New insight into common cause of blindness
2014-11-14
(Press-News.org) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is the major cause of blindness in the western world, affecting around 50 million people. It has been shown that sufferers are genetically predisposed to develop the condition.
One of the most important risk associated genes is called complement factor H (CFH). This encodes a protein called factor H (FH) that is responsible for protecting our eyes from attack by part of our immune system, called the complement system. FH achieves this by sticking to tissues, and when it is present in sufficient quantities it prevents the complement system from causing any damage.
Scientists from the Faculty of Medical and Human Sciences have now discovered that the protein factor H is not the main regulator of immunity in the back of the eye, instead it is a different protein that is made from the same CFH gene. This is called factor H-like protein 1 (FHL-1). The research has been published in the Journal of Immunology.
Dr Simon Clark, a Medical Research Council Career Development Fellow, led the research: "FHL-1 is a smaller version of FH, in fact it is about a third of the size. However, it has all the necessary components to regulate the immune system and is still subject to the genetic alterations that affect AMD risk. Our research has shown that the FHL-1, because it is smaller than FH, can get into structures of the back of the eye which cannot be reached by the larger FH."
He continues: "Therefore, this research suggests that it is FHL-1 rather than FH which protects the back of the eye from immune attack and that insufficient FHL-1 in the back of the eye may result in inflammation that eventually results in vision loss from AMD. FHL-1, although very similar to FH in many ways, does have a totally unique 'tail' structure at its end. This tail seems to mediate how FHL-1 binds tissue. As such, this work has identified a new target for therapeutics aimed at readdressing immune imbalance in the eye, thereby preventing or slowing down AMD."
Dr Clark successfully identified FHL-1 in human eye tissue that was donated with consent for research following removal of the corneas for transplantation.
He says: "There is no better way to understand and prevent blindness than to use actual human tissue."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-14
Animal growth is closely regulated by environmental factors such as nutrition. If the nutrition of a growing animal is limited, growth slows down and the eventual size of the animal remains smaller. Insulin-like signaling plays a key role in coordinating growth in response to dietary status in multicellular animals.
Doctoral student Kiran Hasygar and Assistant Professor Ville Hietakangas from the Department of Biosciences and Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, Finland, have now uncovered a new regulatory mechanism coordinating animal growth in response ...
2014-11-14
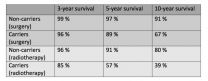
Prostate cancer patients carrying inherited mutations in the BRCA genes respond less well to conventional treatment, including surgery and/or radiotherapy - and they also have a lower survival rate than those who are non-carriers of these genetic mutations. Data from the study, which has been published in the journal European Urology, points to the need for new clinical trials aimed at targeting these mutations in order to tailor treatment for these patients.
The study has been led by David Olmos and Elena Castro at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) ...
2014-11-14
The expression of SIP1 protein in pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma tumours often indicates an advanced tumour stage, a high risk of recurrence and a poor prognosis, according to research from the University of Eastern Finland. Based on the results, SIP1 is a potential new prognostic factor for clinical use, helping to single out patients with more aggressive tumour behaviour requiring more intensive therapy and closer follow-up. Ms Anna Jouppila-Mättö, MD, presented the results in her doctoral thesis.
Although pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) is a ...
2014-11-14
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A new study documents the stark health dangers of the male sex trade in the streets, hotels, and discotheques of Mexico City. Lead author and health economist Omar Galárraga's point in making the grim assessment of the legal but perilous market is to find an incentive that might reduce the spread of HIV and other diseases in the nation's community of men who have sex with men.
"It's a very highly at-risk population," said Galárraga, assistant professor of health services, policy and practice in the Brown University School ...
2014-11-14
Since the 1850's scientists have known that crystalline materials are organized into fourteen different basic lattice structures. However, a team of researchers from Vanderbilt University and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) now reports that it has discovered an entirely new form of crystalline order that simultaneously exhibits both crystal and polycrystalline properties, which they describe as "interlaced crystals."
Writing in the Nov. 14 issue of the journal Nature Communications, the researchers describe finding this unusual arrangement of atoms while studying ...
2014-11-14
A team of Cardiff University researchers have made a breakthrough in helping scientists discover hundreds of black holes throughout the universe.
When two detectors are switched on in the US next year, the Cardiff team hope their research will help scientists pick up the faint ripples of black hole collisions millions of years ago, known as gravitational waves.
Black holes cannot be seen, but scientists hope the revamped detectors - which act like giant microphones - will find remnants of black hole collisions.
Led by Dr Mark Hannam from the School of Physics and Astronomy, ...
2014-11-14
(PHILADELPHIA) - Although radiation treatments have become much more refined in recent years, it remains a challenge to both sufficiently dose the tumor while sparing the surrounding tissue. A new anti-cancer drug, already in clinical development, may help address this issue by protecting normal cells - but not the cancer - from the effects of radiation. The research, published November 14th in Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, further suggests this drug may also be useful in treating accidental exposure to radiation.
"It was a stroke of luck that the drug that most effectively ...
2014-11-14
Nonsmokers sitting in an automobile with a smoker for one hour had markers of significantly increased levels of carcinogens and other toxins in their urine, indicating that secondhand smoke in motor vehicles poses a potentially major health risk according to a groundbreaking study led by UC San Francisco researchers.
The nonsmoking passengers showed elevated levels of butadiene, acrylonitrile, benzene, methylating agents and ethylene oxide. This group of toxic chemicals is "thought to be the most important among the thousands in tobacco smoke that cause smoking-related ...
2014-11-14
Cancer Research UK scientists have found more than 400 'blind spots' in DNA which could hide cancer-causing gene faults, according to research published* today (Friday) in Cancer Research.
The researchers found hidden faults in areas that are tricky for gene-reading technology to decode. This technique, which unravels cancer's genetic blueprint, is an important part of the research that scientists carry out to understand more about cancer's biology.
By finding new ways to unlock these blind spots in the future, the researchers hope this will help us understand these ...
2014-11-14
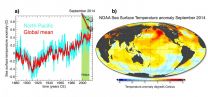
"This summer has seen the highest global mean sea surface temperatures ever recorded since their systematic measuring started. Temperatures even exceed those of the record-breaking 1998 El Niño year," says Axel Timmermann, climate scientist and professor, studying variability of the global climate system at the International Pacific Research Center, University of Hawaii at Manoa.
From 2000-2013 the global ocean surface temperature rise paused, in spite of increasing greenhouse gas concentrations. This period, referred to as the Global Warming Hiatus, raised a lot ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New insight into common cause of blindness