Many dialysis patients unprepared for emergencies and disasters
2014-11-13
(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA (November 13, 2014) -- Patients on dialysis are very vulnerable during emergencies or disasters, but many are unprepared for such situations, according to two studies that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Dialysis patients are highly dependent on technologies to sustain their lives, with ongoing needs for transportation, electricity, and water for the dialysis apparatus. Interruption of these needs by a natural disaster can be devastating.
Naoka Murakami, MD, PhD (Mount Sinai Beth Israel) and her colleagues assessed the preparedness of adults receiving outpatient dialysis during the landfall of Hurricane Sandy in New York City in October 2012 at 5 regional centers where electricity had been deprived.
The researchers found that 26.3% of patients missed dialysis sessions and 66.1% received dialysis at non-regular dialysis unit(s). Seventeen percent of patients reported improvement in their dialysis-specific preparedness from before the storm. The improvement was significantly higher in the centers that distributed an "emergency information packet"--which includes information on a patient's medications, dialysis schedule, comorbid conditions, and geographical/contact information for dialysis centers--after the storm.
"Hemodialysis patients are generally unprepared for natural disasters and there is a need to strengthen both patient and dialysis facility disease-awareness and preparedness to improve outcomes in natural disasters," said Dr. Murakami. "Our survey showed a positive effect of being prepared through the distribution of a 'dialysis emergency packet,' and we propose that this be more conveniently located on a mobile electronic application."
In another study Anuradha Wadhwa, MD (Loyola University Medical Center) and her colleagues assessed disaster preparedness in their hemodialysis patients and evaluated an approach to disseminate this information by having physicians, nurses, dieticians, and social workers review preparedness-relevant topics with patients.
While 60% of the patients thought they were prepared for an emergency, 80% of were actually not prepared. About 50% of them did not have a plan or know about a backup facility; 35% were unaware of an emergency diet plan. The researchers found that 95% of the patients were interested in learning about emergency preparedness, and 99% found the information provided during the project useful. Using similar criteria for preparedness, a follow up survey showed 80% of the patients were better prepared.
"Emergency preparedness in dialysis patients was lacking, but they were willing to learn. This study highlights that a multidisciplinary approach in an outpatient dialysis unit setting is feasible and effective in educating patients about disaster preparedness," said Dr. Wadhwa.
INFORMATION:
Studies:
"Impact of Hurricane Sandy on Hemodialysis (HD) Patients and Preparedness for Natural Disasters" (Abstract TH-PO979)
"Disaster Preparedness in Dialysis Patients via Multidisciplinary Approach" (Abstract TH-PO980)
Disclosure information is available at
http://www.asn-online.org/education/kidneyweek/2014/program-faculty.aspx.
ASN Kidney Week 2014, the largest nephrology meeting of its kind, will provide a forum for more than 13,000 professionals to discuss the latest findings in renal research and engage in educational sessions related to advances in the care of patients with kidney and related disorders. Kidney Week 2014 will take place November 11-16, 2014 in Philadelphia, PA.
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with nearly 15,000 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-13
TORONTO, Nov. 13, 2014--Canadians with cystic fibrosis are living almost 20 years longer than they did two decades ago, according to a research paper published today.
The median survival age was 49.7 years in 2012, up from 31.9 years in 1990, Dr. Anne Stephenson, a respirologist and research at St. Michael's Hospital wrote in the European Respiratory Journal. Since the paper was written, Dr. Stephenson has updated the median survival age to include Cystic Fibrosis Canada data from 2013 and reported the median age of survival has in fact reached 50.9 years.
In addition, ...
2014-11-13
Scientists from the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles describe a new distinctive fly species of the highly diverse genus Megaselia. The study published in the Biodiversity Data Journal proposes an innovative method for streamlining Megaselia species descriptions to save hours of literature reviews and comparisons.
The new species, M. shadeae, is easily distinguished by a large, central, pigmented and bubble-like wing spot. The description is part of the the Zurquí All Diptera Biodiversity Inventory (ZADBI) project, and represents the first of an incredible ...
2014-11-13
Mice bred to carry a gene variant found in a third of ALS patients have a faster disease progression and die sooner than mice with the standard genetic model of the disease, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. Understanding the molecular pathway of this accelerated model could lead to more successful drug trials for all ALS patients.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, commonly known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a degeneration of lower and upper motor neurons in the brainstem, spinal cord and the motor cortex. The disease, which affects 12,000 Americans, ...
2014-11-13
Philadelphia, November 13, 2014 - Associations between opioid-related overdoses and increased prescription of opioids for chronic noncancer pain are well known. But some suggest that overdose occurs predominately in individuals who obtain opioids from nonmedical sources. In a new study published in the November issue of the journal PAIN®, researchers in Denmark found an increased risk of death associated with chronic pain without opioid treatment, as well as an even higher risk among those prescribed opioids for long-term use and a somewhat lower risk associated with ...
2014-11-13
Scientists at the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS) and their collaborators have developed a scoring scheme that predicts the ability of cancer cells to spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis. This system, which is the first of its kind, opens up the possibility to explore new treatments that suppress metastasis in cancer patients. The findings were published in EMBO Molecular Medicine in September.
Led by Professor Jean Paul Thiery, Senior Principal Investigator, and Dr Ruby Huang, ...
2014-11-13
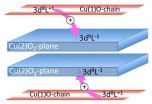
Swedish materials researchers at Linköping and Uppsala University and Chalmers University of Technology, in collaboration with researchers at the Swiss Synchrotron Light Source (SLS) in Switzerland investigated the superconductor YBa2Cu3O7-x (abbreviated YBCO) using advanced X-ray spectroscopy.
Their findings are published in the Nature journal Science Reports.
YBCO is a well-known ceramic copper-based material that can conduct electricity without loss (superconductivity) when it is cooled below its critical temperature Tc=-183° C. Since the resistance and ...
2014-11-13
People on the autistic spectrum may struggle to recognise social cues, unfamiliar people or even someone's gender because of an inability to interpret changing facial expressions, new research has found.
According to the study by academics at Brunel University London, adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD), though able to recognise static faces, struggle with tasks that require them to discriminate between sequences of facial motion or to use facial motion as a cue to identity.
The research supports previous evidence to suggest that impairments in perceiving biological ...
2014-11-13
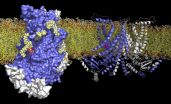
Membranes are thin walls that surround cells and protect their interior from the environment. These walls are composed of phospholipids, which, due to their amphiphilic nature, form bilayers with dis-tinct chemical properties: While the outward-facing headgroups are charged, the core of the bilayer is hydrophobic, which prevents charged molecules from passing through. The controlled flow of ions across the membrane, which is essential for the transmission of nerve impulses, is facilitated by ion channels, membrane proteins that provide gated pathways for ions. Analogous ...
2014-11-13
A cat always lands on its feet. At least, that's how the adage goes. Karen Liu hopes that in the future, this will be true of robots as well.
To understand the way feline or human behavior during falls might be applied to robot landings, Liu, an associate professor in the School of Interactive Computing (IC) at Georgia Tech, delved into the physics of everything from falling cats to the mid-air orientation of divers and astronauts.
In research presented at the 2014 IEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Liu shared her studies of mid-air ...
2014-11-13
Weather, which changes day-to-day due to constant fluctuations in the atmosphere, and climate, which varies over decades, are familiar. More recently, a third regime, called "macroweather," has been used to describe the relatively stable regime between weather and climate.
A new study by researchers at McGill University and UCL finds that this same three-part pattern applies to atmospheric conditions on Mars. The results, published in Geophysical Research Letters, also show that the sun plays a major role in determining macroweather.
The research promises to advance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Many dialysis patients unprepared for emergencies and disasters