gary W. Rubloff
A billion holes can make a battery
2014-11-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Good vibrations give electrons excitations that rock an insulator to go metallic
2014-11-10
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Nov. 10, 2014--For more than 50 years, scientists have debated what turns particular oxide insulators, in which electrons barely move, into metals, in which electrons flow freely. Some scientists sided with Nobel Prize-winning physicist Nevill Mott in thinking direct interactions between electrons were the key. Others believed, as did physicist Rudolf Peierls, that atomic vibrations and distortions trumped all. Now, a team led by the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has made an important advancement in understanding a classic transition-metal ...
Re-learning how to read a genome
2014-11-10
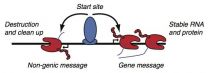
Cold Spring Harbor, NY - There are roughly 20,000 genes and thousands of other regulatory "elements" stored within the three billion letters of the human genome. Genes encode information that is used to create proteins, while other genomic elements help regulate the activation of genes, among other tasks. Somehow all of this coded information within our DNA needs to be read by complex molecular machinery and transcribed into messages that can be used by our cells.
Usually, reading a gene is thought to be a lot like reading a sentence. The reading machinery is guided ...
Thousands of never-before-seen human genome variations uncovered
2014-11-10
Thousands of never-before-seen genetic variants in the human genome have been uncovered using a new genome sequencing technology. These discoveries close many human genome mapping gaps that have long resisted sequencing.
The technique, called single-molecule, real-time DNA sequencing (SMRT), may now make it possible for researchers to identify potential genetic mutations behind many conditions whose genetic causes have long eluded scientists, said Evan Eichler, professor of genome sciences at the University of Washington, who led the team that conducted the study.
"We ...
Statins reverse learning disabilities caused by genetic disorder
2014-11-10
UCLA neuroscientists discovered that statins, a popular class of cholesterol drugs, reverse the learning deficits caused by a mutation linked to a common genetic cause of learning disabilities. Published in the Nov. 10 advance online edition of Nature Neuroscience, the findings were studied in mice genetically engineered to develop the disease, called Noonan syndrome.
The disorder can disrupt a child's development in many ways, often causing unusual facial features, short stature, heart defects and developmental delays. No treatment is currently available.
"Noonan ...
A greasy way to take better protein snapshots
2014-11-10
Thanks to research performed at RIKEN's SACLA x-ray free electron laser facility in Japan, the dream of analyzing the structure of large, hard-to-crystallize proteins and other bio molecules has come one step closer to reality. In the study published in Nature Methods, researchers used a newly developed grease to suspend small crystals of lysozyme, glucose isomerase, thaumatin, and fatty acid-binding protein type-3, which they then analyzed using the revolutionary serial femtosecond crystallography method.
Crystallography, which was first performed just a century ago, ...
Heat transfer sets the noise floor for ultrasensitive electronics
2014-11-10
A team of engineers and scientists has identified a source of electronic noise that could affect the functioning of instruments operating at very low temperatures, such as devices used in radio telescopes and advanced physics experiments.
The findings, detailed in the November 10 issue of the journal Nature Materials, could have implications for the future design of transistors and other electronic components.
The electronic noise the team identified is related to the temperature of the electrons in a given device, which in turn is governed by heat transfer due to packets ...
For enterics, adaptability could be an Achilles heel
2014-11-10
In research published in Nature Chemical Biology, scientists from RIKEN in Japan have discovered a surprisingly simple mechanism through which enterics can adjust to the very different oxygen environments inside the human gut and outside. This research, which was led by Shigeyuki Yokoyama and Wataru Nishii of the Structural Biology Laboratory, opens a new potential target against these bacteria, which are the most-frequently encountered causative microorganisms of infectious diseases. The family includes well-known symbionts and facultative or obligate pathogens such as ...
Kīlauea, 1790 and today
2014-11-10
Boulder, Colo., USA - Scores of people were killed by an explosive eruption of Kīlauea Volcano, Hawai'i, in 1790. Research presented in GSA Bulletin by D.A. Swanson of the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory and colleagues suggests that most of the fatalities were caused by hot, rapidly moving surges of volcanic debris and steam that engulfed the victims. Deposits of such surges occur on the surface on the west summit area and cover an ash bed indented with human footprints.
The footprints, made by warriors and their families, appear along a major trail in use at the time. ...
Researchers discover new target for blood cancer treatment
2014-11-10
Scientists at the University of York have identified a therapeutic target which could lead to the development of new treatments for specific blood cancers.
The study, by researchers from the Centre for Immunology and Infection at York working with scientists in the Department of Medicine at Stony Brook University in the USA, could lead to improved therapies for a group of haematological cancers called myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).
These are characterised by increases in one or more blood cell types, usually red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body ...
Anxiety can damage brain
2014-11-10
Toronto, Canada - People with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are at increased risk of converting to Alzheimer's disease within a few years, but a new study warns the risk increases significantly if they suffer from anxiety.
The findings were reported on Oct. 29 online by The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, ahead of print publication, scheduled for May 2015.
Led by researchers at Baycrest Health Sciences' Rotman Research Institute, the study has shown clearly for the first time that anxiety symptoms in individuals diagnosed with MCI increase the risk of a ...