Researchers discover natural resistance gene against spruce budworm
2014-11-21
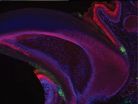
(Press-News.org) Quebec City, November 21, 2014--Scientists from Université Laval, the University of British Columbia and the University of Oxford have discovered a natural resistance gene against spruce budworm in the white spruce. The breakthrough, reported in The Plant Journal, paves the way to identifying and selecting naturally resistant trees to replant forests devastated by the destructive pest.
A research team composed of professors Éric Bauce, Joerg Bohlmann and John Mackay as well as their students and postdocs discovered the gene in spruces that had remained relatively undamaged by a local budworm outbreak. The scientists compared the genomes of the more resilient trees and those that suffered substantial damage. "We measured expression levels of nearly 24,000 genes in the two groups of trees, explains Professor Mackay. We discovered a gene, betaglucosidase-1, whose expression in the needles of resistant spruce trees is up to 1,000 times higher than in non-resistant trees."
Postdoctoral scientist Melissa Mageroy then produced the protein encoded by the gene. Tests showed that the protein plays an essential part in chemical reactions resulting in the production of two compounds that are toxic to the budworm, piceol and pungenol, identified in 2011 by a research team supervised by Dr. Éric Bauce. "We could say the gene we discovered produces natural insecticides in the tree foliage," sums up Dr. Mackay.
The resistance gene is present in all white spruces, but is expressed to varying degrees. "Theoretically, we could create white spruce stands that are less vulnerable to the budworm by reforesting areas with plantings from trees with a high expression of the resistance gene," says postdoctoral fellow and study coauthor Geneviève Parent. Université Laval and University of British Columbia researchers have partnered with Quebec's Ministère des Forêts, de la Faune et des Parcs and the British Columbia Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations to evaluate applications of their discoveries.
The spruce budworm is a moth whose caterpillar feeds primarily on balsam fir and white spruce needles. It is the most devastating insect to coniferous stands in Eastern North America. The last major outbreak that took place between 1970 and 1990 caused an estimated loss of half a billion cubic meters of wood in the province of Quebec alone, roughly the equivalent of 15 years of harvesting. Since 2003, the total affected forest area has been increasing steadily. Related caterpillars are affecting other types of conifer trees across Canada.
INFORMATION:
The study's coauthors are: Geneviève Parent, Gaby Germanos, Isabelle Giguère, Nathalie Delvas, Halim Maaroufi, and Éric Bauce (Université Laval); John Mackay (Université Laval and University of Oxford); Melissa Mageroy and Joerg Bohlmann (University of British Columbia). The research was supported by Genome Canada, Genome Québec, Genome British Columbia, the iFor Research Consortium and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-21
Employees who work at small, locally owned businesses have the highest level of loyalty to their employers -- and for rural workers, size and ownership of their company figure even more into their commitment than job satisfaction does, according to Baylor University researchers.
Higher levels of commitment are associated with less absenteeism, lower turnover and less seeking of jobs outside the company. The study -- "Small, local and loyal: How firm attributes affect workers' organizational commitment" -- is published in the journal Local Economy.
"It's an interesting ...
2014-11-21
LA JOLLA, CA - November 20, 2014 - Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have discovered how one gene is essential to hearing, uncovering a cause of deafness and suggesting new avenues for therapies.
The new study, published November 20 in the journal Neuron, shows how mutations in a gene called Tmie can cause deafness from birth. Underlining the critical nature of their findings, researchers were able to reintroduce the gene in mice and restore the process underpinning hearing.
"This raises hopes that we could, in principle, use gene-therapy approaches ...
2014-11-21
There are plenty of body parts that don't grow back when you lose them. Nails are an exception, and a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) reveals some of the reasons why.
A team of USC Stem Cell researchers led by principal investigator Krzysztof Kobielak and co-first authors Yvonne Leung and Eve Kandyba has identified a new population of nail stem cells, which have the ability to either self-renew or undergo specialization or differentiation into multiple tissues.
To find these elusive stem cells, the team used a sophisticated ...
2014-11-21
Stress activates the immune system
The team focused mainly on a certain type of phagocytes, namely microglia. Under normal circumstances, they repair synapses between nerves cells in the brain and stimulate their growth. Once activated, however, microglia may damage nerve cells and trigger inflammation processes. The studies carried out in Bochum have shown that the more frequently microglia get triggered due to stress, the more they are inclined to remain in the destructive mode - a risk factor for mental diseases such as schizophrenia.
Susceptibility for stress effects ...
2014-11-21
A protein kinase or enzyme known as PKM2 has proven to control cell division, potentially providing a molecular basis for tumor diagnosis and treatment.
A study, led by Zhimin Lu, M.D., Ph.D., professor of neuro-oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, showcased the non-metabolic abilities of PKM2 (pyruvate kinase M2) in promoting tumor cell proliferation when cells produce more of the enzyme.
The study results were published in today's issue of Nature Communications.
Dr. Lu's group previously demonstrated that PKM2 controls gene expression ...
2014-11-21
Immunity is a thankless job. Though the army of cells known as the immune system continuously keeps us safe from a barrage of viruses, bacteria and even precancerous cells, we mainly notice it when something goes wrong: "Why did I get the flu this year even though I got vaccinated?" "Why does innocent pollen turn me into a red-eyed, sniffling mess?"
A new study from Johns Hopkins takes a big step toward answering this and other questions about immunity, shedding light on how the body recognizes enemies on the molecular level -- and how that process can go wrong. The results ...
2014-11-21
A genome of a rare species of tapeworm found living inside a patient's brain has been sequenced for the first time, in research published in the open access journal Genome Biology. The study provides insights into potential drug targets within the genome for future treatments.
Tapeworms are parasites that are most commonly found living in the gut, causing symptoms such as weakness, weight loss and abdominal pain. However, the larvae of some species of tapeworm are able to travel further afield to areas such as the eyes, the brain and spinal cord.
A 50-year-old man ...
2014-11-21
For the first time, the genome of a rarely seen tapeworm has been sequenced. The genetic information of this invasive parasite, which lived for four years in a UK resident's brain, offers new opportunities to diagnose and treat this invasive parasite.
The tapeworm, Spirometra erinaceieuropaei, has been reported only 300 times worldwide since 1953 and has never been seen before in the UK. The worm causes sparganosis: inflammation of the body's tissues in response to the parasite. When this occurs in the brain, it can cause seizures, memory loss and headaches. The worm's ...
2014-11-21
Current efforts to prevent violence against women and girls are inadequate, according to a new Series published in The Lancet. Estimates suggest that globally, 1 in 3 women has experienced either physical or sexual violence from their partner, and that 7% of women will experience sexual assault by a non-partner at some point in their lives.
Yet, despite increased global attention to violence perpetrated against women and girls, and recent advances in knowledge about how to tackle these abuses (Paper 1, Paper 3), levels of violence against women - including intimate ...
2014-11-21
WASHINGTON--Levels of violence against women and girls--such as female genital mutilation, trafficking, forced marriage and intimate partner violence--remain high across the world despite the global attention the issue has received. The focus needs to shift to preventing violence, rather than just dealing with the consequences, according to a new series on violence against women and girls published Friday in The Lancet.
Mary Ellsberg, director of the George Washington University's Global Women's Institute (GWI), co-authored one of the five papers published in the special ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers discover natural resistance gene against spruce budworm