Paper electronics could make health care more accessible
2014-11-19
(Press-News.org) Flexible electronic sensors based on paper -- an inexpensive material -- have the potential to some day cut the price of a wide range of medical tools, from helpful robots to diagnostic tests. Scientists have now developed a fast, low-cost way of making these sensors by directly printing conductive ink on paper. They published their advance in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Anming Hu and colleagues point out that because paper is available worldwide at low cost, it makes an excellent surface for lightweight, foldable electronics that could be made and used nearly anywhere. Scientists have already fabricated paper-based point-of-care diagnostic tests and portable DNA detectors. But these require complicated and expensive manufacturing techniques. Silver nanowire ink, which is highly conductive and stable, offers a more practical solution. Hu's team wanted to develop a way to print it directly on paper to make a sensor that could respond to touch or specific molecules, such as glucose.
The researchers developed a system for printing a pattern of silver ink on paper within a few minutes and then hardening it with the light of a camera flash. The resulting device responded to touch even when curved, folded and unfolded 15 times, and rolled and unrolled 5,000 times. The team concluded their durable, lightweight sensor could serve as the basis for many useful applications.
INFORMATION:
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-19
Now that car makers have demonstrated through hybrid vehicle success that consumers want less-polluting tailpipes, they are shifting even greener. In 2015, Toyota will roll out the first hydrogen fuel-cell car for personal use that emits only water. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, explains how hydrogen could supplant hybrid and electric car technology -- and someday, even spur the demise of the gasoline engine.
Melody M. Bomgardner, a senior editor at C&EN, notes that the first fuel-cell vehicles ...
2014-11-19
Exposure to peanut proteins in household dust may be a trigger of peanut allergy, according to a study published today in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
The study was conducted in 359 children aged 3-15 months taking part in the NIH-sponsored Consortium for Food Allergy Research (CoFAR) study. These children were at high risk of developing a peanut allergy based on having likely milk or egg allergy or eczema. The study found that the risk of having strong positive allergy tests to peanut increased with increasingly higher amounts of peanut found in ...
2014-11-19
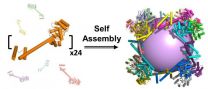
UCLA biochemists have created the largest-ever protein that self-assembles into a molecular "cage." The research could lead to synthetic vaccines that protect people from the flu, HIV and other diseases.
At a size hundreds of times smaller than a human cell, it also could lead to new methods of delivering pharmaceuticals inside of cells, or to the creation of new nanoscale materials.
The protein assembly, which is shaped like a cube, was constructed from 24 copies of a protein designed in the laboratory of Todd Yeates, a UCLA professor of chemistry and biochemistry. ...
2014-11-19
A new treatment for Marfan syndrome, a rare genetic disease that can lead to heart problems, works as well as the currently recommended medical therapy, beta blockers, according to an article in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Angela Sharkey, M.D., professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University, and a study author, said researchers found losartan, which had been more effective in an animal model of Marfan syndrome, was equally effective to a high dose of the beta blocker atenolol.
"While there may be certain patients who respond better to one drug or another, ...
2014-11-19
Researchers from the University of Melbourne found unlike other laser treatments, this new faster laser did not result in damage to the retina, the sensitive light detecting tissue at the back of the eye.
Associate Professor Erica Fletcher from the Department of Anatomy and Neuroscience said this was the first report detailing how this new laser treatment may improve eye health in those with AMD. In the early stages, the disease is characterised by the presence of small fatty deposits called drusen and thickening in a membrane at the back of the eye.
Published this ...
2014-11-19
Barcelona, Spain: A new drug that targets not only common cancer-causing genetic mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but also a form of the mutation that causes resistance to treatment, has shown promising results in patients in a phase I/II clinical trial. The research will be presented today (Friday) at the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
Approximately 10-15% of Caucasian and 30-35% of Asian patients with NSCLC have a mutation in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which ...
2014-11-19
If it's help a woman needs, maybe she should wear high heels. That's the message from Nicolas Guéguen of the Université de Bretagne-Sud in France, after he observed how helpful men are towards women in high heels versus those wearing flat, sensible shoes. The study, published in Springer's journal Archives of Sexual Behavior, is the first ever to investigate how the height of a woman's shoe heel influences how men behave towards her.
Research across various cultures has shown at length how important physical features, such as body size and the style and color ...
2014-11-19
Approximately 40 percent of the earth's surface is covered by drylands in which average annual precipitation is lower than evaporation. The changes projected to unfold in these areas in the course of climate change are alarming. Greater variations in annual and seasonal precipitation will lead to more frequent droughts and, presumably, longer drought periods. This means that drylands are among those areas most severely affected by climate change.
Research has thus far not adequately addressed the question of how strongly annual plant growth in pasture landscapes - hence ...
2014-11-19
Time ravages mountains, as it does people. Sharp features soften, and bodies grow shorter and rounder. But under the right conditions, some mountains refuse to age. In a new study, scientists explain why the ice-covered Gamburtsev Mountains in the middle of Antarctica looks as young as they do.
The Gamburtsevs were discovered in the 1950s, but remained unexplored until scientists flew ice-penetrating instruments over the mountains 60 years later. As this ancient hidden landscape came into focus, scientists were stunned to see the saw-toothed and towering crags of much ...
2014-11-19
Researchers from China, the Philippines and LSTM have today published a new systematic review of reminder systems to improve patient adherence to tuberculosis (TB) treatment. Reminder systems include prompts in advance of a forthcoming appointment to help ensure the patients attend, and also actions when people miss an appointment, such as phoning them or arranging a home visit. This review is the latest in a suite of reviews produced by authors from the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group, hosted at LSTM, evaluating interventions to improve adherence to TB treatment. Effective ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Paper electronics could make health care more accessible