(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA (November 14, 2014) -- Many young patients with chronic conditions don't take their medications correctly, but 2 new studies point to ways to address such medication non-adherence. The studies will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
In one study, researchers led by Frederick Kaskel, MD, PhD (Albert Einstein College of Medicine) and Oleh Akchurin, MD (Weill Cornell College of Medicine) looked to see how young patients are using smart phones to help them take their medications. They surveyed patients at a pediatric kidney clinic. The researchers found that the majority of teens continued to use traditional techniques of improving medication adherence, such as filling pillboxes and incorporating medications into their daily routines. Ninety-three percent of surveyed teens had a smart phone in their personal possession, but only 29% were aware about medical mobile apps, even though 50% said they used cell phones for some kind of reminders to take medications. Boys were more likely to use cell phones to remember to take medications than girls and the prevalence of 100% self-reported medication adherence was higher in teens who used cell phones for reminders.
"This study demonstrates that a number of inner city teenagers with kidney disorders are utilizing their cell phones for the management of medication administration even in the absence of organized program promoting such use," said Dr. Akchurin. "Further research efforts are required to fully describe the contemporary pattern of smart phone-based technology use in medication adherence in this population in order to allow health care providers a meaningful way to incorporate these existing practices into daily clinical activity."
In another study of kidney transplant recipients aged 17 to 30 years, Jeroen Bastiaan van der Net, MD, PhD, Paul Harden, FRCP (Oxford University Hospital, in the UK) and their colleagues found that patients who were involved in a dedicated Young Adult Service were 4 times less likely to experience loss of function of their donated organ than young adult patients who were not involved in this service. Key features of a successful Young Adult Service are a dedicated team comprised of a key physician, nurse practitioner, and youth worker; Young Adult Clinics for patients within a community setting such as a sports club or university; and peer interactions through social events such as bowling or other activities.
"Young adult patients are at a critical point in their educational, psychological, and professional development that will shape their future life. Increasing the survival of their transplants will lead to higher levels of education and employment rates, which will be financially beneficial to society," said Dr. Harden.
INFORMATION:
Studies:
"Utilization of Smart Phones and Medication Adherence in Adolescents with Kidney Disorders" (Abstract FR-PO402)
"Reduced Rejection Rates and Improved Graft Survival with a Dedicated Young Adult Service" (Abstract TH-PO1119)
Disclosure information is available at
http://www.asn-online.org/education/kidneyweek/2014/program-faculty.aspx.
ASN Kidney Week 2014, the largest nephrology meeting of its kind, will provide a forum for more than 13,000 professionals to discuss the latest findings in renal research and engage in educational sessions related to advances in the care of patients with kidney and related disorders. Kidney Week 2014 will take place November 11-16, 2014, in Philadelphia, PA.
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with more than 15,000 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients.
WASHINGTON, Nov. 14, 2014--Quick Response (QR) codes -- the box-shaped symbols that appear on signs, posters, and even business cards -- are a convenient and efficient way of accessing specific web pages with a smartphone or other mobile device. However, new research published today in The Optical Society's (OSA) new high-impact journal Optica, explains how QR codes can do much more.
By adding an array of tiny lenses to an ordinary smartphone, a team of optical engineers from the University of Connecticut has found a way to securely display three-dimensional (3-D) images ...
Researchers at the University of Liverpool have found that screening for Ebola at airports could be an effective method for preventing the spread of the disease into the UK and US, but due to the long incubation period of the virus, screening won't detect all cases.
Published in the Lancet medical journal, the study used a mathematical model to test the probability of infected travellers from West Africa entering the UK and US.
The team, from the University's Institute of Infection and Global Health, examined the current growth rate of the epidemic in West Africa alongside ...
People with bipolar disorder who are being treated with the drug lithium are at risk of acute kidney damage and need careful monitoring, according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Norfolk and Suffolk NHS Foundation Trust.
Lithium is a mainstay treatment for bipolar disorder and it is known that the drug can cause a loss of kidney function. The new research establishes the link between short-term exposure to high levels and potential damage to the kidneys.
It is still not known what the impact of more than a single exposure to high levels ...
Scientists from the University of Liverpool have sequenced the mitochondrial genome in glaucoma patients to help further understanding into the genetic basis for the disease.
Glaucoma is a major cause of irreversible blindness, affecting more than 60 million people worldwide, increasing to an estimated 79.6 million people by 2020. It is thought that the condition has genetic origins and many experiments have shown that new sequencing approaches could help understand how the condition develops.
Studies on primary open-angle glaucoma - the most common form of glaucoma ...
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is the major cause of blindness in the western world, affecting around 50 million people. It has been shown that sufferers are genetically predisposed to develop the condition.
One of the most important risk associated genes is called complement factor H (CFH). This encodes a protein called factor H (FH) that is responsible for protecting our eyes from attack by part of our immune system, called the complement system. FH achieves this by sticking to tissues, and when it is present in sufficient quantities it prevents the complement ...
Animal growth is closely regulated by environmental factors such as nutrition. If the nutrition of a growing animal is limited, growth slows down and the eventual size of the animal remains smaller. Insulin-like signaling plays a key role in coordinating growth in response to dietary status in multicellular animals.
Doctoral student Kiran Hasygar and Assistant Professor Ville Hietakangas from the Department of Biosciences and Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, Finland, have now uncovered a new regulatory mechanism coordinating animal growth in response ...
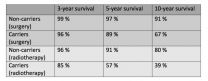
Prostate cancer patients carrying inherited mutations in the BRCA genes respond less well to conventional treatment, including surgery and/or radiotherapy - and they also have a lower survival rate than those who are non-carriers of these genetic mutations. Data from the study, which has been published in the journal European Urology, points to the need for new clinical trials aimed at targeting these mutations in order to tailor treatment for these patients.
The study has been led by David Olmos and Elena Castro at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) ...
The expression of SIP1 protein in pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma tumours often indicates an advanced tumour stage, a high risk of recurrence and a poor prognosis, according to research from the University of Eastern Finland. Based on the results, SIP1 is a potential new prognostic factor for clinical use, helping to single out patients with more aggressive tumour behaviour requiring more intensive therapy and closer follow-up. Ms Anna Jouppila-Mättö, MD, presented the results in her doctoral thesis.
Although pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) is a ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A new study documents the stark health dangers of the male sex trade in the streets, hotels, and discotheques of Mexico City. Lead author and health economist Omar Galárraga's point in making the grim assessment of the legal but perilous market is to find an incentive that might reduce the spread of HIV and other diseases in the nation's community of men who have sex with men.
"It's a very highly at-risk population," said Galárraga, assistant professor of health services, policy and practice in the Brown University School ...
Since the 1850's scientists have known that crystalline materials are organized into fourteen different basic lattice structures. However, a team of researchers from Vanderbilt University and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) now reports that it has discovered an entirely new form of crystalline order that simultaneously exhibits both crystal and polycrystalline properties, which they describe as "interlaced crystals."
Writing in the Nov. 14 issue of the journal Nature Communications, the researchers describe finding this unusual arrangement of atoms while studying ...